How to generate the DDL and DML statements for database objects
In dbForge Studio for SQL Server, you can generate the DDL, DML, CRUD, and EXECUTE statements based on existing database objects.
Generate DDL statements
In dbForge Studio for SQL Server, you can generate DDL statements for the following database objects.
 Click to open the list of supported objects
Click to open the list of supported objects
- Aggregate function (CREATE, DROP, CREATE OR ALTER, DROP and CREATE)
- Application role (CREATE, DROP, DROP and CREATE)
- Assembly (CREATE, DROP, DROP and CREATE)
- Asymmetric key (CREATE, DROP, DROP and CREATE)
- Broker priority (CREATE, DROP, DROP and CREATE, ALTER)
- Certificate (CREATE, DROP, DROP and CREATE)
- Column Encryption Key (CREATE, DROP, DROP and CREATE)
- Column Master Key (CREATE, DROP, DROP and CREATE)
- Contract (CREATE, DROP, DROP and CREATE, ALTER)
- Constraints (CREATE, DROP and CREATE, DROP)
- Database (CREATE, DROP and CREATE, DROP)
- Database role (CREATE, DROP, DROP and CREATE)
- Database trigger (CREATE, DROP, CREATE OR ALTER, DROP and CREATE)
- Default (CREATE, DROP, DROP and CREATE)
- DML Triggers (CREATE, DROP, ALTER, CREATE OR ALTER, DROP and CREATE)
- Event notification (CREATE, DROP and CREATE, DROP)
- External Data Source (CREATE, DROP, DROP and CREATE)
- Full-text catalog (CREATE, DROP, DROP and CREATE)
- Full-text stoplist (CREATE, DROP, DROP and CREATE)
- Indexes (CREATE, DROP and CREATE, DROP)
- Message type (CREATE, DROP, DROP and CREATE, ALTER)
- Partition Function (CREATE, DROP and CREATE, DROP)
- Partition Scheme (CREATE, DROP and CREATE, DROP)
- Procedure (CREATE, DROP, ALTER, CREATE OR ALTER, DROP and CREATE)
- Queue (CREATE, DROP, DROP and CREATE, ALTER)
- Remote service binding (CREATE, DROP, DROP and CREATE, ALTER)
- Route (CREATE, DROP, DROP and CREATE, ALTER)
- Rule (CREATE, DROP, DROP and CREATE)
- Scalar-valued function (CREATE, DROP, ALTER, CREATE OR ALTER, DROP and CREATE)
- Schema (CREATE, DROP, DROP and CREATE)
- Search Property List (CREATE, DROP and CREATE, DROP)
- Sequence (CREATE, DROP, DROP and CREATE)
- Service (CREATE, DROP, DROP and CREATE, ALTER)
- Statistics (CREATE, DROP and CREATE, DROP)
- Symmetric key (CREATE, DROP, DROP and CREATE)
- Synonym (CREATE, DROP, DROP and CREATE)
- Table (CREATE, DROP and CREATE, DROP)
- Table-valued function (CREATE, DROP, ALTER, CREATE OR ALTER, DROP and CREATE)
- User (CREATE, DROP, DROP and CREATE)
- User-defined data type (CREATE, DROP, DROP and CREATE)
- User-defined table type (CREATE, DROP, DROP and CREATE)
- View (CREATE, DROP, ALTER, CREATE OR ALTER, DROP and CREATE)
- XML schema collection (CREATE, DROP, DROP and CREATE)
You can generate DDL statements either from Database Explorer or Object Viewer.
