PL/SQL Context Prompt
dbForge Studio for Oracle and its embedded PL/SQL prompts give you a chance to implement code routines rationally. PL/SQL context prompt accelerates the writing of SQL code by offering a list of database objects and PL/SQL statements to be inserted, based on the context of what you type in the SQL editor.
The list of PL/SQL context prompts is as follows:
- Quick selection of the column list
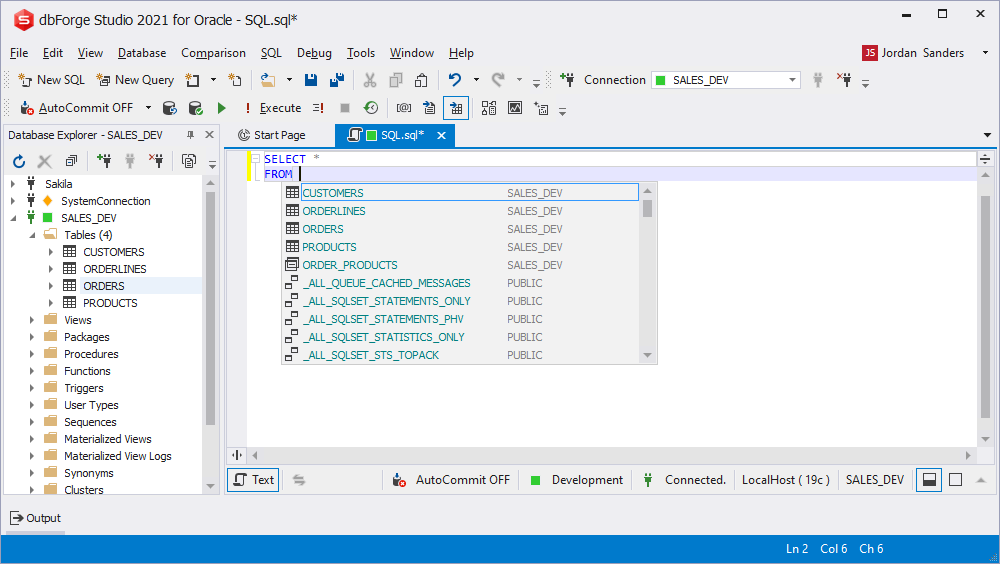
- Table expressions prompt
- Phrase completion
- Automatic generation of JOIN statements
- JOIN conditions prompt
- WHERE conditions prompt
- Columns prompt
- Columns prompt inside functions
- DELETE FROM prompt
- Prompt on selected columns
- UPDATE prompt
- Selection for a different schema
- Cursors prompt
- Prompting cursors with parameters
- RECORD fields prompt
- %ROWTYPE attribute for the RECORD prompt
- Prompting RECORD type variables
- REF-CURSOR variables prompt
- SELECT INTO variables prompt
- Assign a value to a variable
- Variable initialization prompt
- Function parameters prompt
- Stored Procedures parameters prompt
- Recursive calls prompt
- Prompting procedures declared in packages
- Prompting package functions and variables
- SEQUENCE built-in functions prompt
- Prompting built-in methods of the table type
- Prompting built-in array methods
- SELF-type variables prompt
- Prompting objects inside FETCH INTO
- User-defined types prompt
- Prompting objects inside FOR IN
- Variables prompt in the VALUES block
- Objects prompt in the user-defined package
- CREATE TABLE prompt
- CREATE VIEW prompt
- Prompting objects in the DROP statement
- Prompting NEW/OLD variables columns
- Triggers prompt
- Objects prompt inside the ALTER statement
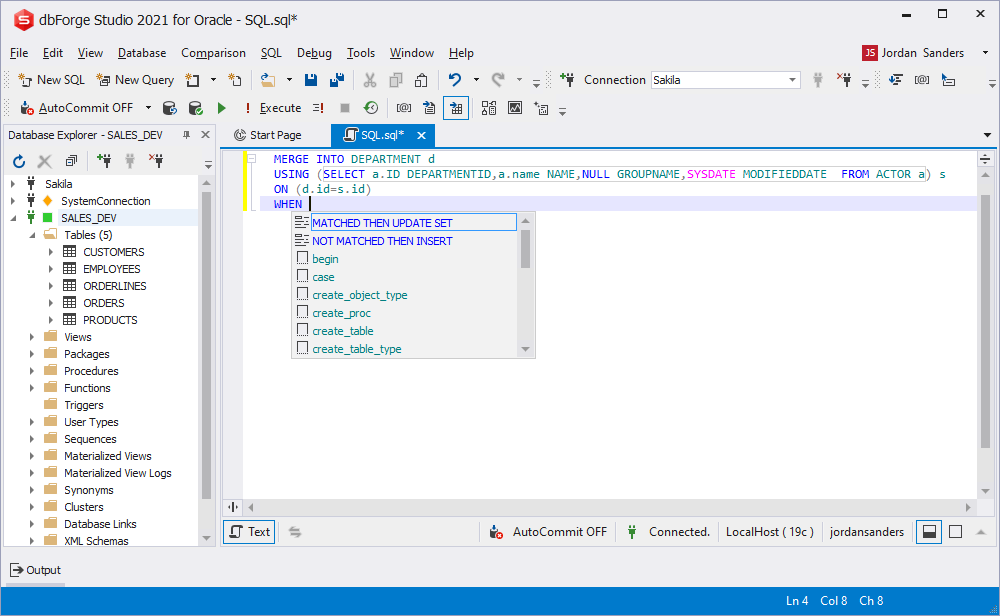
- Clauses prompt of the MERGE statement
Quick selection of the column list
There is a possibility to use the Column Picker in the SELECT statement to simplify required columns selection.
