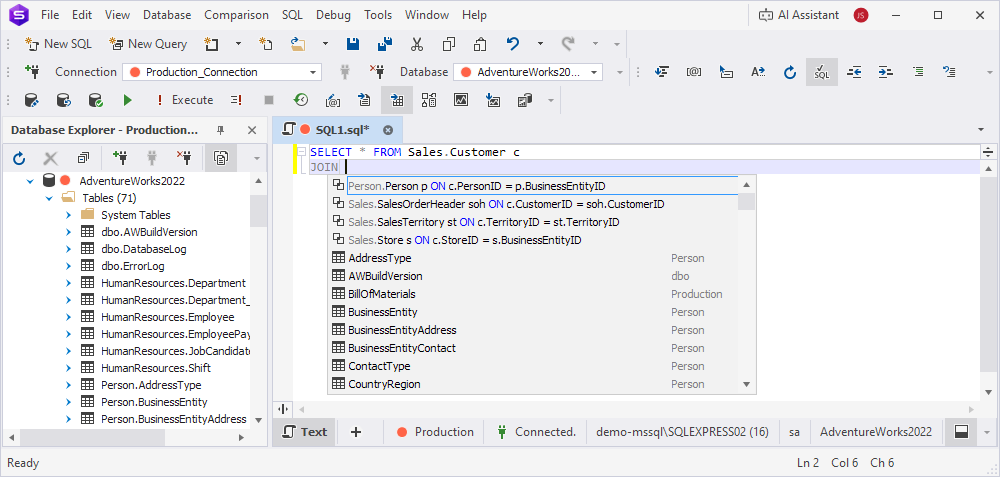
Insert suggestions into code
dbForge Studio for SQL Server provides SQL autocompletion through the suggestion box. The suggestion box displays items based on the current context of a query that you enter in the SQL editor. The suggestions are filtered to match the characters you type.
Invoke or close the suggestion box
The suggestion box appears automatically when you start typing a query in a SQL document.
To invoke the suggestion box manually, press Ctrl+Spacebar.
To close the suggestion box without inserting anything, press Esc. If nothing is selected in the suggestion box, you can close it by pressing Enter. The suggestion box also closes when you click anywhere in the SQL document.
Navigate through the list of suggestions
-
Press the Up and Down arrow keys to move up or down the list one item at a time.
You can enable the cyclic movement through the list–to move from the top to the bottom by pressing the Up arrow key or move from the bottom to the top by pressing the Down arrow key:
1. Select Tools > Options.
2. Select Text Editor > Code Completion > List Members.
3. Under List Members, select Cyclic movement through the suggestion list.
-
Press Page Up and Page Down to move one page up or down.
-
Press Ctrl+Page Up and Ctrl+Page Down to move to the top or bottom of the list.
-
Press the Left and Right arrow keys to show or hide the column list for a table.
-
Press the Spacebar or the Insert key to select or deselect columns in the column picker.
Insert a selected suggestion
By default, you can insert the highlighted suggestion by pressing Tab or Enter.
To configure the keys that insert suggestions:
1. Select Tools > Options.
2. Select Text Editor > Code Completion > List Members.
3. Under Commit Selection, select one or more ways of inserting a selected suggestion:
- Tab – To commit by pressing the Tab key.
- Whitespace – To commit by pressing the Spacebar.
- Following characters – To commit by typing the specified characters.
Change the size of the suggestion box
Drag a border or a corner of the suggestion box to resize it. The next time it opens, it retains the size you previously set.
Make the suggestion box semi-transparent
Press and hold the Ctrl key to make the suggestion box semi-transparent and view the code behind the suggestion box.
Exclude databases from suggestions
To speed up the loading of the suggestion list, you can exclude unnecessary databases and objects:
1. Select Tools > Options.
2. Select Text Editor > Code Completion > Suggestions.
3. Under Suggestions, select Do not load suggestions for the following databases and specify the databases to be excluded in the field below. If you exclude multiple databases, use a semicolon as a delimiter.