Generate DDL statements from Database Explorer
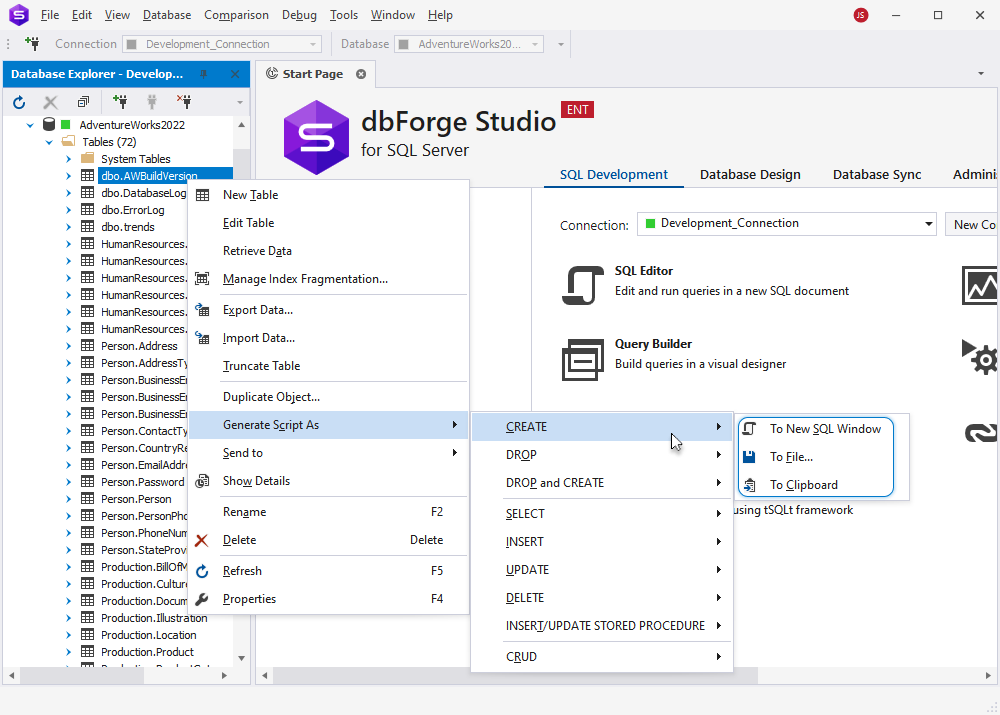
1. In Database Explorer, right-click the required database object and point to Generate Script As.
2. Hover over the DDL statement you want to generate.
3. Select one of the following options:
- To New SQL Window: This will open the statement in a new SQL window in dbForge Studio for SQL Server
- To File: This will save the statement as a SQL file
- To clipboard: This will copy the statement to the clipboard
Generate DDL statements from Object Viewer
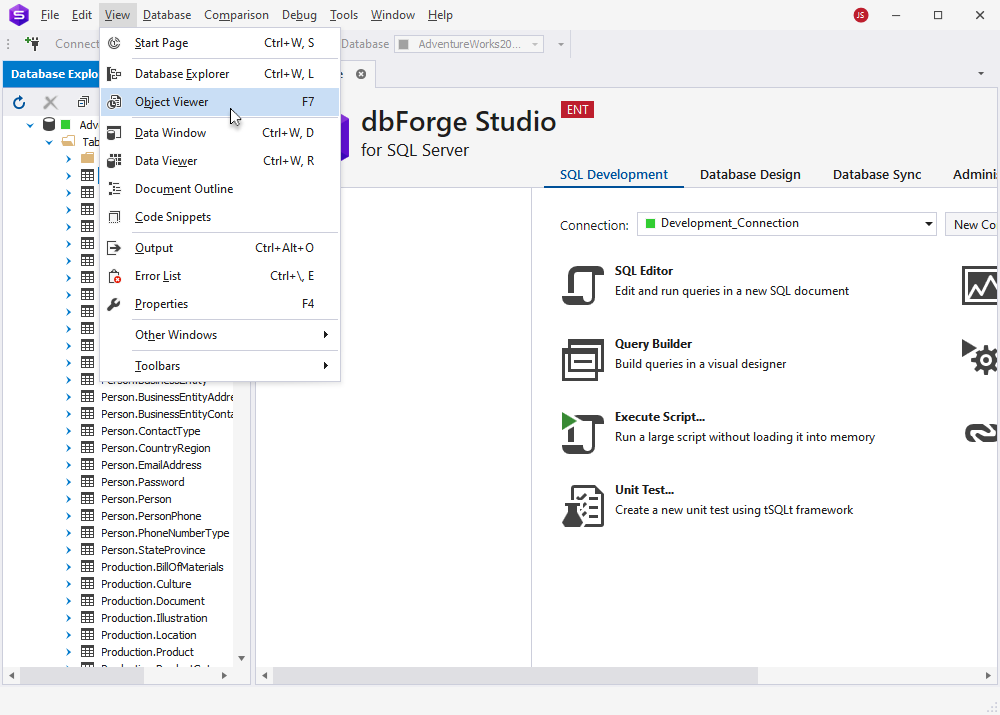
1. To open Object Viewer, select it from the View menu, or simply press F7.
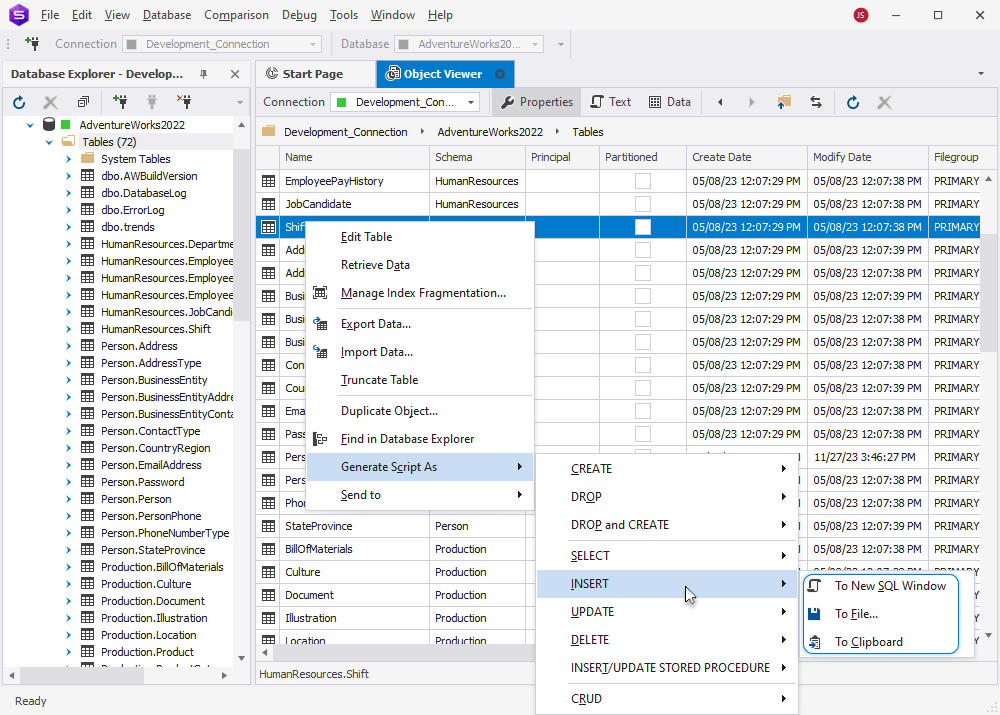
2. To access the database object you need, simply select it from the Database Explorer pane. It will automatically appear in the Object Viewer. Alternatively, you can directly navigate to the desired object within the Object Viewer.
