Using Parameters
What is a Parameter?
Parameter is a placeholder for a variable that contains a value of some type that is passed to a database server along with the SQL text at the query execution time. Also, parameter can hold values returned by a server after a query or stored procedure execution.
You can benefit from parameters usage in the following situations:
-
When you execute a query multiple times with different input values
-
When you debug a query from your application code
Adding Parameters to a Query Text
There are two types of parameters, that you can add to a query text:
- Named parameter
- Positional parameter
Named Parameters
Parameters are declared using : prefix followed by a name of the parameter.
For example:
SELECT * FROM city
where country_id = :par1;
:par1 is a parameter in this query.
Positional Parameters
When using positional $ parameter, you need to go for PREPARE and then EXECUTE statements.
For example:
PREPARE test (int) AS
SELECT * FROM city
where country_id = $1;
EXECUTE test(1);
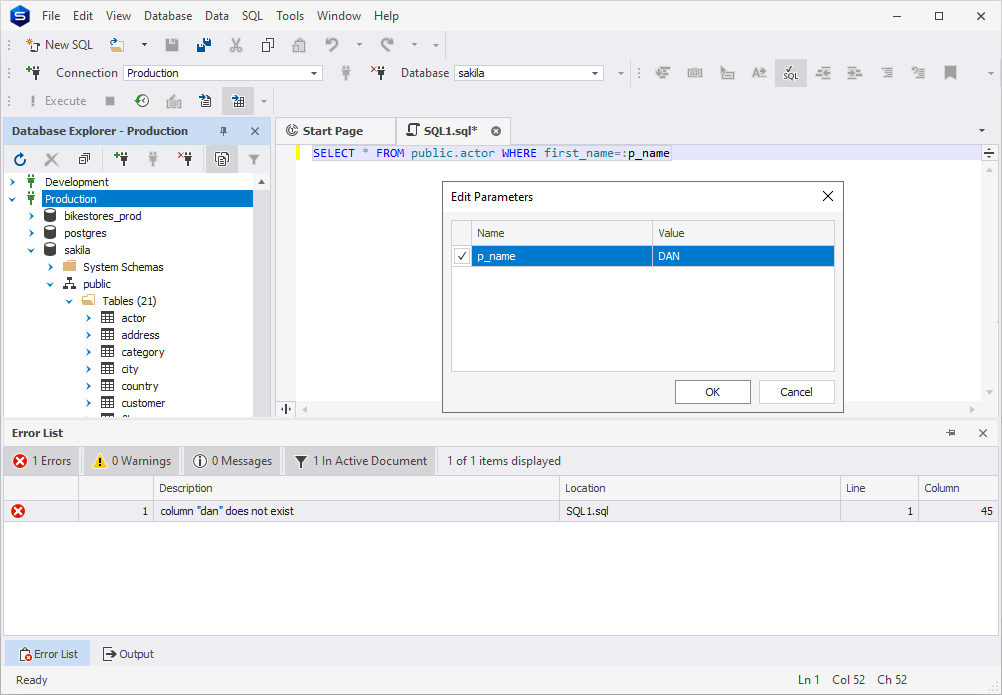
Modifying Parameter Values
To set parameter values, press Ctrl+Shift+P or click Edit Parameters on the SQL toolbar, or in the main menu.
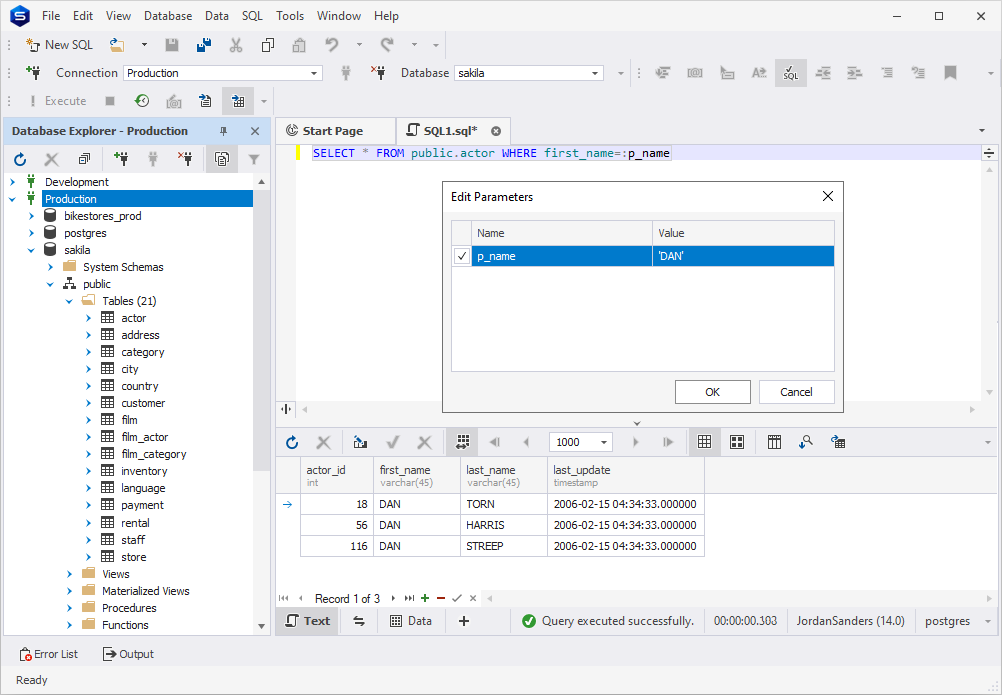
In the Edit Parameters dialog box, choose a parameter and set its value.
Each parameter is to be treated according to its type, the same way it is used in a script. For example, a string should be enclosed in single quotes:
If the parameter type is incorrect, you will get an error: