How to export SQL Server data to Microsoft Access
MDB is the default database file format used in Microsoft Access 2003 and earlier. An MDB file stores data in database tables that are linked to each other via primary and foreign keys. It contains the complete structure of database tables and may also store queries, stored procedures, and database security settings.
Note
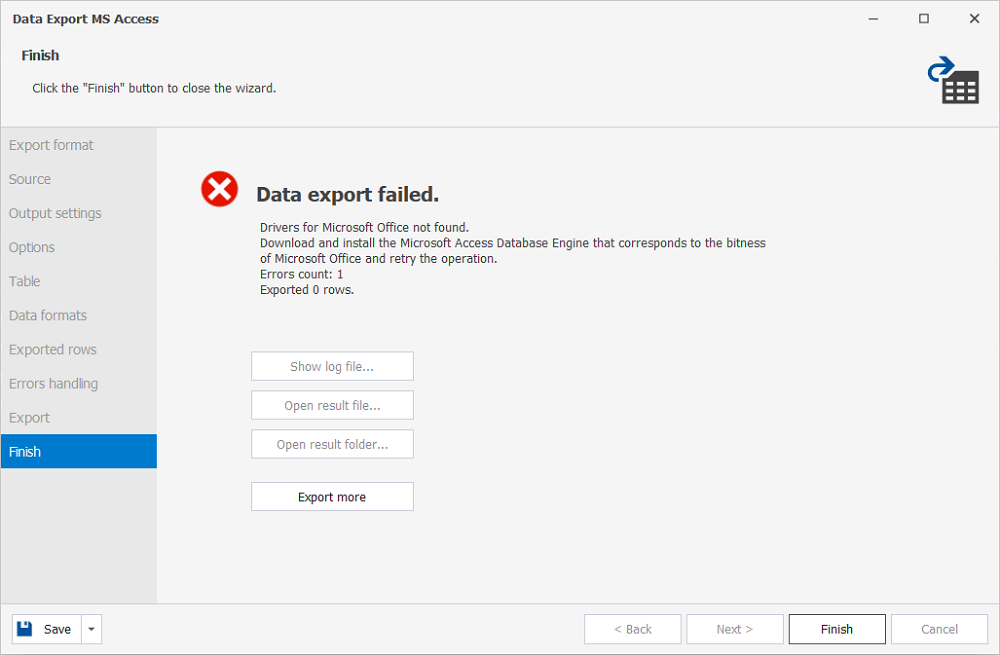
Make sure that Microsoft Access Database Engine 2016 Redistributable x32 and x64 (accessdatabaseengine.exe and accessdatabaseengine_X64.exe) are installed on your computer. Otherwise, you might encounter the following error during data export:
To export data to Microsoft Access:
1. In Object Explorer, right-click a database, point to Data Pump, and then click Export Data.
2. On the Export format page, select the MS Access export format or load export options from a template file if you saved it previously. Click Next.
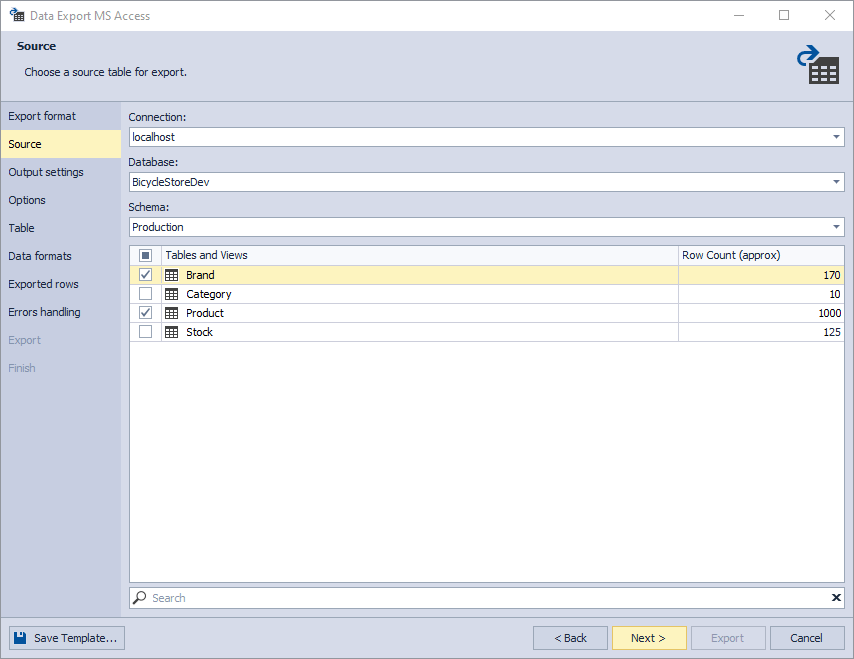
3. On the Source page, select a server connection, a database and its schema, table(s), and view(s) that you want to export, and click Next.
