Link a SQL Server database to a Git repository in GitHub
GitHub is a cloud-based platform that hosts Git repositories and enables collaboration through version control, issue tracking, and integration with CI/CD tools.
This guide describes how to link a SQL Server database in dbForge Studio for SQL Server to a GitHub repository.
Prerequisites
- Install Git for Windows on the machine where you plan to use version control.
- Create a repository on GitHub.
- Clone the repository to your local machine.
Create a new repository on GitHub
1. Sign in to your GitHub account.
2. In the upper-right corner of the page, select the + menu, then select New repository.
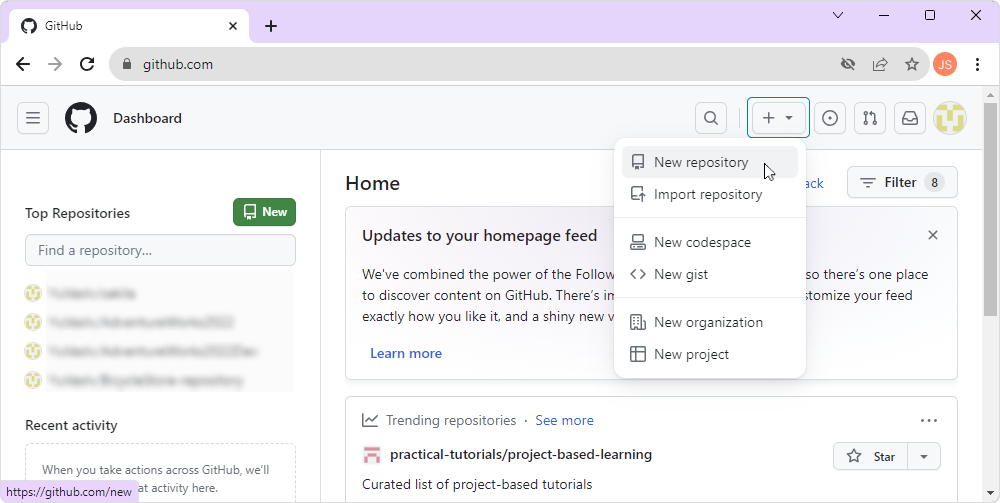
3. On the Create a new repository page, enter a name and optional description.
4. Set the repository visibility:
- Public – Accessible to anyone.
- Private – Accessible only to selected users.
5. Optional: Select initialization options:
- Add a README file – Creates a README file with the project description.
- Add .gitignore – Specifies files or folders to ignore in the repository.
- Choose a license – Grants permissions for using, modifying, and distributing the code.
The default name of the branch is main. To change the name, select settings under the options.
Note
If you import an existing repository, skip this step.
