Introduction to dbForge Source Control
Multiple developers often work across different environments. With dbForge Source Control, you can link each database instance to a shared repository. Source Control tracks every change, synchronizes them with other versions, and keeps the development process consistent and controlled.
What is dbForge Source Control?
dbForge Source Control is an add-in for SQL Server Management Studio that enables you to version-control database schemas and static data by linking databases to the supported version control systems, such as TFS, Apache Subversion (SVN), TFVC, Git (including Azure DevOps, GitHub, GitLab, and Bitbucket), Mercurial (Hg), Perforce (P4), and SourceGear Vault.
You can use Source Control to:
- Commit local changes and pull remote changes.
- View the history of changes for a database or a specific database object to understand what changes were made, who made them, when they were made, and why.
- Revert uncommitted changes.
- Resolve conflicts.
- Switch between branches or merge them.
- Update a database to a specific revision.
dbForge Source Control supports two team models that can work with multi-instance development:
- Dedicated – Developers work with their own copies of the database.
- Shared – All developers work on a single shared database.
dbForge Source Control operations
dbForge Source Control enables you to set up the standard version control process directly from SQL Server Management Studio and to perform all the required version-control operations.
Commit changes to a repository
After you make changes, dbForge Source Control compares your current database copy with the version in source control and detects the differences. You can commit the changes or undo them.
To commit your changes, select them in the Local changes section, write a comment, and click Commit. This updates the source control repository with your local changes.
To discard uncommitted changes, click Undo.

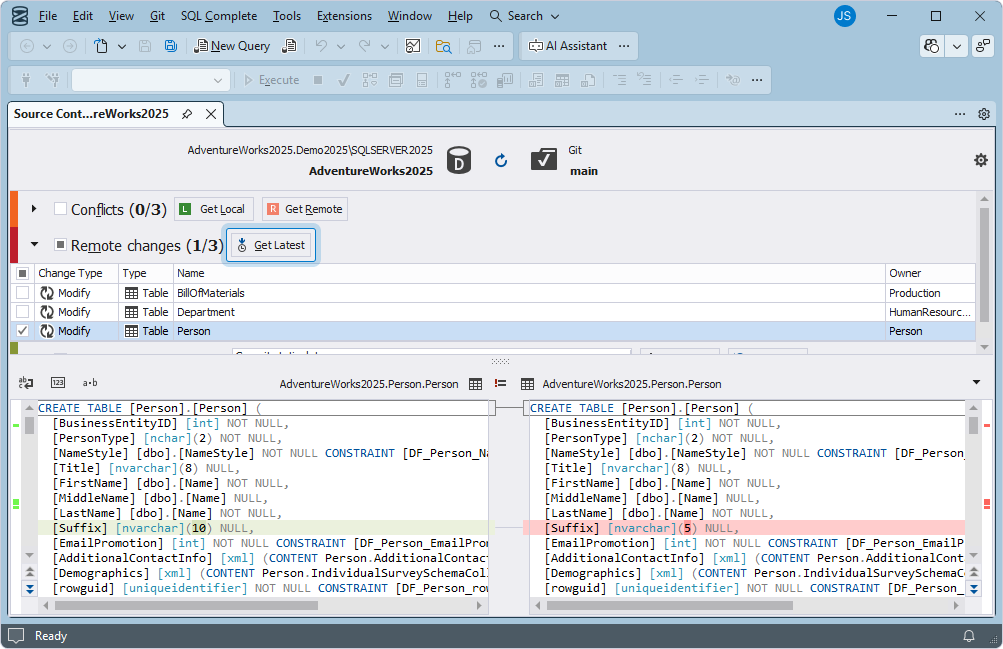
Get remote changes from version control and deploy them to the database
You can update your local database copy to synchronize it with changes made by other developers. All changes appear in Source Control Manager. Refresh it to view updates.
To update your local database copy, select the changes in the Remote changes section and click Get Latest.