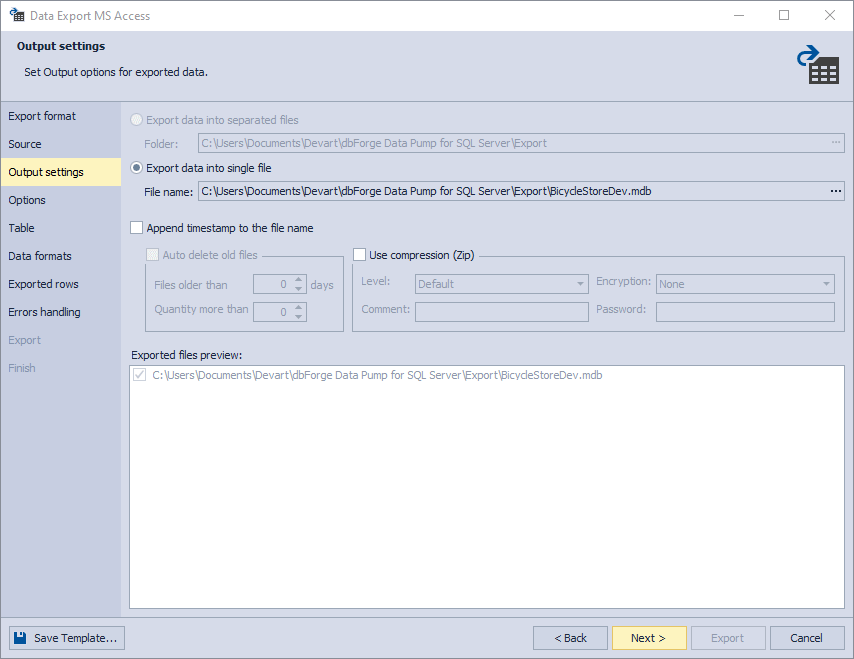
4. On the Output settings page, you have two main options:
-
Export data into separated files, where you specify the path to the folder that they will be saved to.
-
Export data into single file, where you specify the path and the file name.
You will find the list of files to be exported in the Exported files preview box.
You can also enable three additional options:
-
Append timestamp to the file name.
-
Auto delete old files to auto-delete exported files that are older than a specified number of days.
-
Use compression (Zip) to create an archive file with your exported files. Additionally, you can specify the compression level (No Compression, Best Speed, Fast, Default, Good, or Maximum), add a comment, and encrypt your archive with AES128 or AES256 encryption and specify a decryption password.
If the destination folder does not exist, the application will prompt you to create it. Click Yes to proceed.
If you choose to export to an existing password-protected MS Access database, i.e., exporting to an existing .mdb file on the disk, a message window will pop up, requesting you to enter the password in order to continue. Moreover, the password will be disabled on the Options page.