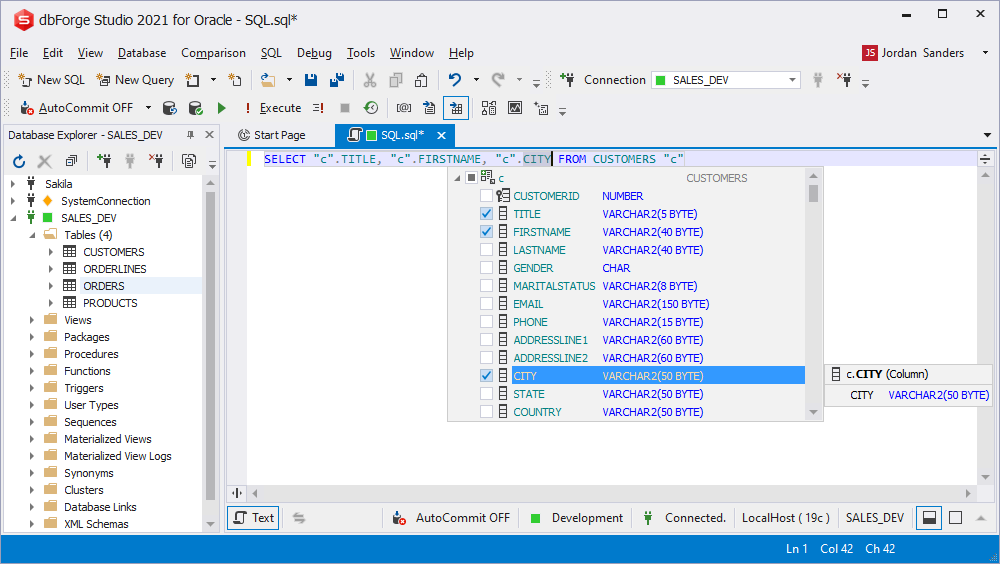
Table expressions prompt
While writing the FROM statement, the table objects (such as tables or views) are listed in the context-dependent suggestion list. The objects related to the current schema are located on top of the list.
Phrase completion
The application suggests not only separate keywords and object names, but entire code phrases. For instance, INNER JOIN is prompted in the SELECT query.
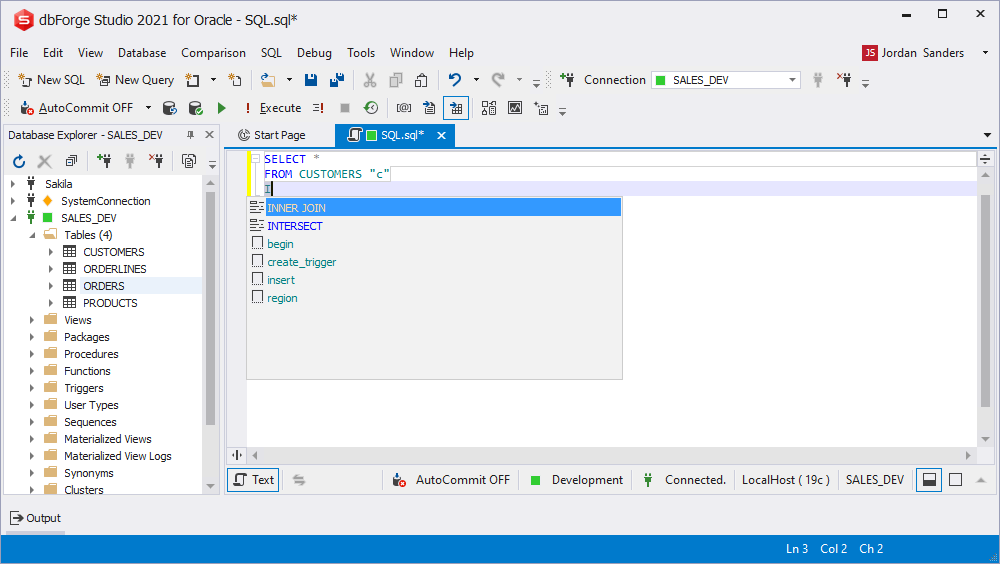
Automatic generation of JOIN statements
While combining tables you can use automatically generated JOIN statements based on the foreign keys. In case the JOIN operation requires custom conditions, you can select required table objects manually.