3. To generate a script for the database object, right-click it in the Object Viewer grid and select Generate Script As. This will provide you with the same options as those in the Database Explorer pane.
Generate DML statements
In dbForge Studio for SQL Server, you can generate DML statements for:
- Aggregate function (SELECT)
- Table (SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE)
- Table-valued function (SELECT)
- Scalar-valued function (SELECT)
- View (SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE)
Generate DML statements from Database Explorer
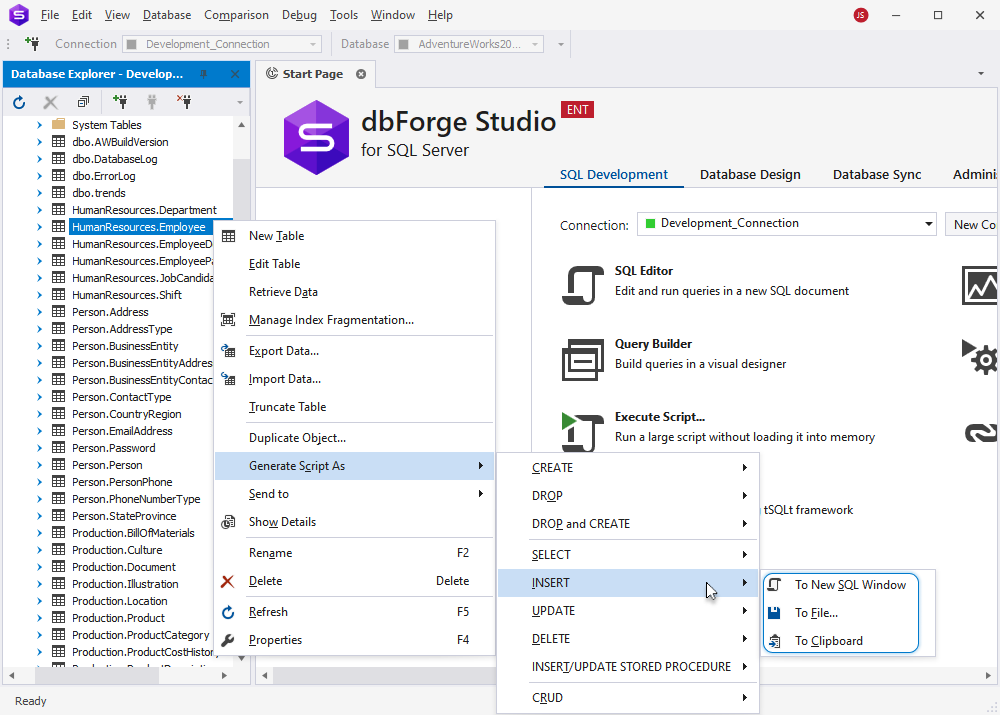
1. Right-click the required database object and point to Generate Script As.
2. Hover over the required DML statement.
3. Select one of the following options:
- To New SQL Window: This will open the statement in a new SQL window
- To File: This will save the statement as a SQL file
- To clipboard: This will copy the statement to the clipboard
Generate DML statements from Object Viewer
1. In Database Explorer, select the folder with the database object you want to generate a DML statement for and navigate to View > Object Viewer:
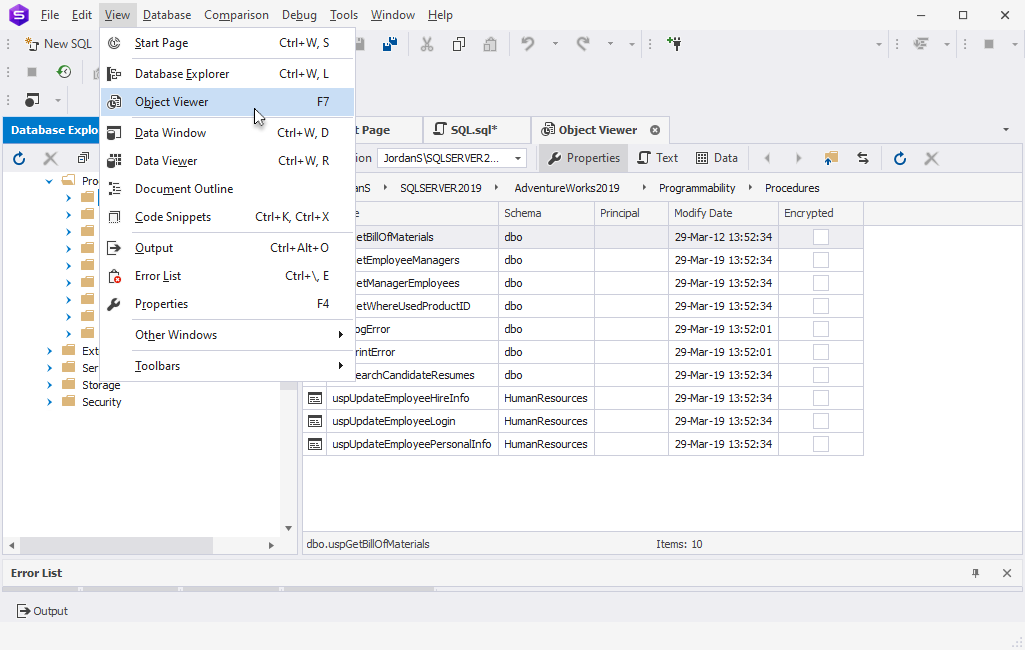
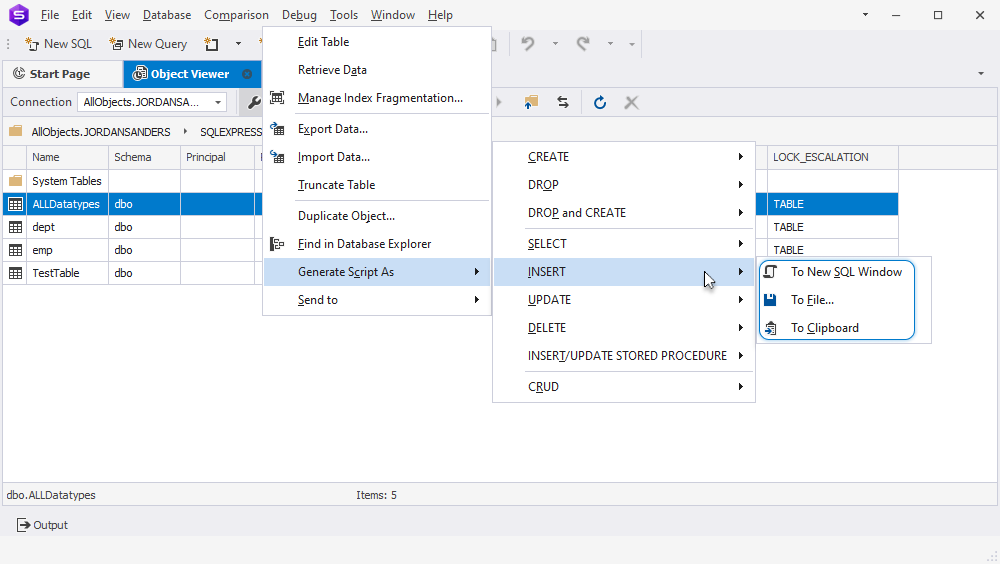
2. Right-click the required object and point to Generate Script As.
3. Hover over the DML statement you want to generate.
4. Select one of the following options:
- To New SQL Window: This will open the statement in a new SQL window in dbForge Studio for SQL Server
- To File: This will save the statement as a SQL file
- To clipboard: This will copy the statement to the clipboard
Generate DML procedures
In dbForge Studio for SQL Server, you can generate DML procedures for the following database objects:
- Table (INSERT/UPDATE STORED PROCEDURE, CRUD)
- View (INSERT/UPDATE STORED PROCEDURE, CRUD)