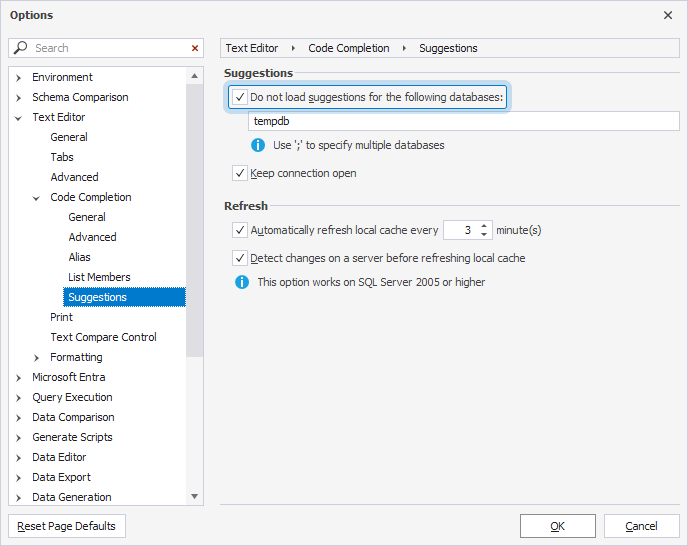
In the same dialog, you can set the local cache to be refreshed automatically at a specified interval (for example, every 3 minutes). If needed, you can also enable the Detect changes on a server before refreshing local cache option.
Refresh suggestions
If you are writing a query while someone else is modifying the structure of the same database, the suggestions provided by the Studio may become outdated.
To reload the suggestion list, click ![]() Refresh Suggestions on the Text toolbar. This action applies only to the database you are currently connected to.
Refresh Suggestions on the Text toolbar. This action applies only to the database you are currently connected to.
To configure how code suggestions are refreshed:
1. Select Tools > Options.
2. Select Text Editor > Code Completion > Suggestions.
3. Under Refresh, you can:
- Configure the local cache to refresh automatically at a specified interval.
- Enable Detect changes on a server before refreshing local cache.
Suggestion filtering
The Studio automatically filters items in the suggestion box based on the characters you type. The item deemed the best match is highlighted.
Filtering operates on the following principles:
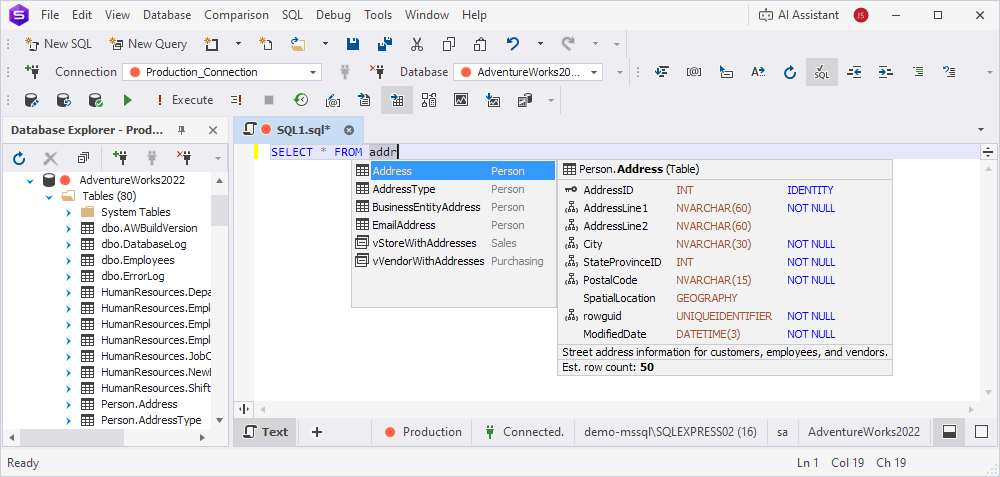
- By prefix – Suggestions include items whose names start with or contain the characters you entered. For example, typing addr will suggest
Address,MyAddress, etc.
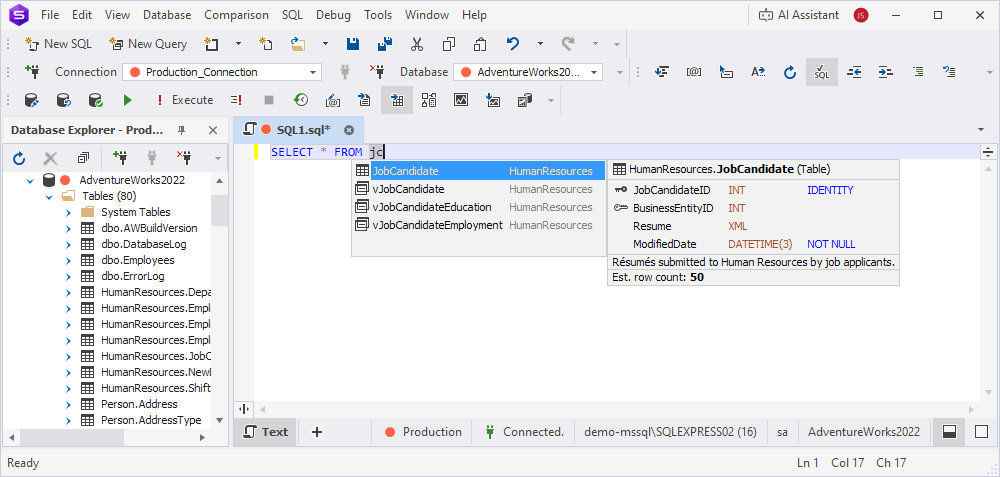
- By CamelHumps – Suggestions are filtered by the initial letters of compound names in camel case. For example, typing jc will suggest the
JobCandidatetable. Prefixes likev,tmp,prc, andfncare ignored.
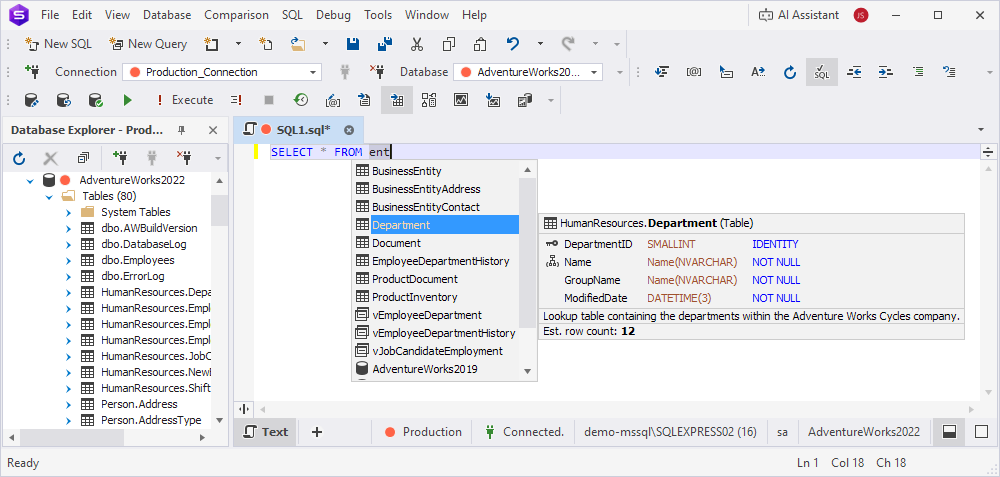
- By mid-string characters – Suggestions are refined to objects containing the characters you entered. For example, typing ent will suggest
BusinessEntity,Department,Document, etc.
Order of suggestions
Suggestions filtered based on the entered characters appear in the following order:
1. Prefix suggestions in alphabetical order.
2. CamelHumps suggestions in alphabetical order.
3. Mid-string suggestions, with the matches closest to the beginning of a name coming first.
Suggestions depending on the context of the query are by default sorted by relevance.