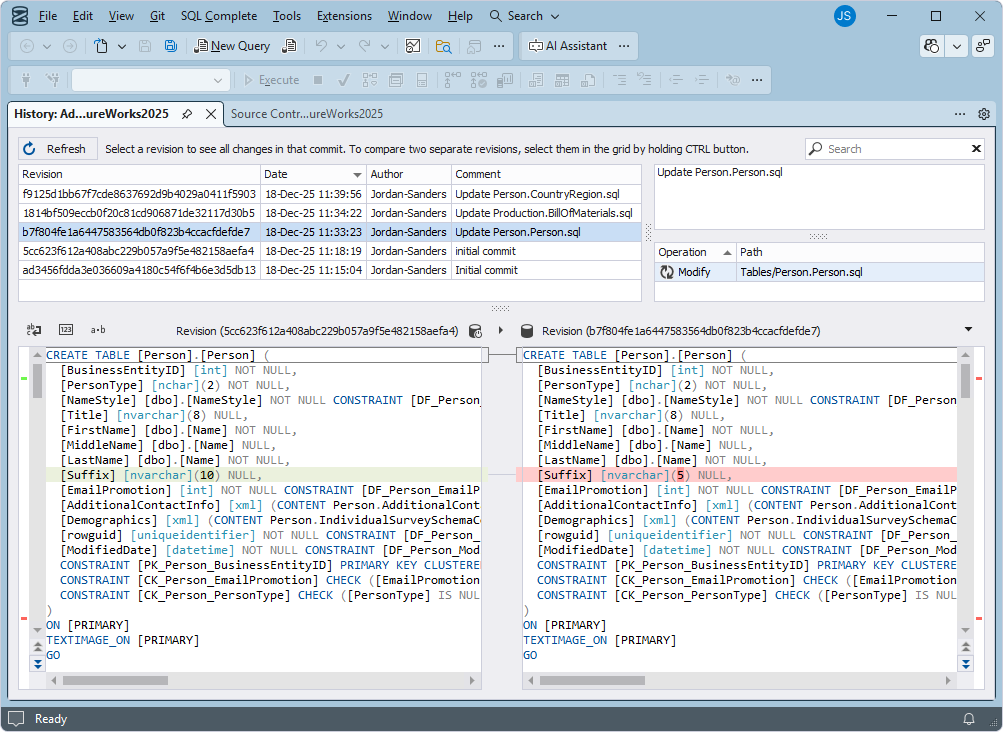
View the history of changes
You can view the change history to see who committed each change, when it was committed, and why. You can also compare versions to review the differences between them.
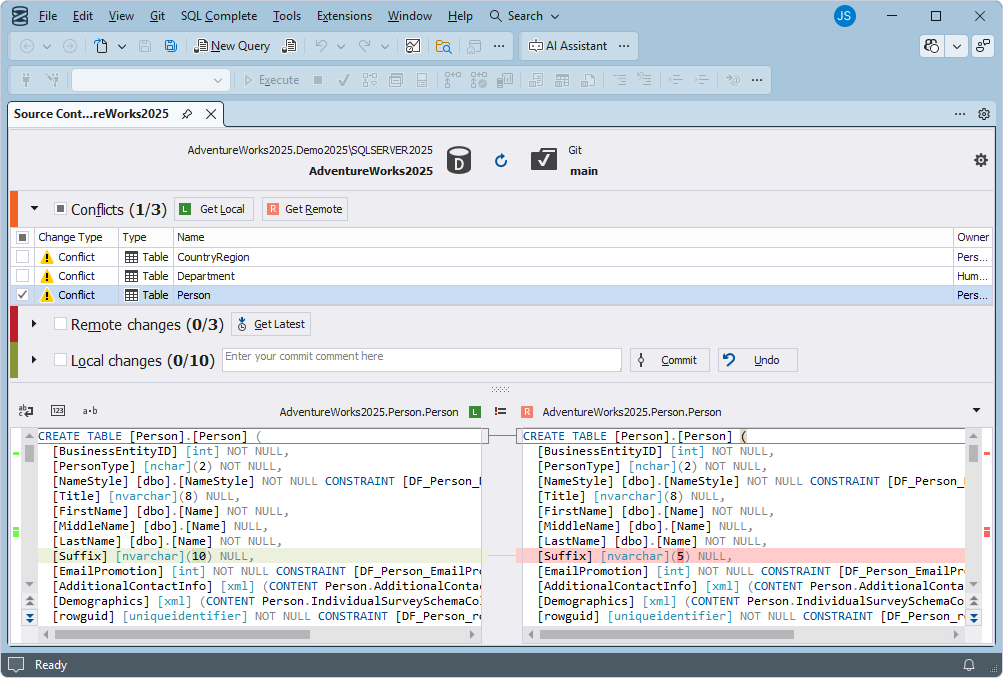
Resolve conflicts
Conflicts may occur when developers simultaneously make different changes to the same database objects or data.
