Detach a database in SQL Server
This topic describes how to detach a database using dbForge Studio for SQL Server.
Detaching a database removes it from the instance of SQL Server but leaves the database intact within its data files and transaction log files. You can later use these files to attach or move the database to any instance of SQL Server, including the server from which the database was detached.
Limitations
Before detaching a database, be aware of the following limitations:
- Replicated databases: Databases involved in replication must be unpublished, and publishing must be disabled.
- Database snapshots: All snapshots associated with the database must be dropped.
- Database mirroring: If the database is part of a mirroring session, the session must be terminated.
- Suspect databases: A database marked as suspect must first be set to emergency mode.
- System databases: System databases cannot be detached.
- Active connections: A database with active connections can’t be detached.
Permissions
You must be a member of the sysadmin or db_owner role.
Prerequisite
When moving a database, check the files associated with it and their current locations by querying the sys.database_files system catalog view before detaching it from the existing SQL Server instance:
SELECT type_desc, name, physical_name
FROM sys.database_files;
where:
type_desc– The description of the file type:ROWS,LOG,FILESTREAM, andFULLTEXT.name– The logical name of the file in the database.physical_name– The operating-system file name.
Detach a database
1. Connect to a server instance.
2. In Database Explorer, right-click the database you want to detach and select Tasks > Detach Database.
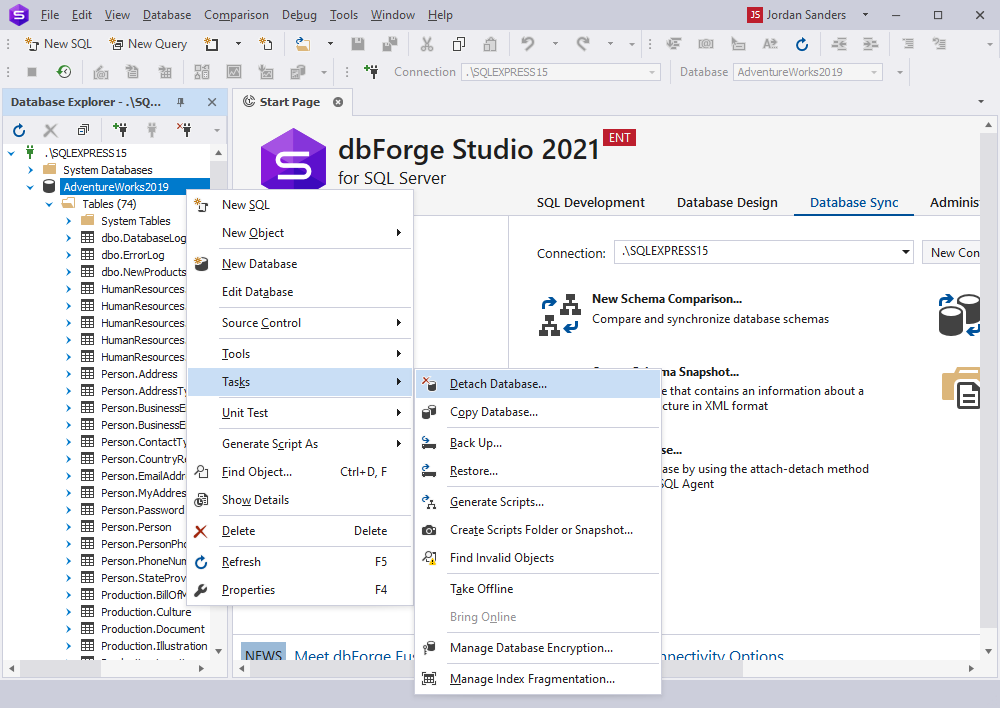
3. In the Detach Database dialog, select the following options:
- Drop Connections – Disconnects active connections to the specified database.
- Update Statistics – Updates the database optimization statistics.
Note
By default, outdated optimization statistics are retained during the detach operation.
4. To view the script of the detached database, in the left-lower corner of the dialog, click Script changes, then select one of these options:
- To New SQL Window – Opens the script in a new SQL document.
- To Clipboard – Copies the script to the clipboard.
The script may be as follows:
USE [master]
GO
EXEC master.dbo.sp_detach_db @dbname = N'<database_name>'
GO
where:
<database_name>– The name of the database you want to detach.
5. Click OK to detach the database.
After the database is detached, the Status column displays the ![]() icon.
icon.

5. Click Close to close the dialog.
Detach multiple databases
1. In Database Explorer, press and hold down Ctrl, then select the required databases.
2. Right-click the databases and select Tasks > Detach Database.
3. In the Detach Database dialog, select the checkboxes for the required options, then click OK.
4. Click Close to close the dialog.
Errors during a detach operation
If the database fails to detach, hover over the  icon in the Status column to view the error details.
icon in the Status column to view the error details.

Detach a database using T-SQL
You can detach a database using the sp_detach_db system stored procedure.
To detach a database using sp_detach_db:
1. On the SQL toolbar, click New SQL to open a new SQL document.
2. Enter the following command and replace the argument with your database name:
EXEC sp_detach_db @dbname = 'database_name';
where:
database_name– The name of the database you want to detach.
3. On the SQL toolbar, click Execute, or press F5.
After the command runs successfully, the database is removed from the SQL Server instance, but the physical files remain in their original locations.