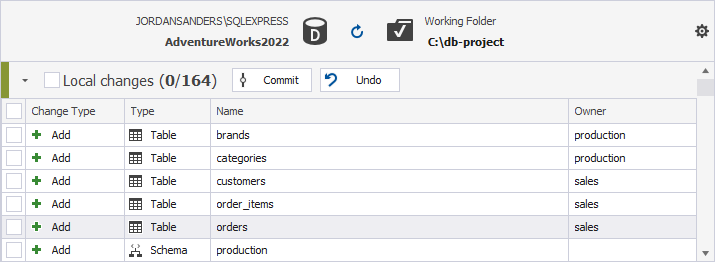
Commit changes
dbForge Source Control helps to update your version control repository by committing changes made in a database. You can manage the changes in Source Control Manager.
Before you can use the Source Control Manager, you must first link a database to the version control repository by following the steps outlined in the relevant how-to topic:
- Link a database to a Git repository in GitHub
- Link a database to a Git repository in Azure DevOps
- Link a database to a Git repository in BitBucket
- Link a database to a Git repository in GitLab
- Link a database to TFVC
- Link a database to SVN
- Link a database to Mercurial
- Link a database to Perforce
- Link a database to Plastic SCM and other systems
- Link a database to SourceGear Vault
The linked database gets the following icon in Object Explorer:
dbForge Source Control checks whether any changes were made to the database locally or remotely and whether these changes were committed to the repository. In the same way, dbForge Source Control checks whether any changes were committed to the version control and whether these changes were deployed to the linked database.
In addition, the tool checks for conflicts that can occur when multiple developers are making changes to the same file both in the repository and in the local database.
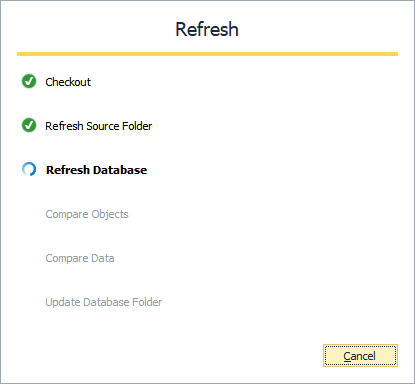
The Refresh progress window opens automatically, showing the stages of the refresh operation.
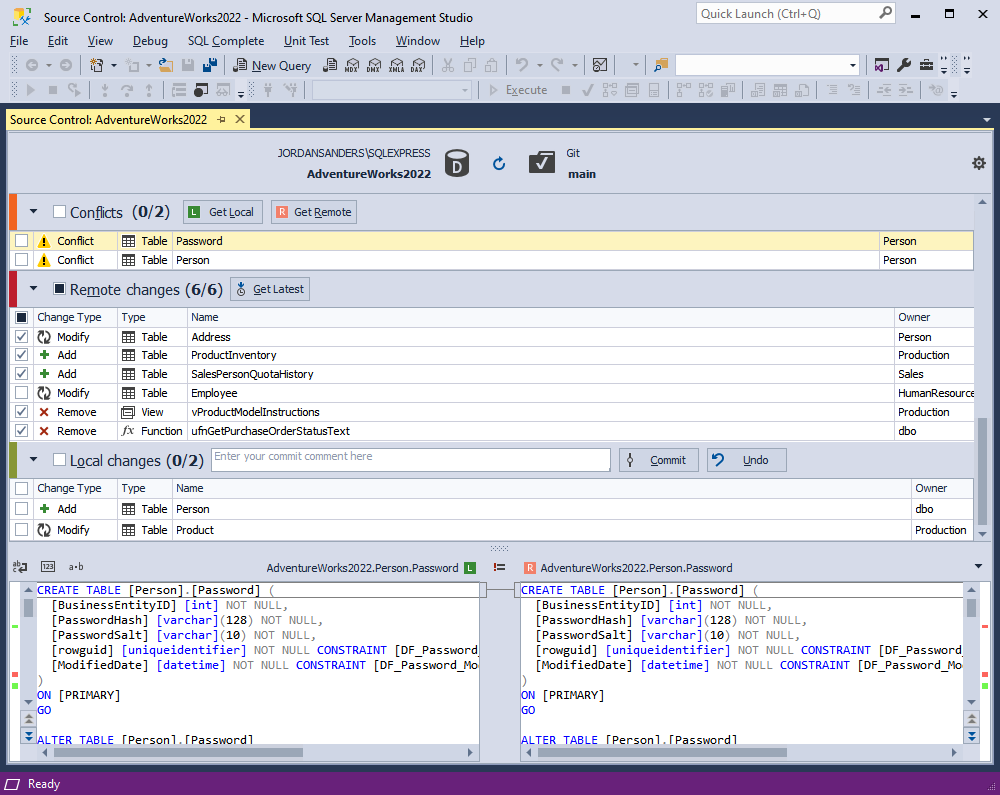
After the refresh operation is complete, Source Control Manager opens displaying all the changes in the following sections:
It should be noted that Source Control Manager can display either all three sections or two of them or just one section.