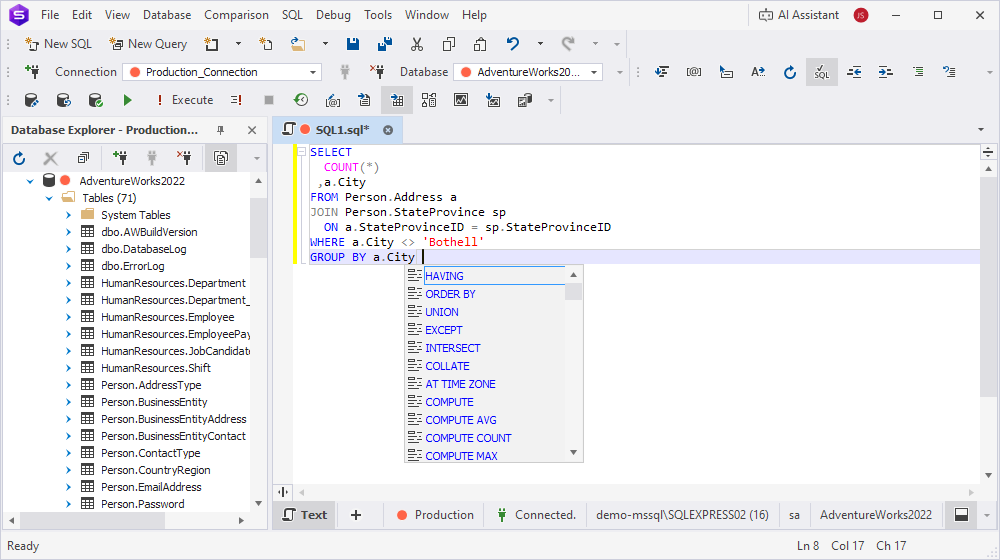
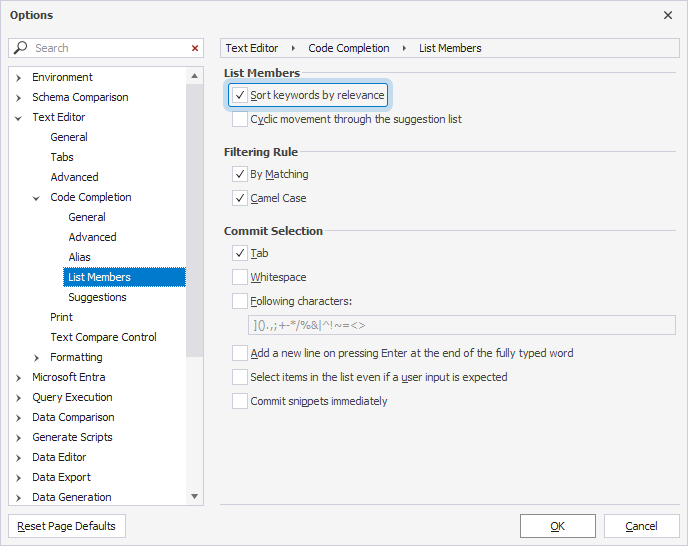
You can enable or disable sorting by relevance:
1. Select Tools > Options.
2. Select Text Editor > Code Completion > List Members.
3. Under List Members, select or clear the Sort keywords by relevance checkbox.
Object types in the suggestion list are sorted by relevance—the suggestion list changes according to the query context.
For example, in SELECT queries, the list first shows tables and views, then schemas, then databases, and finally linked servers. However, if a database has already been selected, the list shows tables, views, and schemas. When you select a table or a view, the schema to which the table or view belongs is automatically added to the query.
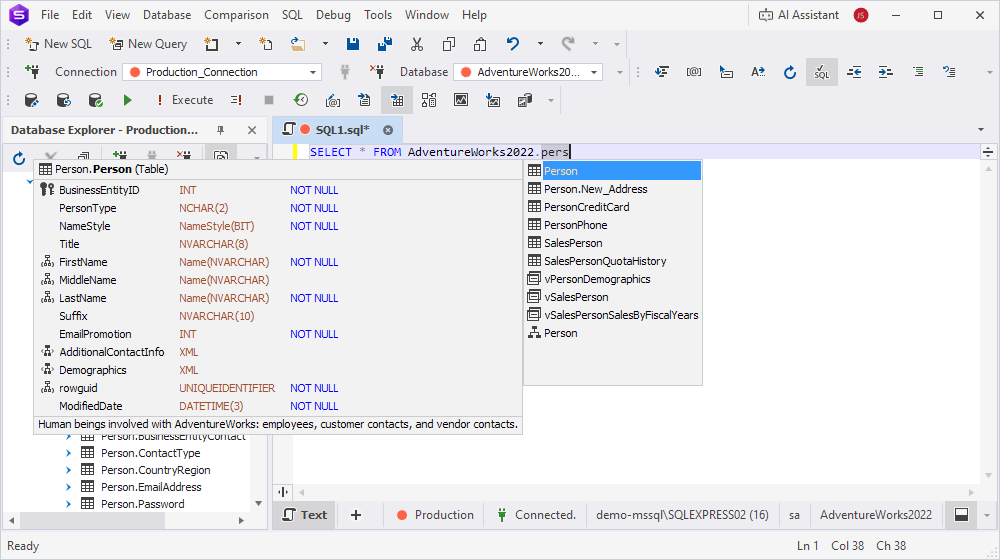
Columns are sorted by the order they were created when the table was formed.