6. Click Create repository.
Clone the repository using the command line
1. Create an empty folder on the disk of your computer where the local repository will be stored.
2. In GitHub, go to Repositories and select the repository you want to clone.
3. Click Code, select HTTPS, and copy the repository URL.
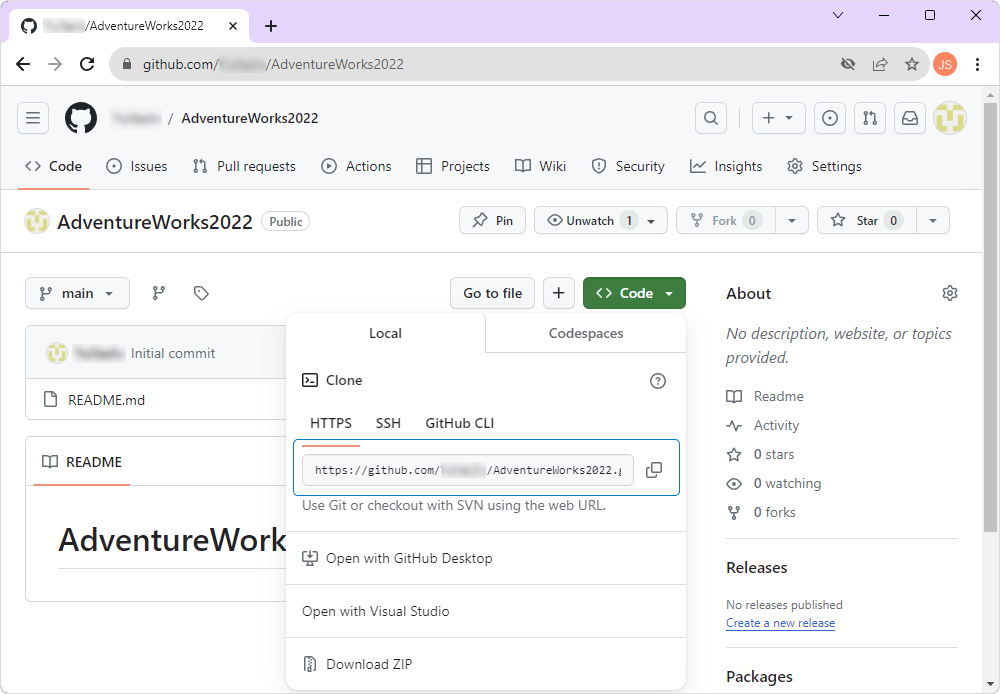
4. Open Command Prompt (CMD).
5. Navigate to the empty folder you created.
Tip
Use the
cdcommand to navigate to a specific folder in the command prompt.
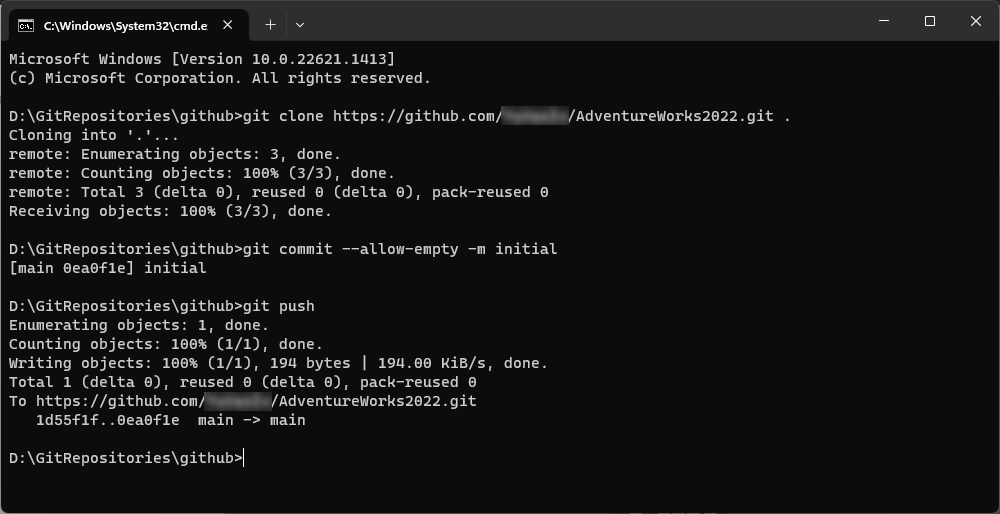
6. Clone the repository by running:
git clone <repository-url> .
Tip
Include a period (.) at the end of the command to clone the repository into the current folder.
7. If no files were added during repository creation, run:
git commit --allow-empty -m initial
git push
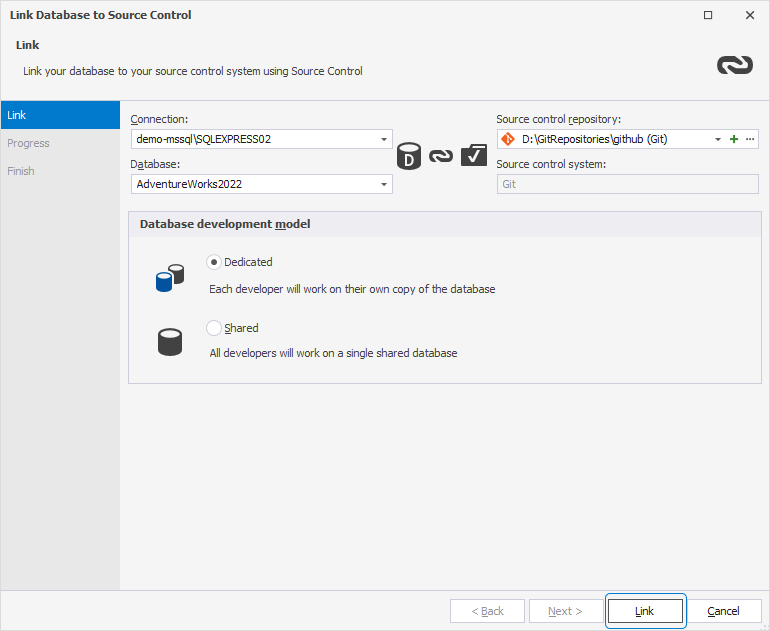
Link a database to the source control in dbForge Studio
1. In Database Explorer, right-click the database you want to link and select Source Control > Link database to Source Control.