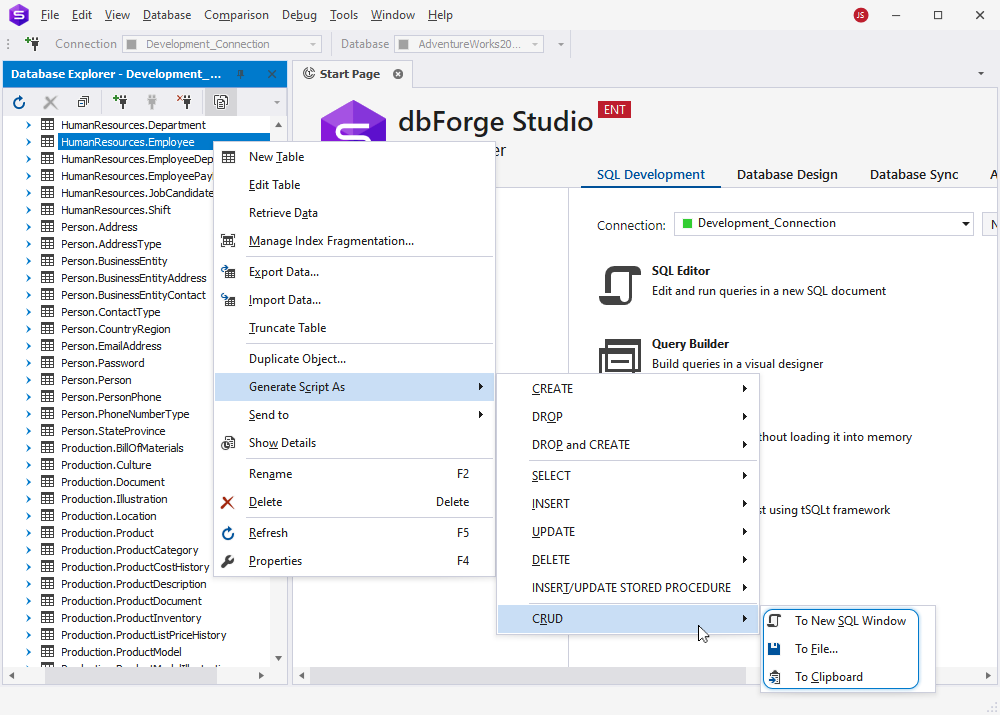
Generate a CRUD statement from Database Explorer
1. Right-click a database object and point to Generate Script As.
2. Hover over the required CRUD statement.
3. Select one of the following options:
- To New SQL Window: This will open the statement in a new SQL window in dbForge Studio for SQL Server
- To File: This will save the statement as a SQL file
- To clipboard: This will copy the statement to the clipboard
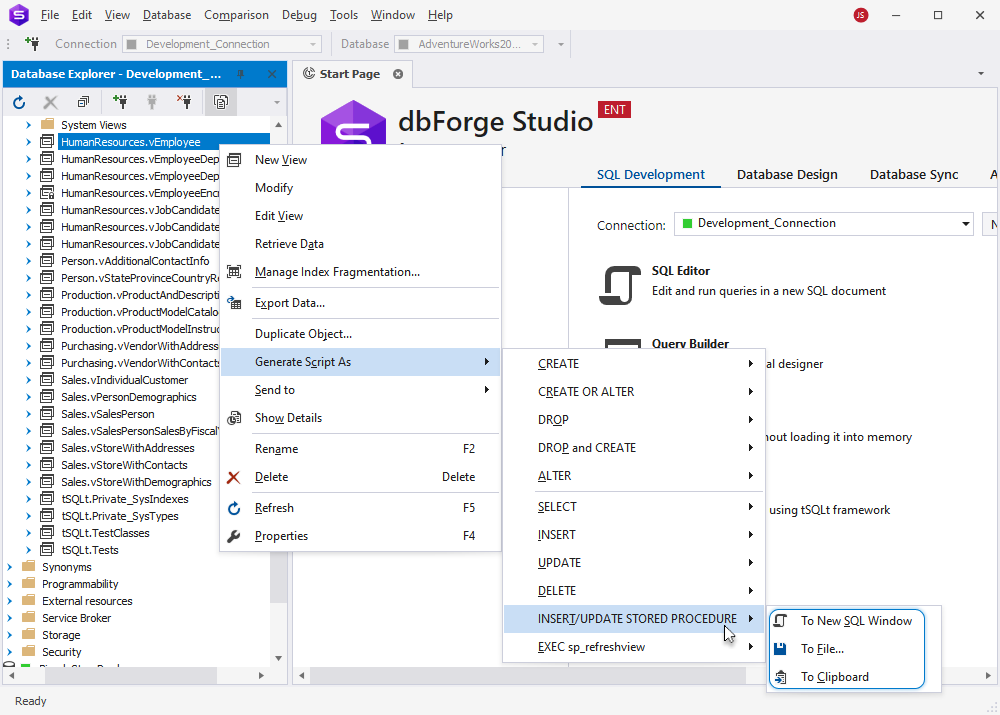