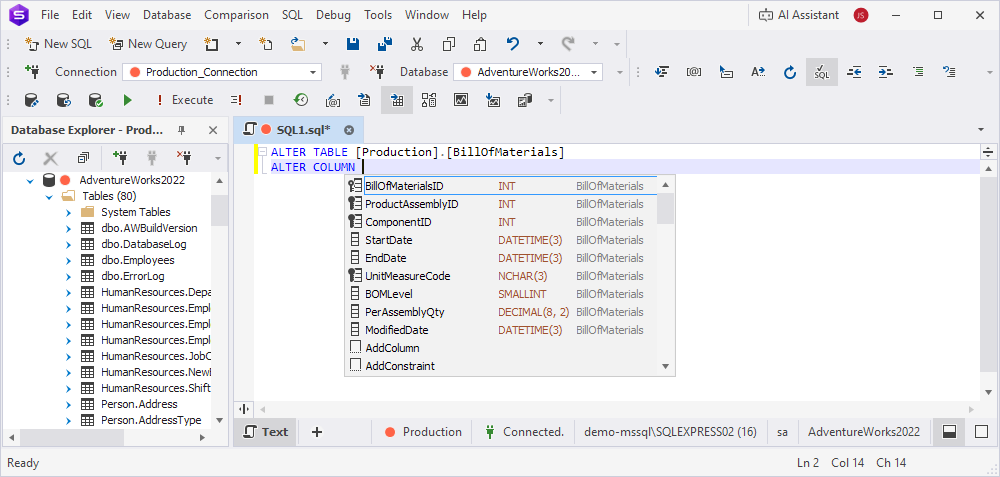
Objects inside their groups are sorted alphabetically.
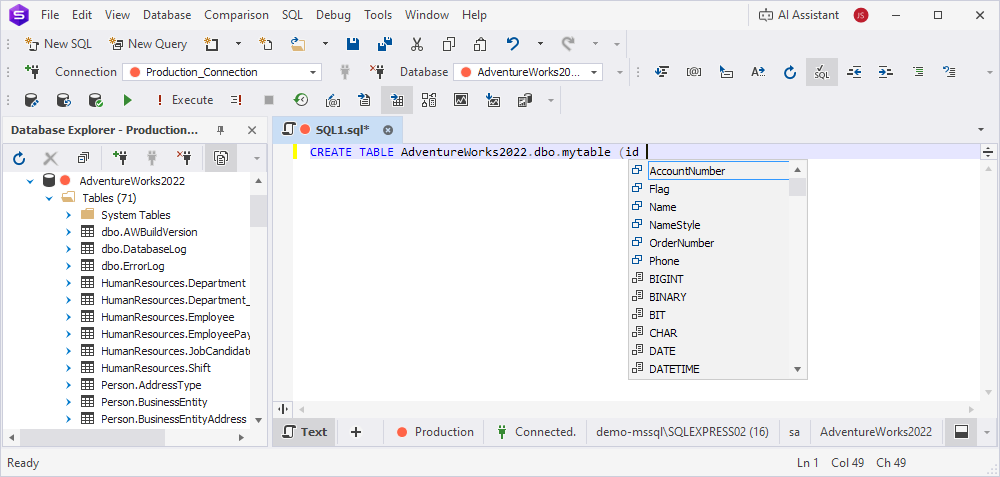
Suggestion inserting rules
When you select an item from the suggestion box, it’s inserted according to the rules set in Tools > Options > Text Editor > Code Completion > Advanced.
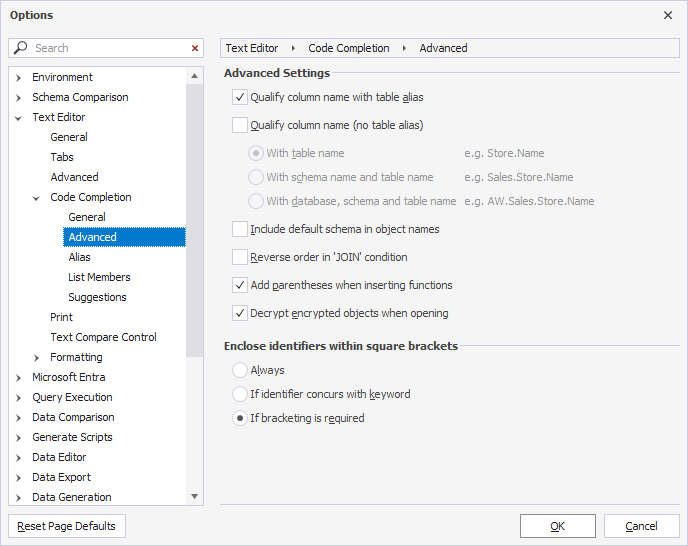
You can change these settings according to your needs. For instance, you can specify how the INSERT and ALTER statements should be inserted, and whether to qualify object names or not.