Note
Local changes section
- The Add change type indicates that the object was created locally in the database that is being version-controlled using Source Control, and has not been committed to the remote repository yet. By selecting the object and clicking Undo, it will be removed from the local database.
- The Remove change type means that the object was deleted from the local database that is being version-controlled using Source Control, but is still present in the remote repository. By selecting the object and clicking Undo, it will be restored in the local database.
- The Modify change type signifies that changes were made to the object in the local database that is being version-controlled using Source Control. As a result, the object’s DDL in the local database differs from the version stored in the remote repository. Selecting the object and clicking Undo will discard the changes made to the object in the local database, reverting it to the version from the repository.
Remote changes section
- The Add change type indicates that the object has been added to the remote repository since the last synchronization, and is not present in the local database that is linked to this repository via Source Control. By clicking Get Latest the object will be added to the local database.
- The Remove change type means that the object has been removed from the remote repository since the last synchronization but is present in the local database that is linked to this repository via Source Control. By clicking Get Latest the object will be removed from the local database.
- The Modify change type indicates that the object has been modified in the remote repository since the last synchronization. As a result, the object’s DDL in the repository differs from the version stored in the local database that is linked to this repository via Source Control. By clicking Get Latest, the object in the local database will be updated to match the version from the repository.
If the database and version control repository are identical and no changes are found, the following window is displayed:
To commit your changes to the version control repository:
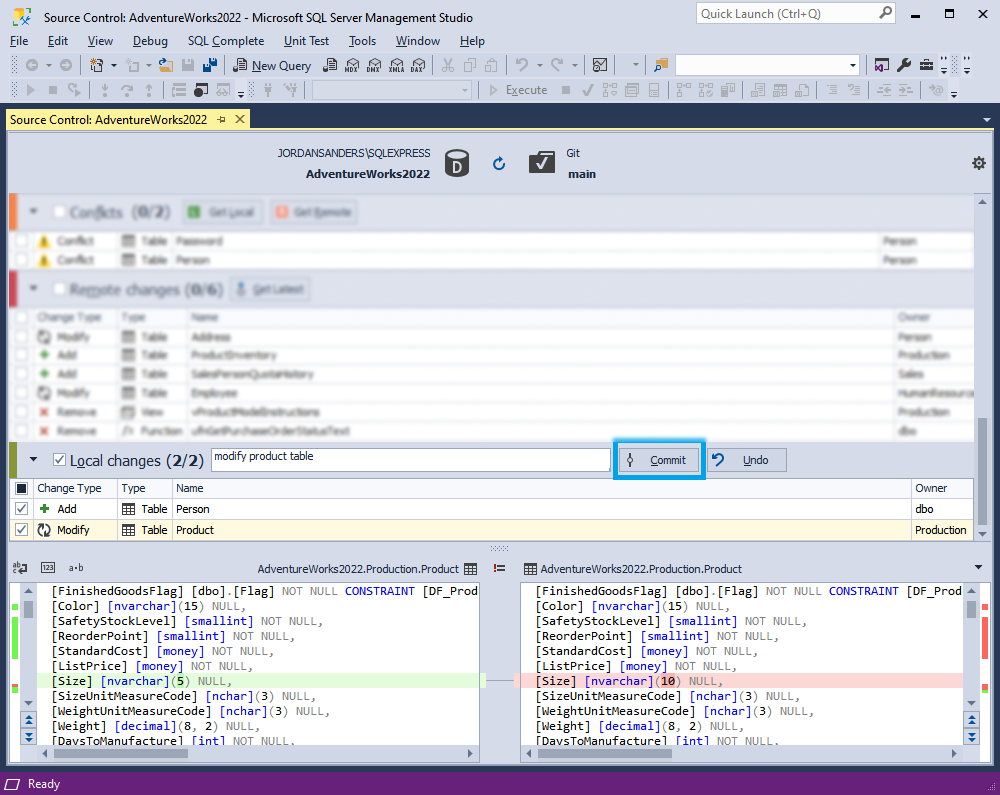
In the Local changes section, select the checkboxes next to the objects and/or static data that you want to commit, enter the comment describing your commit, and then click Commit. When you view the history of changes, the comments you’ve added to the commit will allow you to identify why the changes have been committed.