Generate CRUD statements from Object Viewer
Similarly, you can generate a CRUD statement from Object Viewer.
For views, for example, you can generate the INSERT/UPDATE STORED PROCEDURE statement.
The ready DML procedure script will look like as follows.
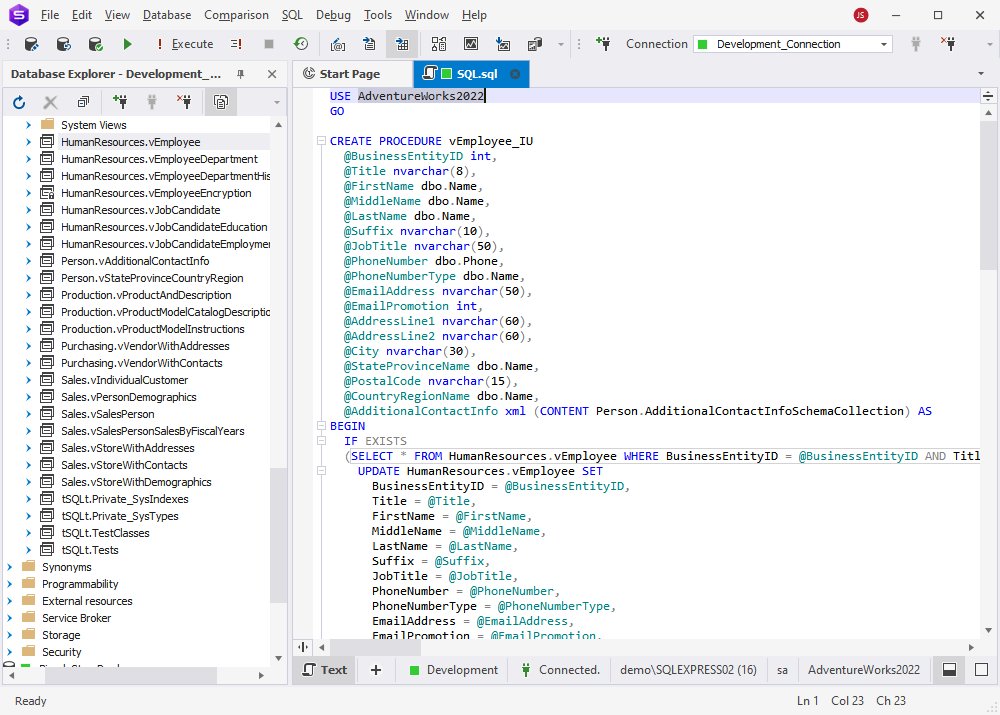
Generate EXECUTE statements
You can generate EXECUTE statements in dbForge Studio for SQL Server for:
- Procedure (EXECUTE)
- Table-valued function (EXECUTE)
- Scalar-valued function (EXECUTE)
- View (EXECUTE sp_refreshview)
