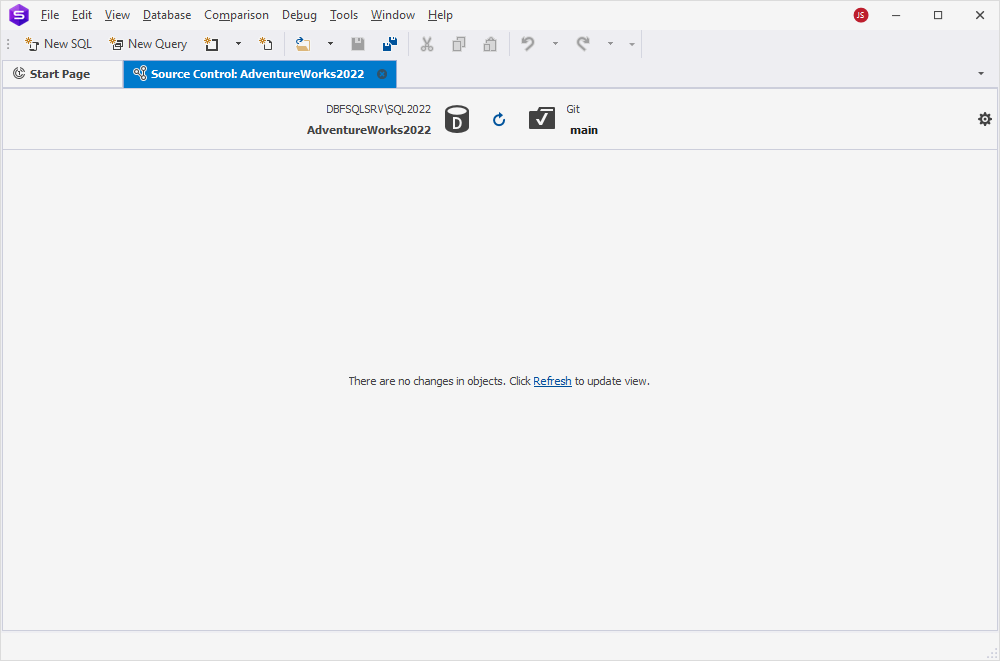
Source Control Manager overview
dbForge Studio for SQL Server provides a built-in Source Control Manager that helps you track and manage changes to database schema and static data.
Before using the Source Control Manager, you must first link a database to a source control repository. For instructions, see the following topics:
- Link a database to Git
- Link a database to a Git repository in GitHub
- Link a database to a Git repository in GitLab
- Link a database to a Git repository in BitBucket
- Link a database to a Git repository in Azure DevOps
- Link a database to TFVC
- Link a database to SVN
- Link a database to Mercurial
- Link a database to Perforce
- Link a database to Plastic SCM and other systems
- Link a database to SourceGear Vault
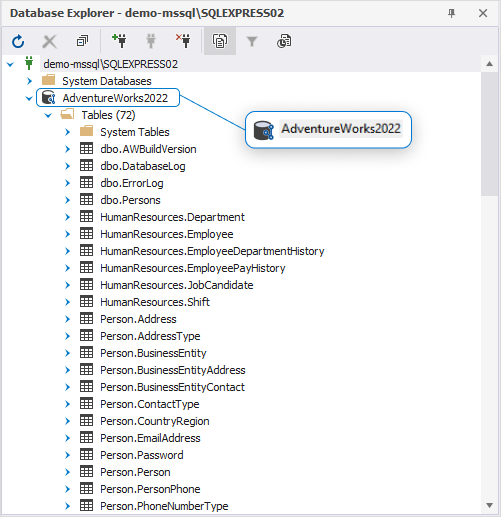
When a database is linked, it is marked with a source control icon in Database Explorer:
How Source Control Manager works
The Source Control Manager checks for:
- Local changes that have not been committed.
- Remote changes that have not been applied to the local database.
- Conflicts caused by simultaneous changes made to the same object in both locations.
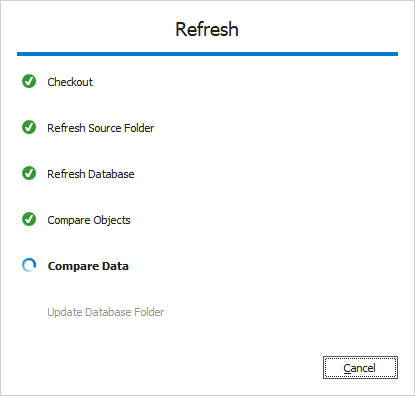
The Refresh operation runs automatically and displays its progress in a separate window.