To prevent conflicts, consider the following:
- Regularly pull changes from the repository.
- Assign object ownership to specific developers.
- Use commit messages and team chat effectively.
- Commit changes frequently with a clear scope.
To resolve conflicts, choose a resolution strategy:
- Get Remote – Accepts a repository version but loses your local changes.
- Get Local – Keeps your local changes but overwrites the remote ones.
Alternatively, use a manual merge strategy when you can edit a SQL script to combine both changes.
After that, test the resolved version.
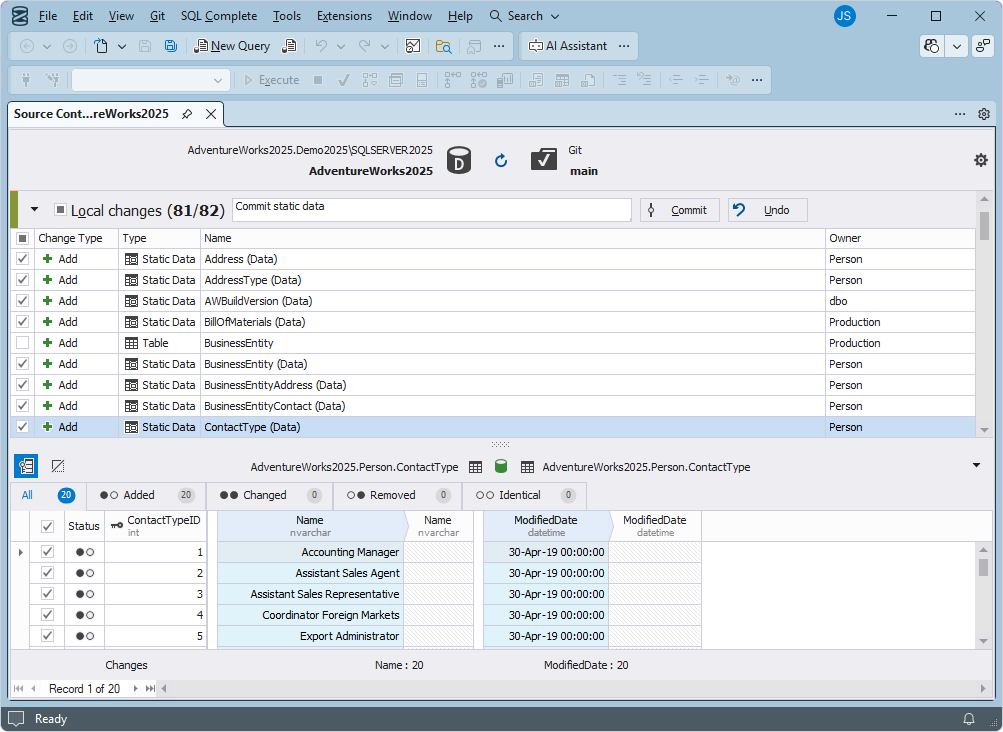
Manage static data
dbForge Source Control supports versioning of static data. You can link static data, modify it, commit changes, and resolve conflicts.
When synchronizing static data to the production environment, consider the following:
- Use separate commits for schema and data changes.
- Review data changes before deploying them to production.
- Prepare a rollback strategy for data changes.
Recommended workflow with dbForge Source Control in a multi-instance environment
1. Set up your repository.
2. Link a development instance to your repository.
3. Link additional instances.
4. Set up the change management process.
5. Automate the deployment process:
- Use dbForge Schema Compare for validation.
- Implement CI/CD pipelines.
- Automate testing in a staging environment.
- Create a deployment script.
Video tutorial
Watch this video to learn how dbForge Source Control works and what version control operations you can perform.

