Alias
SQL Complete automatically generates aliases for each table, view, table-valued function, and synonym referenced in a SQL statement. To customize the generation of aliases, select Alias in the Options dialog.
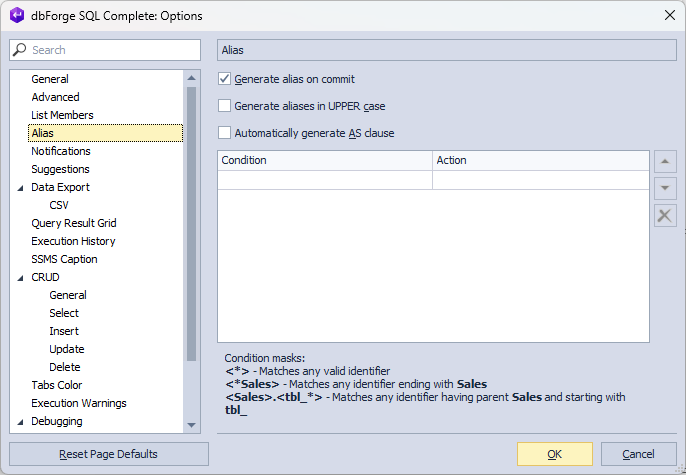
Let us take a look at the options available on the Alias page:
- Generate Alias on Commit
- Generate aliases in UPPER case
- Automatically generate AS clause
- Custom aliases
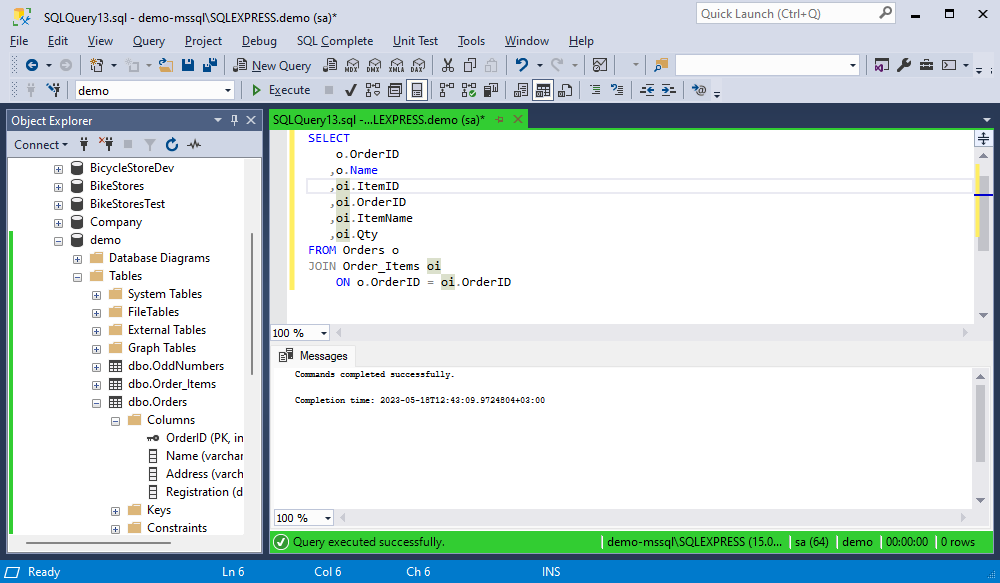
Generate Alias on commit
When the option is enabled (default state), while you are typing the statement, SQL Complete assigns aliases to tables, views, table-valued functions, and synonyms referenced in a SQL statement provided that a list of columns is specified or * is used to select all columns. If the table name consists of MixedCase, underscores, or hyphens, aliases will be generated using the first letters of each word. For example, the alias et will be assigned to ExampleTable, Example_Table, or Example-Table. For detailed customization of the commit action, navigate to the List Members topic and see the Commit Selection section.
It should also be noted that SQL Complete ignores such prefixes as tbl, v, fnc at the beginning of the name and assigns aliases without taking these prefixes into account. For example, the alias et will be set to the name with the tbl prefix - tblExampleTable.
As a result, when you write the SELECT * FROM statement, SQL Complete automatically generates aliases using the first letter of the corresponding objects as follows:
- Alias o will be assigned to the Orders table
- Alias oi will be assigned to the OrderItems table
Generate aliases in UPPER case
When the option is enabled, SQL Complete generates aliases in the UPPER case for tables, views, table-valued functions, and synonyms referenced in a SQL statement as follows:
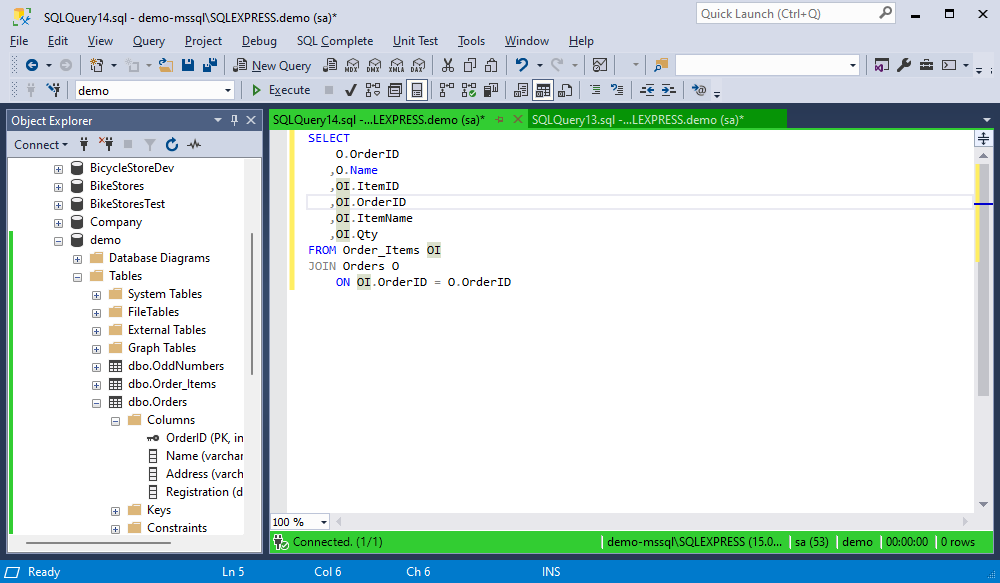
By default, the option is disabled.