If you select the checkbox next to Local changes, all changes will be selected.
Note
dbForge Source Control does not explicitly differentiate commit and push operations. They both are executed simultaneously. It means that when committing changes, the tool automatically pushes them to the repository.
Note
The Commit comment text box is not available when a database is linked to a working folder.
As you can see in the screenshot above, the Source Control grid contains the following columns:
| Column | Description |
|---|---|
| Change Type | For Commit: Actions to be applied to the object or static data in the source control repository; these include Add (the object or data will be added); Modify (the object or data will be modified); Remove (the object or data will be removed). For Undo: Actions to be applied to the object (but not to static data) in the linked database; these include the following action for database objects: Add (the object will be dropped); Modify (the object will be altered); Remove (the object will be created). For more information about how to undo changes, see Undo changes. |
| Type | The type of the object; a Static Data is a table’s data type |
| Name | The name of the object that will undergo changes; a <name> (Data) construction refers to static data |
| Owner | The schema or database in which the object was created |
If you select an object that depends on other objects or changes in the Local Changes section, clicking Commit will display a window with a suggestion to include all related objects:
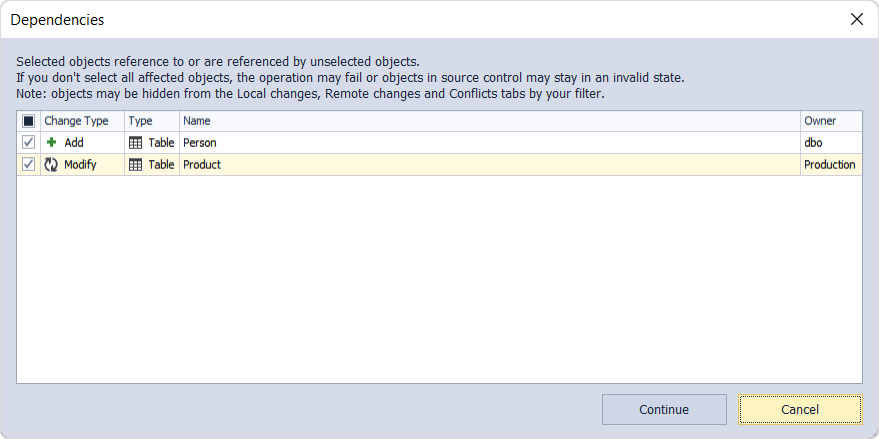
This case may occur when you add two new database objects such as a table and a view which select data from this new table. So, when you choose to commit only the new view, you will be suggested to commit the table associated with this view. In addition, you can exclude any related object from the commit.
After clicking Commit, the Commit progress window opens, showing the stages of the commit operation. When all the stages are complete, click OK to close the window.
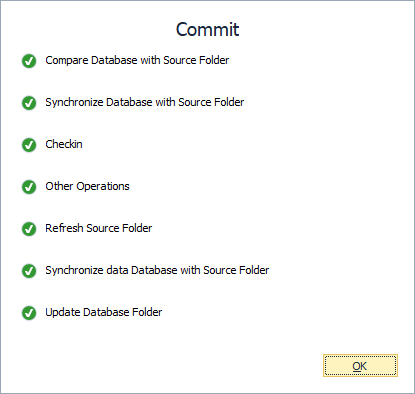
The Commit operation runs the deployment script generated by dbForge Source Control against the linked database to update it with the latest version of the database stored in the remote repository. The script contains CREATE, ALTER, and/or DROP statements for the database objects selected in the Source Control Manager, as well as INSERT, UPDATE, and/or DELETE statements for the changes to static data and the statuses (Remove, Modify, Add) of the objects.
If you want to configure the git-auto-commit action on every change in the structure of databases, refer to How to Automatically Commit SQL Server Database Schema Changes to the GIT Repository.
See also: How to roll back a commit in Git.