After the refresh completes, the Source Control Manager opens and displays the detected changes, organized into the following sections:
- Conflicts – Objects modified both locally and remotely.
- Remote changes – Changes committed to the repository but not yet applied locally.
- Local changes – Uncommitted changes made in the local database.
Note
Depending on the changes detected, the Source Control Manager may show one, two, or all three sections.
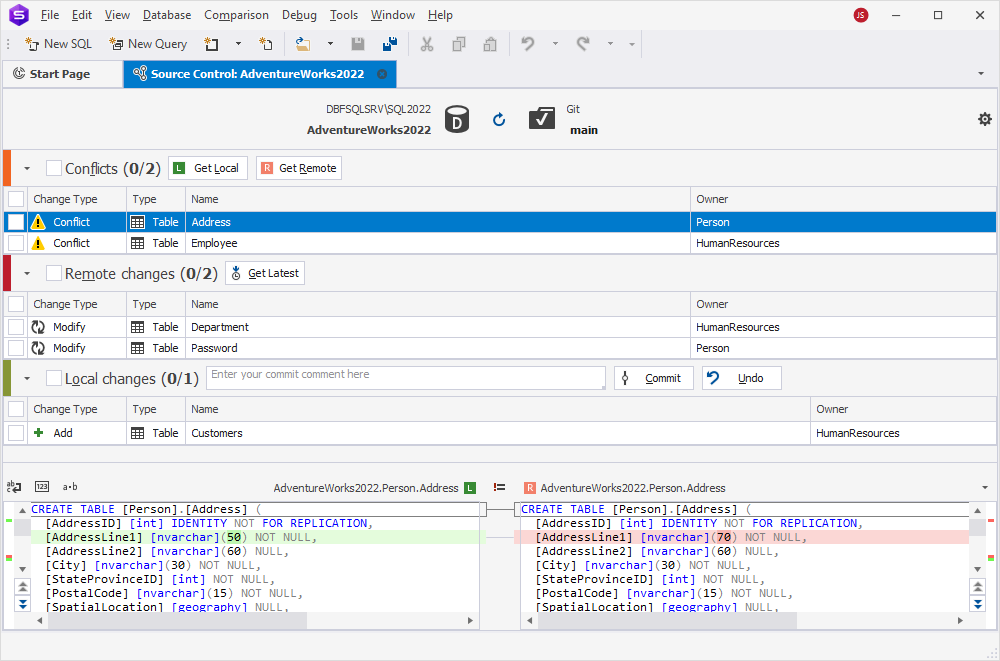
Source Control Manager grid
The grid displays information about each object or data item affected by a change.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Change Type | For Commit – Actions applied to the object or static data in the source control repository:
|
| Type | The type of object affected. For static data, the type is listed as Data. |
| Name | The name of the object. For static data, the name is displayed in the format <TableName> (Data). |
| Owner | The schema or database that contains the object. |
Change types: Local changes section
The table describes the change types in the Local changes section.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Add | Indicates that the object was created locally in the database that is version-controlled using Source Control but has not been committed to the remote repository yet. Selecting the object and Clicking Undo will remove it from the local database. |
| Remove | Indicates that the object was removed from the local database, which is linked to source control, but remains in the remote repository. Selecting the object and clicking Undo will restore it in the local database. |
| Modify | Indicates that the object was modified in the local database, which is linked to source control. As a result, the object’s DDL differs from the version stored in the remote repository. Selecting the object and clicking Undo will discard the local changes and restore the version from the repository. |
Change types: Remote changes section
The table describes the change types in the Remote changes section.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Add | Indicates that the object was added to the remote repository after the last synchronization and is not present in the linked local database. Selecting the object and clicking Get Latest will add it to the local database. |
| Remove | Indicates that the object has been removed from the remote repository since the last synchronization, but it exists in the local database that is linked to this repository via Source Control. Selecting the object and clicking Get Latest will remove the object from the local database. |
| Modify | Indicates that the object was modified in the remote repository after the last synchronization. The object’s DDL now differs from the version in the linked local database. Selecting the object and clicking Get Latest will update the object in the local database to match the version from the repository. |
No changes detected
If the local database and the version control repository are fully synchronized, a message appears indicating that no changes were found.