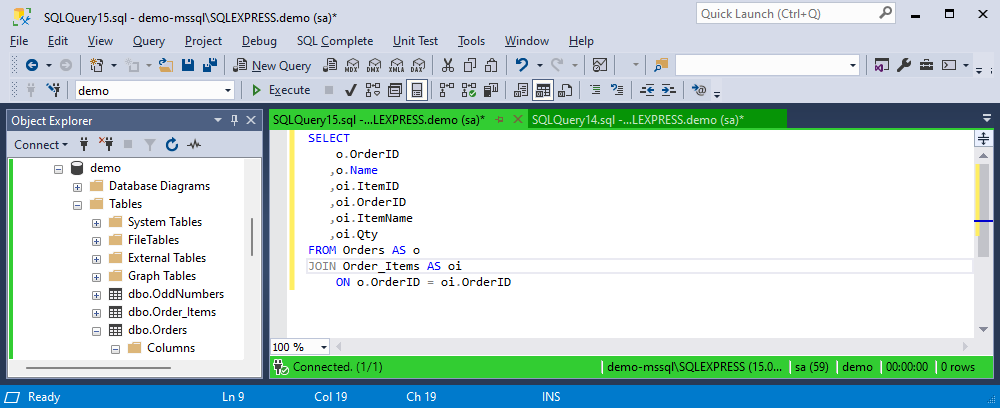
Automatically generate AS clause
To include the AS keyword when assigning aliases for tables, views, table-valued functions, or synonyms, select the Automatically generate AS clause checkbox.
Custom aliases
If you do not want to use the aliases that SQL Complete auto-generates, you can create custom aliases for tables, views, table-valued functions, synonyms, databases, servers, and linked servers.
In the Condition column, specify an identifier using one of the condition masks, as required. And in the Action column, specify the alias name using one of the action masks.
Let’s create a custom alias for the tables whose name starts with orders. Go to Alias and specify <\Ord*> as a condition and alias1 as an action. Then, click OK to save the changes.
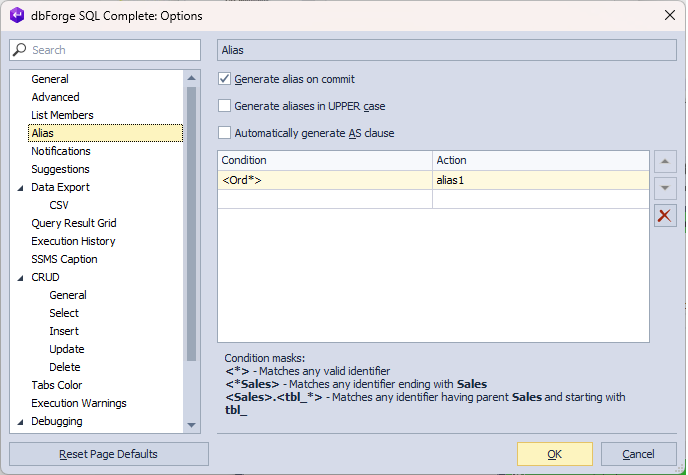
As a result, when typing the SELECT * FROM statement to retrieve data from the Orders table, SQL Complete will assign your custom alias if it matches the specified condition.
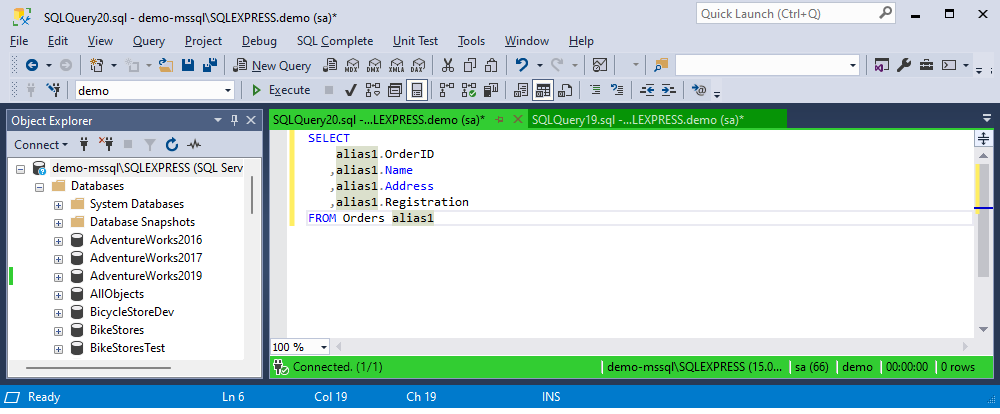
To restore the default settings, select Reset Page Defaults.
For more information about alias generation, see Operations with aliases.