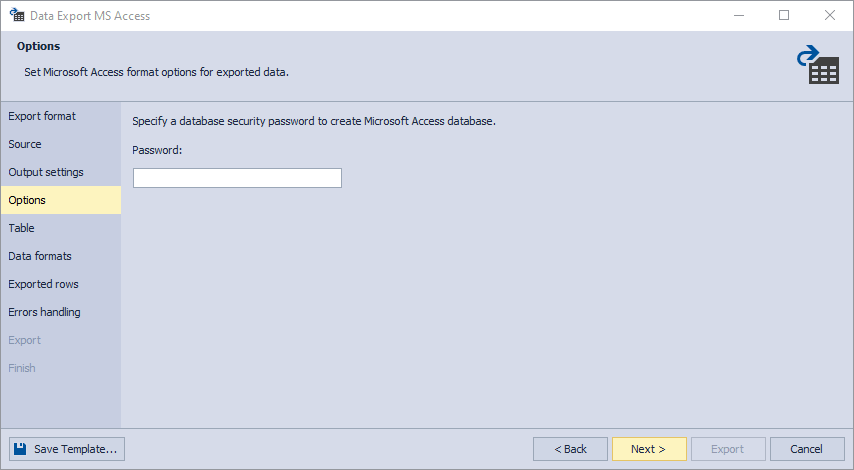
5. On the Options page, you can set a security password to create a Microsoft Access database.
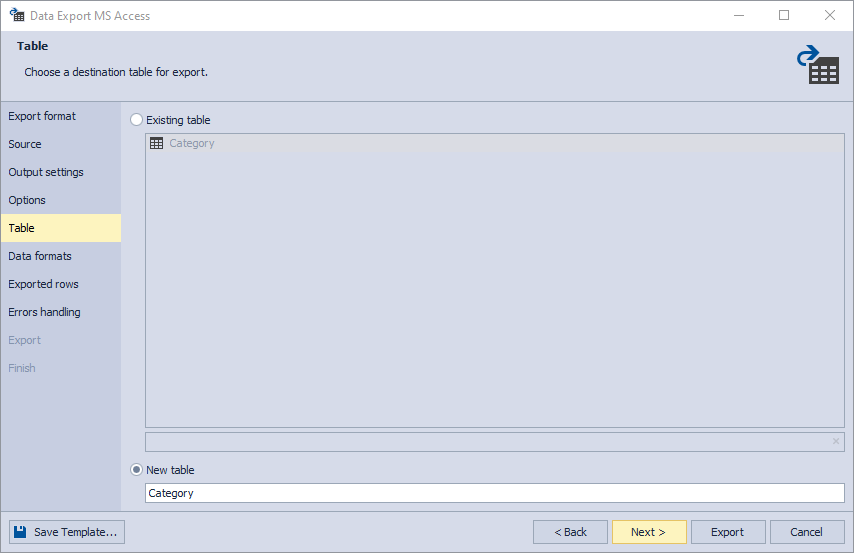
6. The Table page appears when you choose to export data to an existing .mdb file on the disk, which already contains one or more tables. However, if the export is selected to a file that does not yet exist on the disk, the Table page will not appear. Furthermore, if you choose to export more than one table on the Source page, the Table page will not be visible either.
On the Table page, you have the option to either export data to an already created table in the .mdb file, allowing you to add more data to the existing table, or create a completely new table in the database and export data into it:
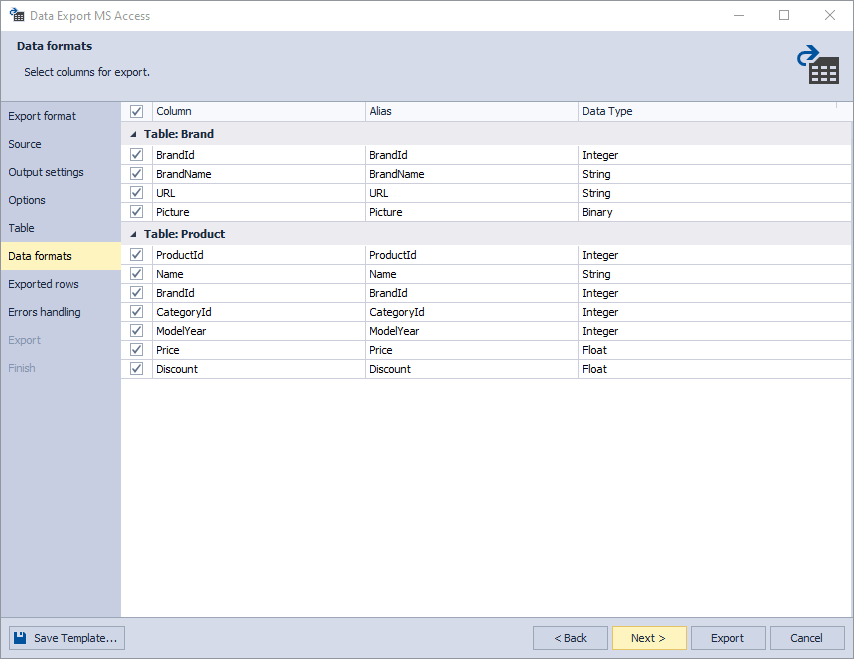
7. On the Data formats page, you can select columns for export and check their aliases and data types.
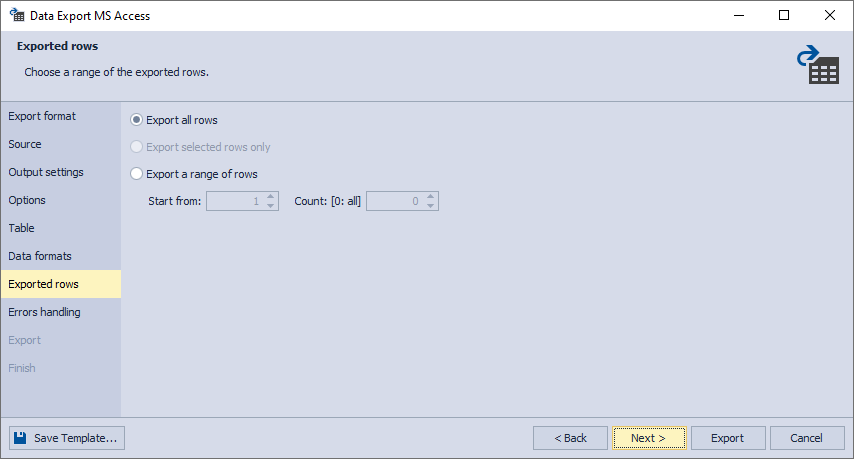
8. On the Exported rows page, you can select to export all rows, export the rows selected on the Data formats page, or export a specified range of rows.
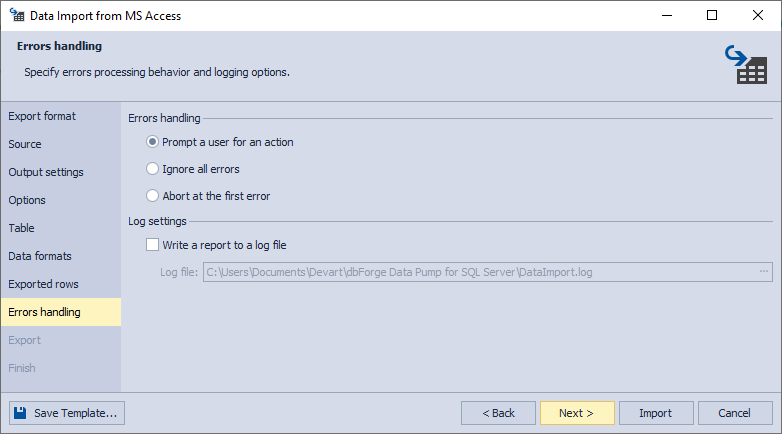
9. On the Errors handling page, you can specify the error processing behavior (using one of the three available options: Prompt the user for an action, Ignore all errors, or Abort at the first error) and opt to write reports to a log file with a specified path.
Note
If you want to save your export settings as templates for recurring scenarios, click Save Template.
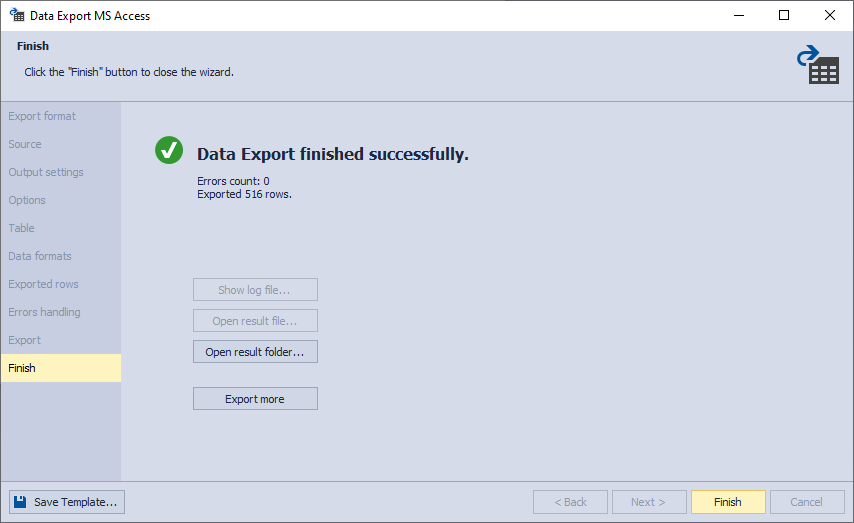
10. Click Export. When your data export is completed, you have several options: you can open the exported file or folder, perform another export operation, view the log file, or simply click Finish.