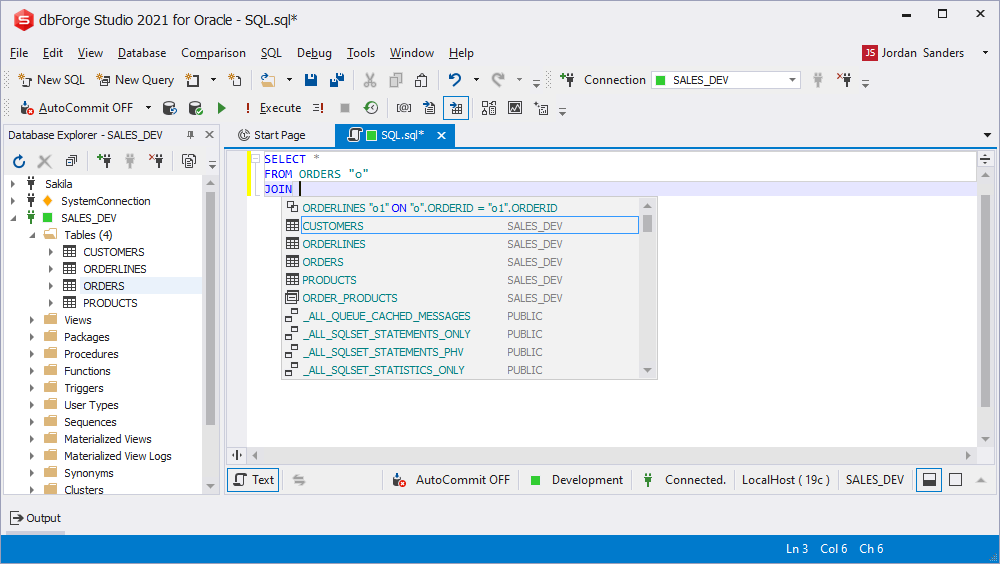
JOIN conditions prompt
In case a foreign key joins two tables, there is a possibility to select automatically generated join condition. Optionally you can set this condition based on the columns used in the query. Object prompts that return the result (e.g. custom functions) are also available.
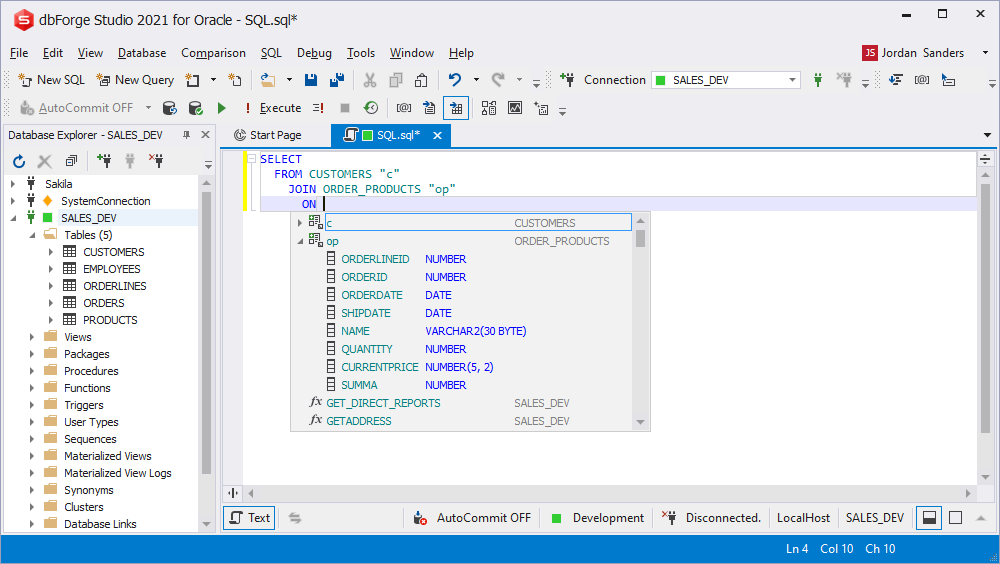
WHERE conditions prompt
The WHERE block displays the list of columns grouped by aliases. In addition the list contains objects that return results (e.g. custom functions) and user-defined custom columns.