Generate EXECUTE statements from Database Explorer
1. In Database Explorer, right-click the necessary object and hover over Generate Script As.
2. Point to EXECUTE.
3. Select one of the following options:
- To New SQL Window: This will open the statement in a new SQL window in dbForge Studio for SQL Server
- To File: This will save the statement as a SQL file
- To clipboard: This will copy the statement to the clipboard
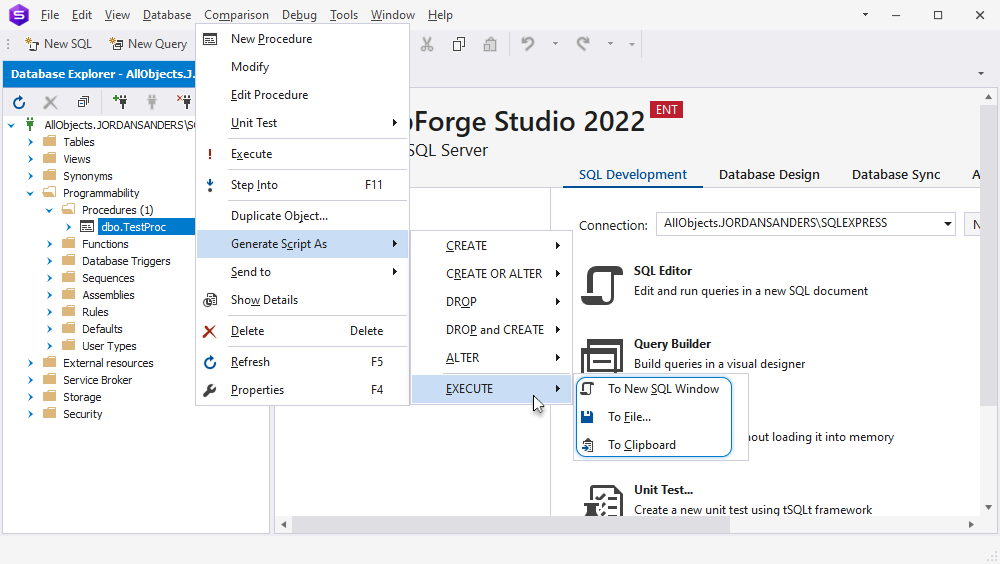
Generate EXECUTE statements from Object Viewer
1. Select the folder with a database object you want to generate the EXECUTE query for and navigate to View > Object Viewer:
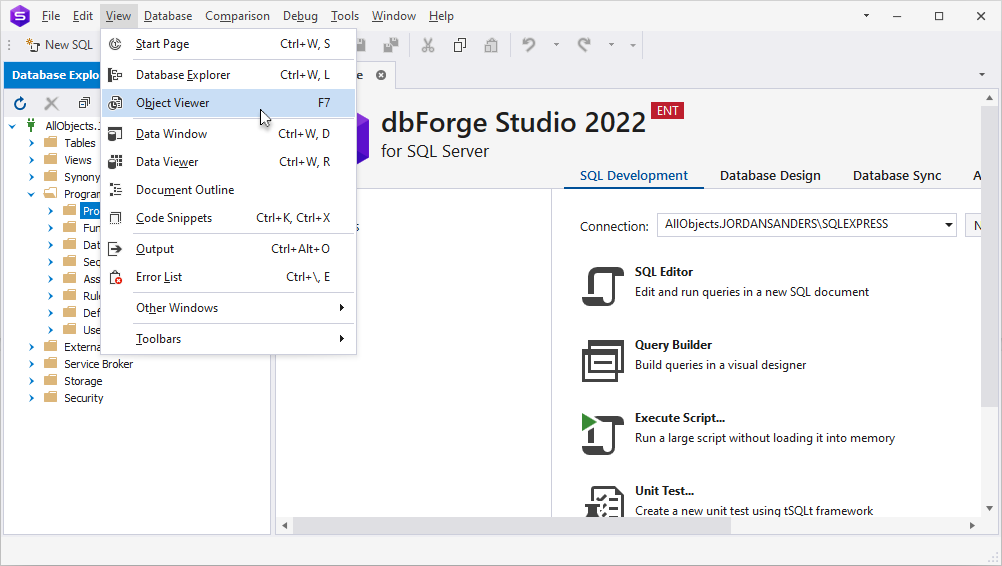
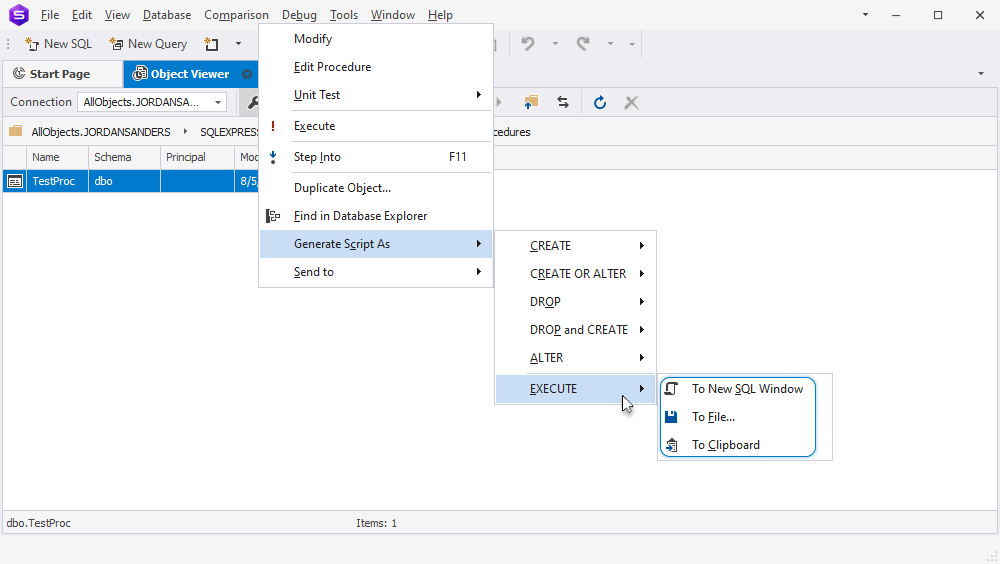
2. Right-click a database object and hover over Generate Script As.
3. Point to EXECUTE.
4. Select one of the following options:
- To New SQL Window: This will open the statement in a new SQL window in dbForge Studio for SQL Server
- To File: This will save the statement as a SQL file
- To clipboard: This will copy the statement to the clipboard
If you want to generate a script for an entire database, refer to the Generate Scripts Wizard topic.
Customize statement templates
dbForge Studio for SQL Server allows for configuring statement templates. To access the configuration options, follow these steps.
1. Navigate to Tools > Options:
2. Switch to Generate Scripts and select General:
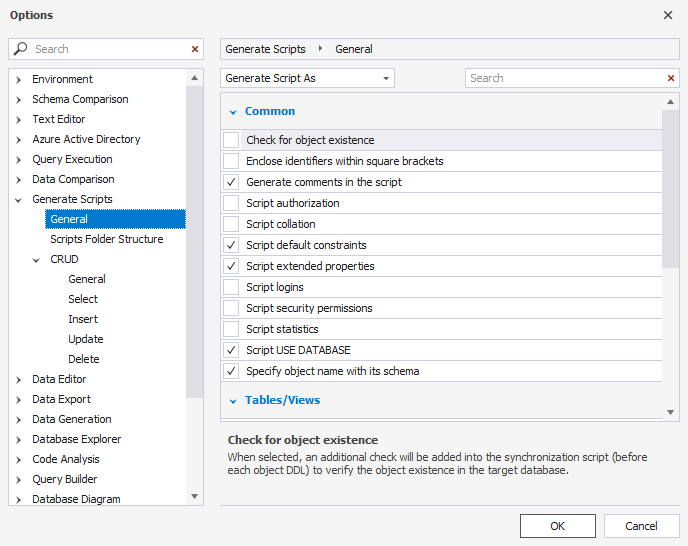
3. Adjust the scripts options to your needs and click OK.
4. To configure the CRUD templates, switch to CRUD and select General, Select, Insert, Update, or Delete. Once you have completed the configuration, click OK.