Encrypted objects
The Studio can automatically decrypt encrypted objects to show their creation script in the object definition box. If you don’t have permission to decrypt objects, you can still view encrypted objects in the suggestion box and insert them into queries.
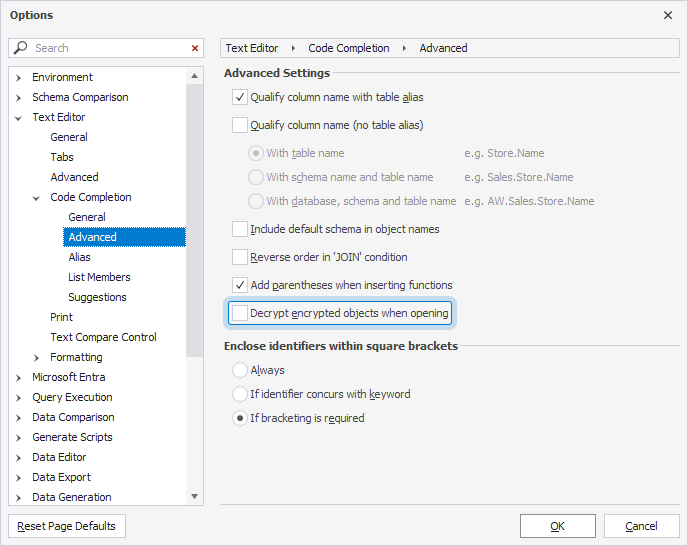
By default, the decryption of encrypted objects is enabled in the Studio. To disable this option:
1. Select Tools > Options.
2. Select Text Editor > Code Completion > Advanced.
3. Clear Decrypt encrypted objects when opening.
Types of suggested objects
The following table describes the object types suggested by the Studio.
| Icon | Object type |
|---|---|
| Aliases for table objects (tables, views, functions, synonyms, subqueries) | |
| Built-in data types | |
| Built-in functions | |
| Check constraints | |
| Collations | |
| Column master keys (A green plus indicates that the object is defined in the current script but doesn’t yet exist in the database.) |
|
| Columns classified with the critical sensitivity rank | |
| Columns classified with the high sensitivity rank | |
| Columns classified with the medium sensitivity rank | |
| Columns classified with the low sensitivity rank | |
| Columns without any sensitivity rank assigned | |
| Columns of table objects (A green plus indicates that the object is defined in the current script but doesn’t yet exist in the database.) |
|
| Columns with a primary key (A green plus indicates that the object is defined in the current script but doesn’t yet exist in the database.) |
|
| Columns with a unique key (A green plus indicates that the object is defined in the current script but doesn’t yet exist in the database.) |
|
| Columns with primary and foreign keys | |
| Contracts (A green plus indicates that the object is defined in the current script but doesn’t yet exist in the database.) |
|
| Cursors | |
| Database-level triggers (A green plus indicates that the object is defined in the current script but doesn’t yet exist in the database.) |
|
| Databases (A green plus indicates that the object is defined in the current script but doesn’t yet exist on the server.) |
|
| Default constraints | |
| Defaults | |
| Encrypted database-level triggers | |
| Encrypted scalar functions | |
| Encrypted server-level triggers | |
| Encrypted table-level triggers | |
| Encrypted table-valued (including CLR) functions | |
| Encrypted views | |
| Filegroups | |
| Foreign keys | |
| Full text stop lists | |
| Global system variables | |
IN parameters for procedures and functions (A green plus indicates that the object is defined in the current script but doesn’t yet exist in the database.) |
|
| Indexes | |
| Labels | |
| Languages | |
| Linked servers | |
| Local variables | |
| Logins | |
| Message types | |
OUT parameters for procedures and functions (A green plus indicates that the object is defined in the current script but doesn’t yet exist in the database.) |
|
| Primary keys | |
| Procedures (A green plus indicates that the object is defined in the current script but doesn’t yet exist in the database.) |
|
| Queues (A green plus indicates that the object is defined in the current script but doesn’t yet exist in the database.) |