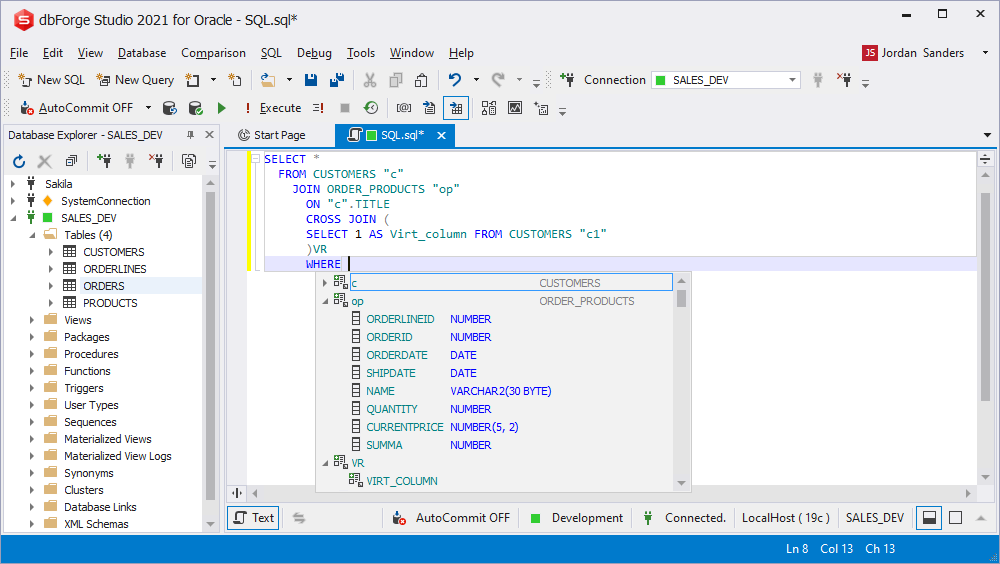
Columns prompt
While creating queries the application analyzes current location in order to display columns aliases correctly.
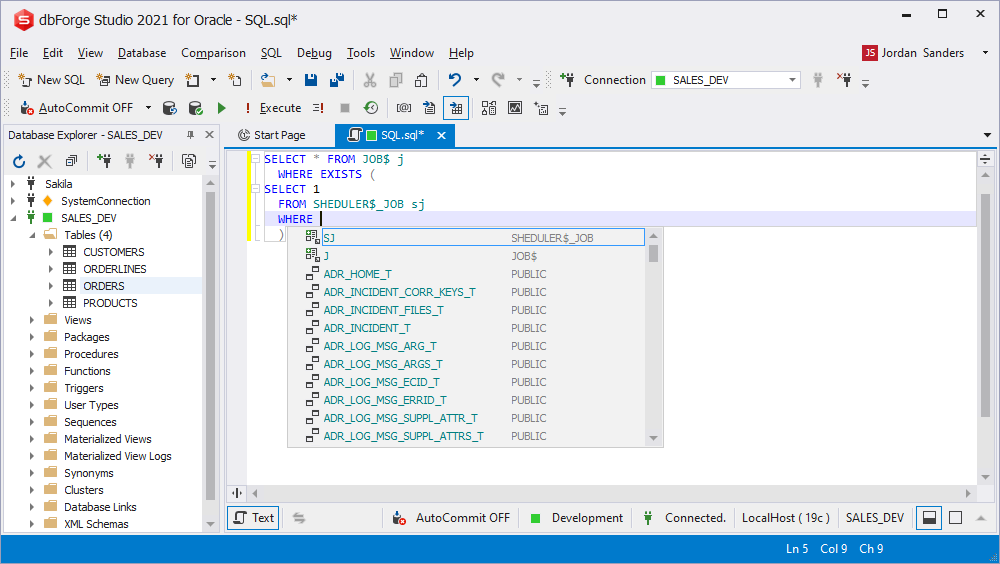
Columns prompt inside functions
While calling an object that returns the result, the Parameter Info tooltip shows the list of available parameters. In case the object is a system function, a short summary is additionally displayed.
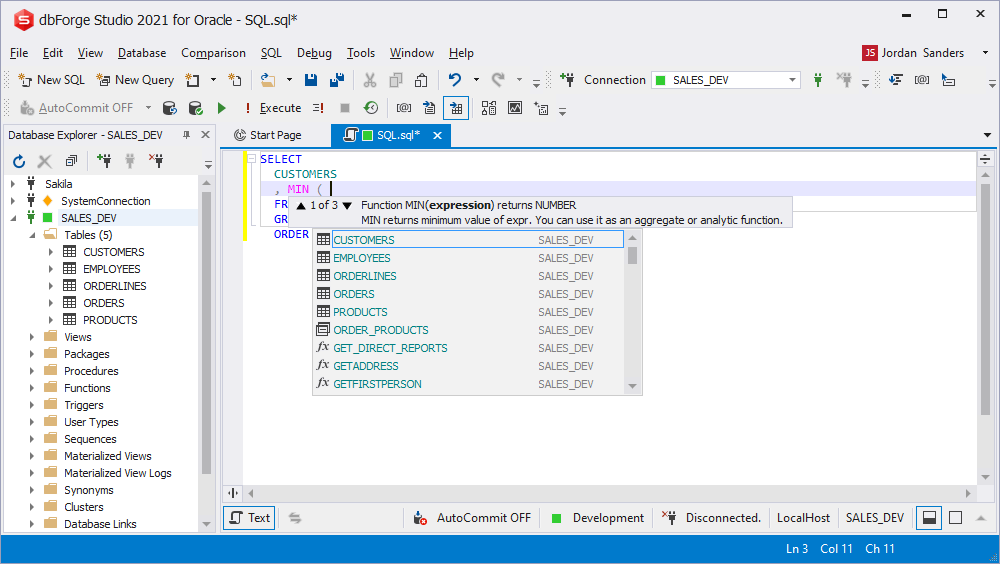
DELETE FROM prompt
The prompt of available values in any DML prompt is based on the current code block. For instance, the top-priority in the WHERE block (while deleting an entry) will be the column list of the initial table.
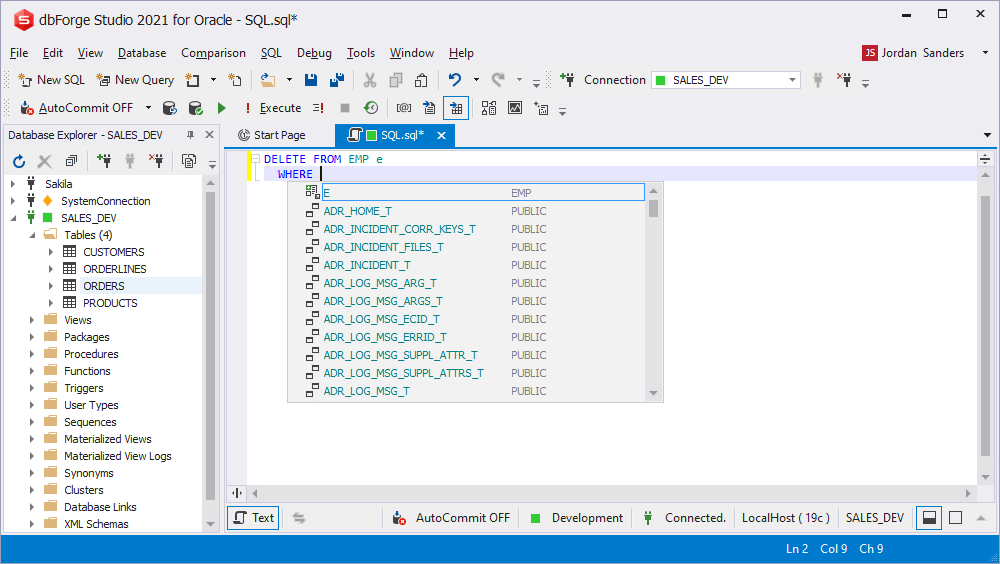
Prompt on selected columns
When writing the INSERT statement, you can select the columns to insert the data in. To perform the query automatically, only specify the required columns.
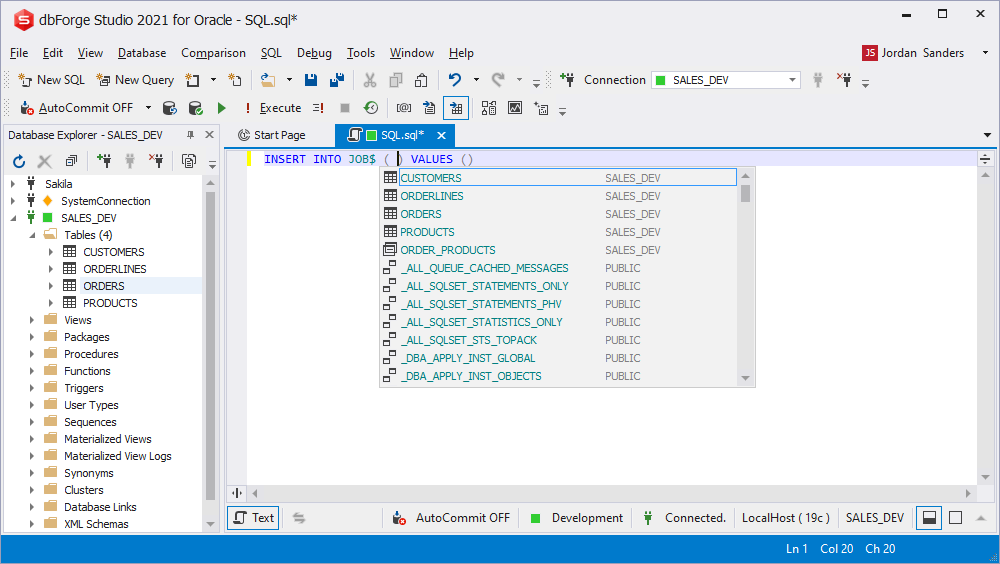
UPDATE prompt
Since update queries are mostly related to tables, the suggestion list displays tables first and then views.