General options
When you access the settings of the statements templates, you can see the following options:
| Option name | Option group | Option description |
|---|---|---|
| Check for object existence | Common | Verifies whether an object exists in a target database. |
| Enclose identifiers within square brackets | Common | Inserts all identifiers into square brackets. |
| Generate comments in the script | Common | Puts comments to the script. |
| Script authorization | Common | Scripts authorization clauses. |
| Script collation | Common | Inserts collation infomation to the script. |
| Script default constraints | Common | Includes default constraints and schema defaults. |
| Script extended properties | Common | Adds extended properties of database objects to the script. |
| Script logins | Common | Places all logins available on a server. |
| Script security permissions | Common | Includes security permissions. |
| Script statistics | Common | Involves statistics. |
| Script USE DATABASE | Common | Generates the USE DATABASE query. |
| Security object name with its schema | Common | Prefixes object names with object schema. |
| Decrypt encrypted objects | Tables/Views | Decrypts bodies of encrypted objects for comparison and synchronization. |
| Enforce full column list | Tables/Views | Generates the INSERT statements with full-specified column list. |
| Script change tracking | Tables/Views | Adds CHANGE_TRACKING clauses and statements when the tool compares and synchronizes databases. |
| Script check constraints | Tables/Views | Includes the CHECK constraints to the script. |
| Script DATA_COMPRESSION for indexes, primary and unique constraints | Tables/Views | Involves the DATA_COMPRESSION claue for indexes, primary, and unique key constraints. |
| Script DML triggers | Tables/Views | Puts the CREATE statement of triggers on tables. |
| Script foreign keys | Tables/Views | Includes the CREATE query of foreign keys on tables. |
| Script full-text search | Tables/Views | Adds full-text stoplists, full-text catalogs, and full-text indexes. |
| Script indexes | Tables/Views | Puts the CREATE statement of indexes on tables. |
| Script primary keys | Tables/Views | Includes the CREATE query of primary keys on tables. |
| Script unique keys | Tables/Views | Involves the CREATE query of unique keys on tables. |
CRUD options
The CRUD templates includes such options:
| Option name | Option description |
|---|---|
| General | Allows you to configure whether to inlclude the SELECT/INSERT/UPDATE/DELETE statements. |
| Select | Lets adjust the code template to your needs. |
| Insert | Permits to tune the statement template. |
| Update | Allows configuring the UPDATE query template. |
| Delete | Empowers to alter the DELETE statement template. |
Snippet placeholders
General placeholders
| Placeholder | Description |
|---|---|
$table$ |
Specifies the name of the table for which you generate the CRUD procedures. |
$schema$ |
Defines the name of the schema. |
$col.Name$ |
States the column name of the table. |
$col.AsParameter$ |
Determines the name of the procedure parameter converted from the column name of the table. |
$col.Type$ |
Specifies the name of data type of the table column. |
$parameters$ |
Defines the parameters of the $col.AsParameter$ and $col.Type$ separated by such symbols: “,” (comma) and “\n”(line feed). |
$col.WhereName$ |
Verifies data type of the column. If it’s geography or geometry, the STEquals($col.AsParameter$) method call will be added. |
$col.WhereAsParameter$ |
Specifies the name of the table column converted to the name of the procedure parameter or “1” if data type of the column is geography or geometry. |
;format="id" |
States the formatting for any name. If a name is quoted, it will be quoted again. For example, ‘id’ will be ‘‘id’’. |
SELECT template
| Placeholder | Description |
|---|---|
$procedure$ |
Specifies the name of the procedure. For example, usp_$table$_Select. |
$parameters$ |
Defines the procedure parameters only for the PRIMARY KEY columns. |
$columns$ |
States the columns list (specified in $col.Name$) separated by “,” (comma). |
$where$ |
Determines the list of selection conditions combined with the AND operator. If “Return all data if input parameters are null” is selected, then ($col.WhereName$ = $col.WhereAsParameter$ OR $col.AsParameter$ IS NULL) the conditions will be vaialbale only for the PRIMARY KEY columns. Otherwise, “$col.WhereName$ = $col.WhereAsParameter$” will be available only for the PRIMARY KEY columns. |
INSERT template
| Placeholder | Description |
|---|---|
$procedure$ |
Defines the name of the procedure. For example, usp_$table$_Insert. |
$columns$ |
Specifies the columns list of the table, except AUTO INCREMENT (IDENTITY) and GENERATED ALWAYS. |
$values$ |
States inserted data $col.AsParameter$ separated by “,” (comma) for all the columns, except AUTO INCREMENT (IDENTITY) and GENERATED ALWAYS. |
$where$ |
Determines the list of selection conditions combined with the AND operator. If “Return inserted row” is selected and if the table has the AUTO INCREMENT (IDENTITY) and GENERATED ALWAYS columns, then the “$col.Name$ = SCOPE_IDENTITY()” condition will be available only for the AUTO INCREMENT (IDENTITY) columns. Otherwise, “$col.WhereName$ = $col.WhereAsParameter$” will be available for all the columns, except GENERATED ALWAYS. |
Delete template
| Placeholder | Description |
|---|---|
$procedure$ |
Specifes the name of the procedure. For example, usp_$table$_Delete. |
$parameters$ |
Defines the procedure parameters only for the PRIMARY KEY columns. |
$where$ |
States the deletion conditions “$col.WhereName$ = $col.WhereAsParameter$” combined with the AND operator only for the PRIMARY KEY columns. |
Update template
| Placeholder | Description |
|---|---|
$procedure$ |
Defines the name of the procedure. For example, usp_$table$_Update. |
$parameters$ |
Specifies the procedure parameters for all the columns, except GENERATED ALWAYS. |
$columns$ |
States the columns list of the table, except AUTO INCREMENT (IDENTITY) and GENERATED ALWAYS. |
$assignments$ |
Determines the list of updated data “$col.WhereName$ = $col.WhereAsParameter$” combined with the AND operator only for the PRIMARY KEY columns. |