|
| Roles | |
| Routes (A green plus indicates that the object is defined in the current script but doesn’t yet exist in the database.) |
|
| Rules (A green plus indicates that the object is defined in the current script but doesn’t yet exist in the database.) |
|
| Scalar functions (A green plus indicates that the object is defined in the current script but doesn’t yet exist in the database.) |
|
| Schemas | |
| Sequences (A green plus indicates that the object is defined in the current script but doesn’t yet exist in the database.) |
|
| Server-level triggers (A green plus indicates that the object is defined in the current script but doesn’t yet exist on the server.) |
|
| Servers | |
| Services (A green plus indicates that the object is defined in the current script but doesn’t yet exist in the database.) |
|
| Snippets | |
Suggested conditions for the ON keyword |
|
Suggested conditions for JOIN statements |
|
| Suggested keywords | |
| Synonyms for supported objects (A green plus indicates that the object is defined in the current script but doesn’t yet exist in the database.) |
|
| Table-level triggers (A green plus indicates that the object is defined in the current script but doesn’t yet exist in the database.) |
|
| Table-valued (including CLR) functions (A green plus indicates that the object is defined in the current script but doesn’t yet exist in the database.) |
|
| Tables (A green plus indicates that the object is defined in the current script but doesn’t yet exist in the database.) |
|
| Transactions | |
| User-defined data types (A green plus indicates that the object is defined in the current script but doesn’t yet exist in the database.) |
|
| User-defined table types (A green plus indicates that the object is defined in the current script but doesn’t yet exist in the database.) |
|
| User-defined types | |
| Users | |
| Views (A green plus indicates that the object is defined in the current script but doesn’t yet exist in the database.) |
|
| XML indexes | |
| XML schema collections |
Note
If an object with the same name exists in the database and the script, the Studio analyzes the current context and suggests the script-defined object first in the suggestion list.
Word autocompletion
When you type the first several characters of a database object name or a keyword, and the Studio finds only one match, it automatically inserts it to complete the word.
Example 1.
Press Ctrl+Spacebar after entering an incomplete SQL statement.
SELECT * FROM [AdventureWorks2022].[Sales].[vIndividual
The statement is autocompleted.
SELECT * FROM [AdventureWorks2022].[Sales].[vIndividualCustomer]
Example 2.
Press Ctrl+Spacebar after entering an incomplete SQL statement.
SELECT * FROM [AdventureWorks2022].[Sales].[CurrencyRate] [cr] jo
The statement is autocompleted.
SELECT * FROM [AdventureWorks2022].[Sales].[CurrencyRate] [cr] JOIN
Phrase suggestions
The Studio suggests not only separate keywords and object names, but also complete code phrases.
Example 1.
If you type o in a SELECT query, OUTER APPLY and ORDER BY appear in the autocomplete suggestions.