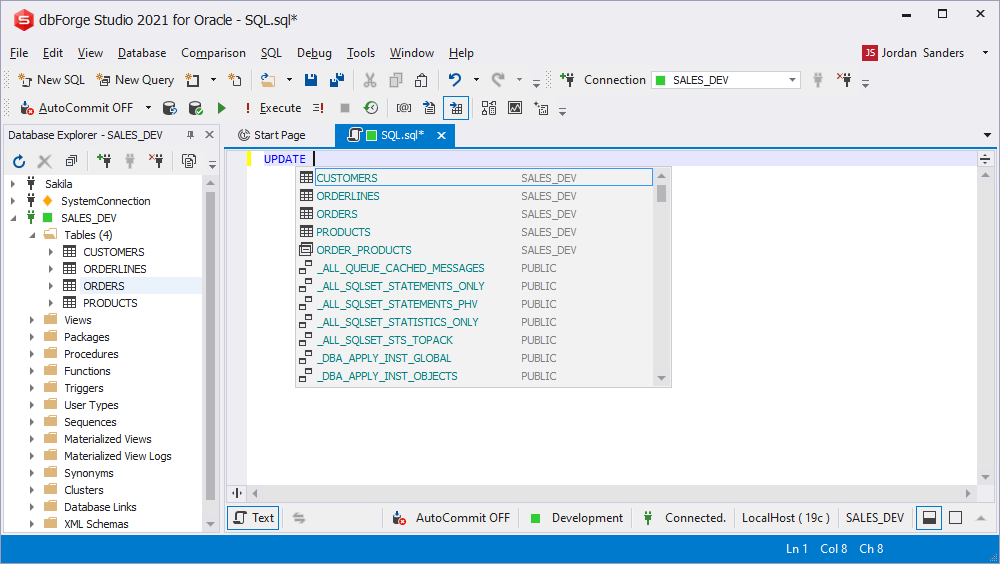
Selection for a different schema
The suggestion list displays objects from the default schema. To access objects from other schemas, simply select a required schema name in the list.
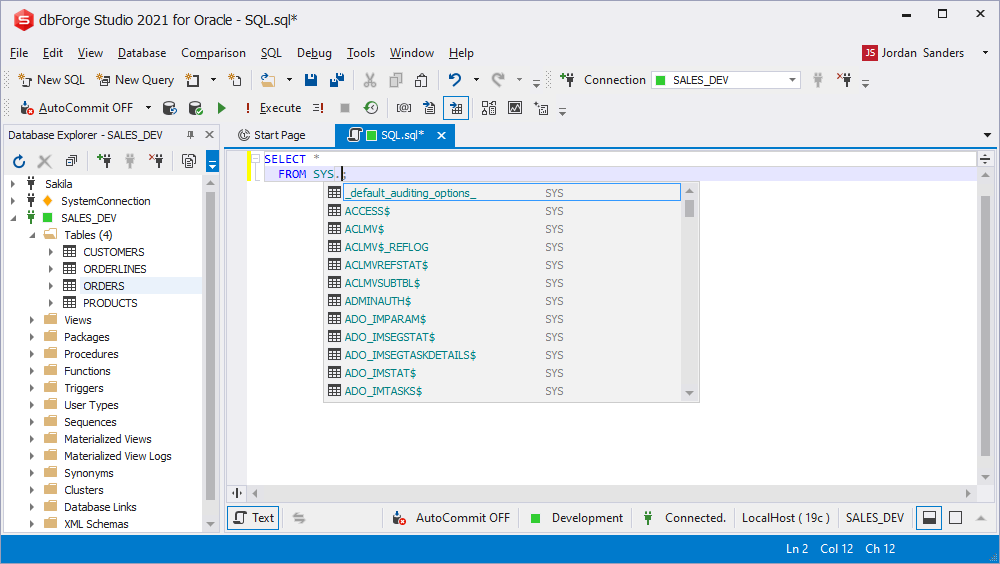
Cursors prompt
The suggestion list shows cursor variables and objects that store cursor variables (for example, packages).
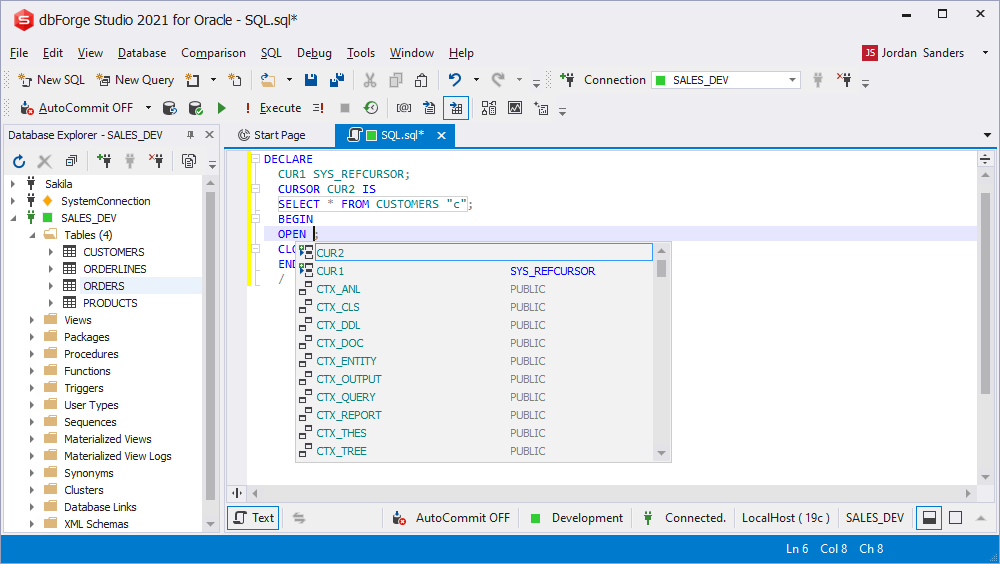
Cursors with parameters prompt
Specify a cursor parameter value to display the prompt.