Alternatively, on the top menu, select Database > Link Database to Source Control.
2. In the Link Database to Source Control dialog, click + in the Source control repository field.
Note
By default, dbForge Studio automatically selects the repository that was previously linked.
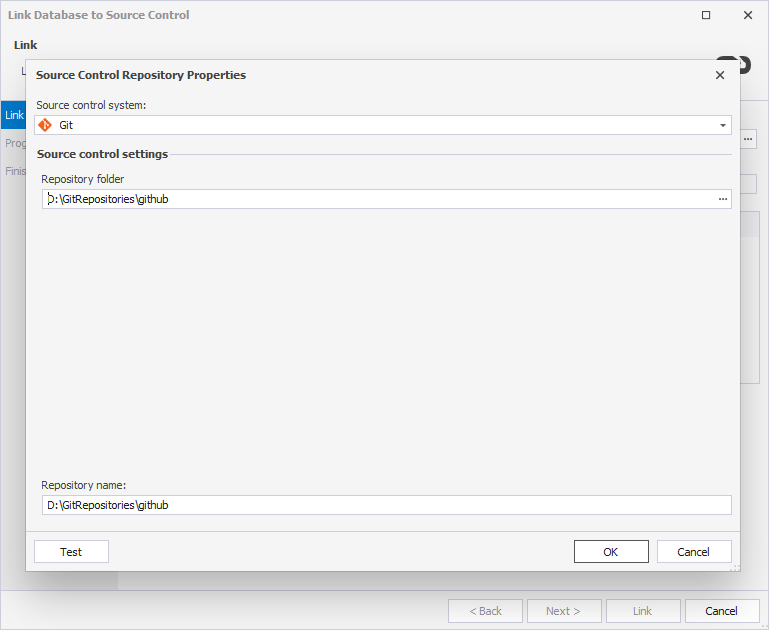
3. In the Source Control Repository Properties dialog, enter the required repository settings:
- Set Source control system to Git.
- In the Repository folder field, enter the full path to the local clone of your GitHub repository, or click the ellipsis (…).
Note
To work with a remote repository, you must first create a local clone using the
git clone <url> <path>command or a Git GUI tool. Enter the path to that local folder (not the remote URL) in the Repository folder field.You can also specify a subfolder within the repository, excluding the
.gitfolder.
Warning
The Repository folder must point to a local folder. Do not enter a remote URL.
- Optional: To verify the repository settings, click Test.
Note
Ensure the repository has at least one commit before proceeding.
- To save the settings and close the dialog, click OK.
4. Choose a database development model:
- Shared – Developers collaborate on a single shared database.
- Dedicated – Each developer works on a local copy of the database.
5. To connect the database to the repository, click Link.
The Refresh window opens and displays the progress of the refresh operation.
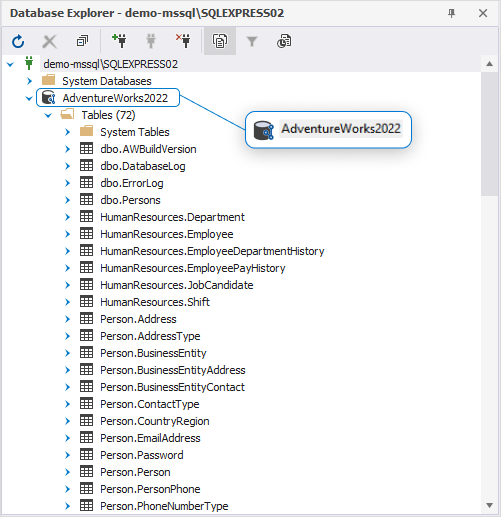
After the database is linked, it appears in Database Explorer with the source control icon:
Set up version control after linking
After linking the database, your next step depends on whether the repository is new or already in use by your team:
- If this is the first time the database is linked:
In the Local changes section of the Source Control Manager, select the objects you want to add to version control, then click Commit.
For instructions, see Commit changes.
- If the database is already under source control:
In the Remote changes section, select the objects you want to retrieve, then click Get Latest.
Note
The Get Latest option is available only in the dedicated development model.
For instructions, see Get the latest version.