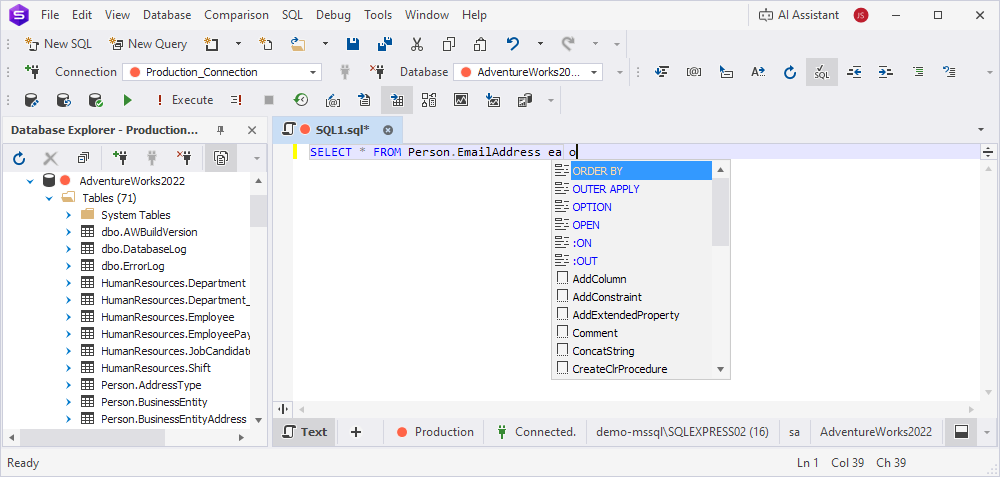
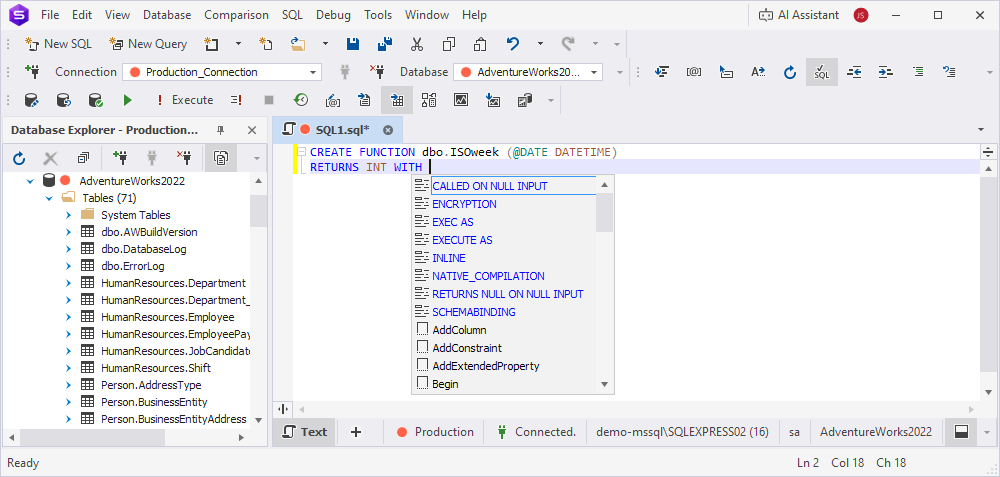
Example 2.
A list of attributes is suggested for the created scalar-valued function.
JOIN suggestions
When you combine tables based on foreign keys, the Studio suggests conditions based on column names or a complete JOIN statement. The IDE scans column names and detects primary and foreign key relationships in the joined tables.
JOIN conditions
The Studio suggests JOIN conditions by analyzing foreign key constraints and identifying columns with matching names and data types across tables. A key icon indicates that the suggestion is based on a foreign key relationship.
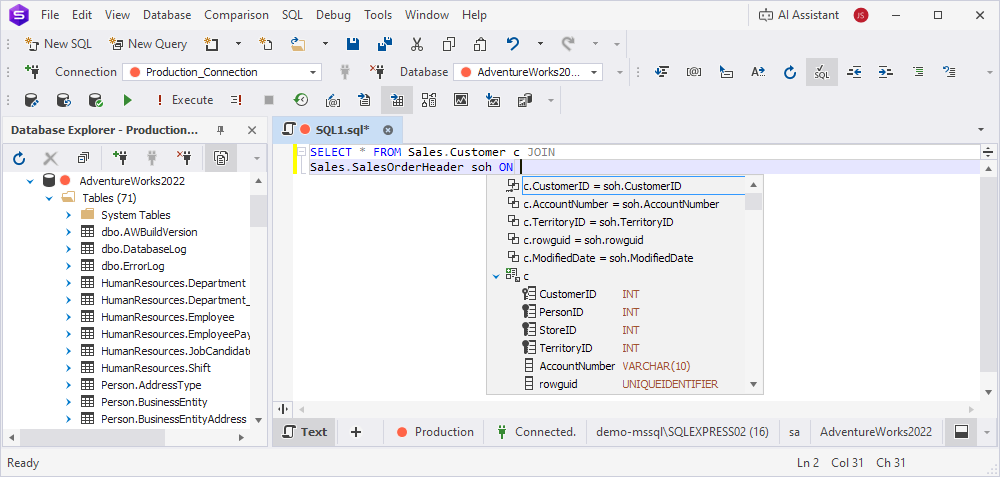
Complete JOIN statements
The Studio suggests a complete JOIN statement that links the specified tables, including the JOIN condition.