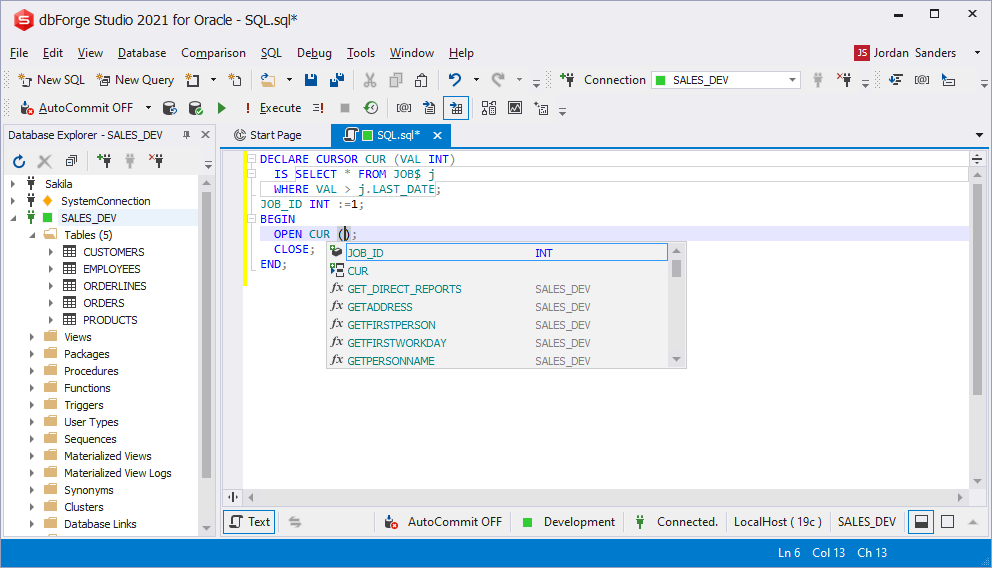
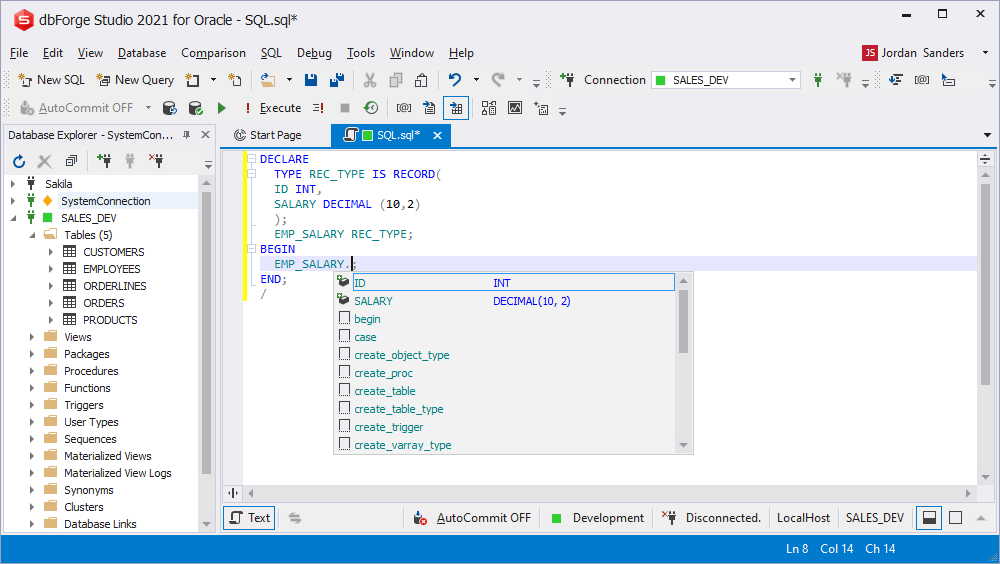
RECORD fields prompt
If a variable is used inside a cursor, it is implicitly considered as the RECORD type variable. Here you can use the prompt for such variables.
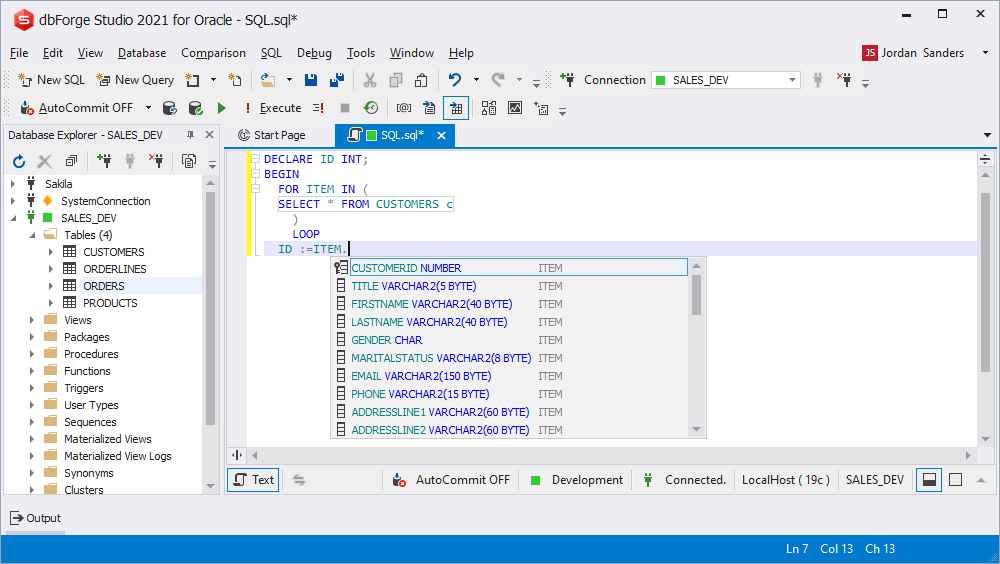
%ROWTYPE attribute for the RECORD prompt
You can use prompts for variables that are declared via the % attribute. You can refer to a current script object or to an object specified inside another object.
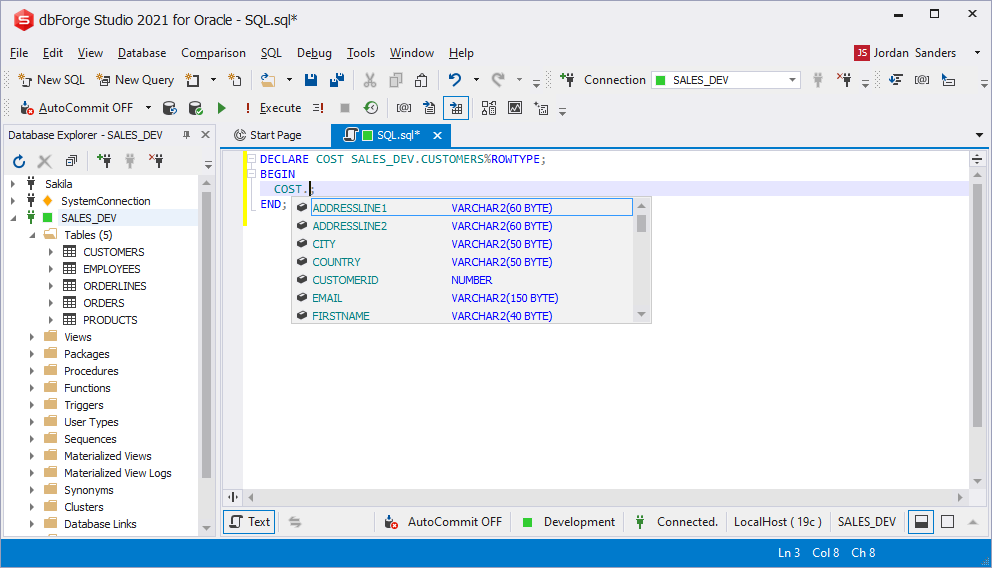
RECORD type variables prompt
There is a possibility to declare the RECORD data type and use prompts for var fields.
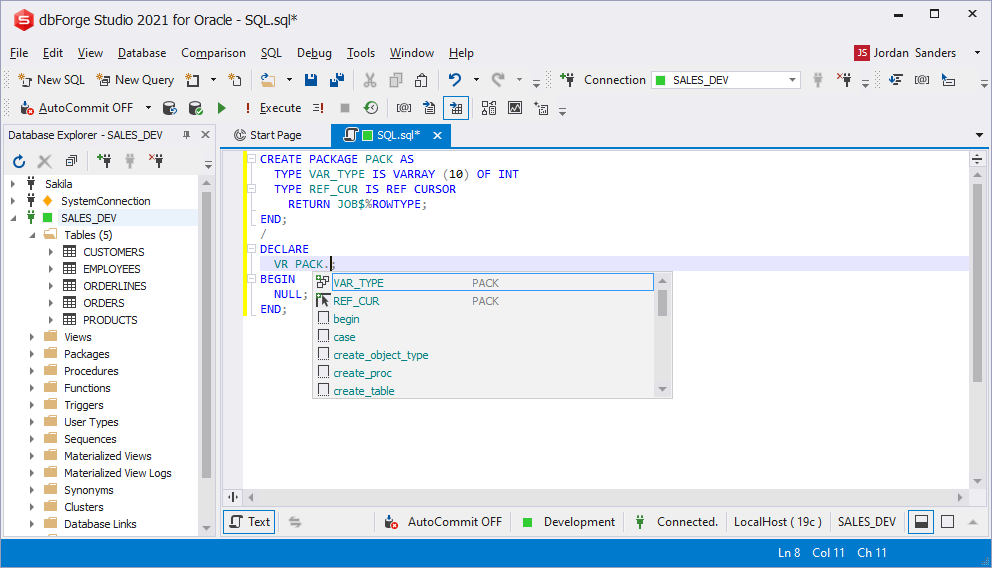
REF-CURSOR variables prompt
The prompt allows you to specify a variable type declared in another object. Even if you do not create an object in the database but describe one in the current script, the application will also show the prompt on objects.
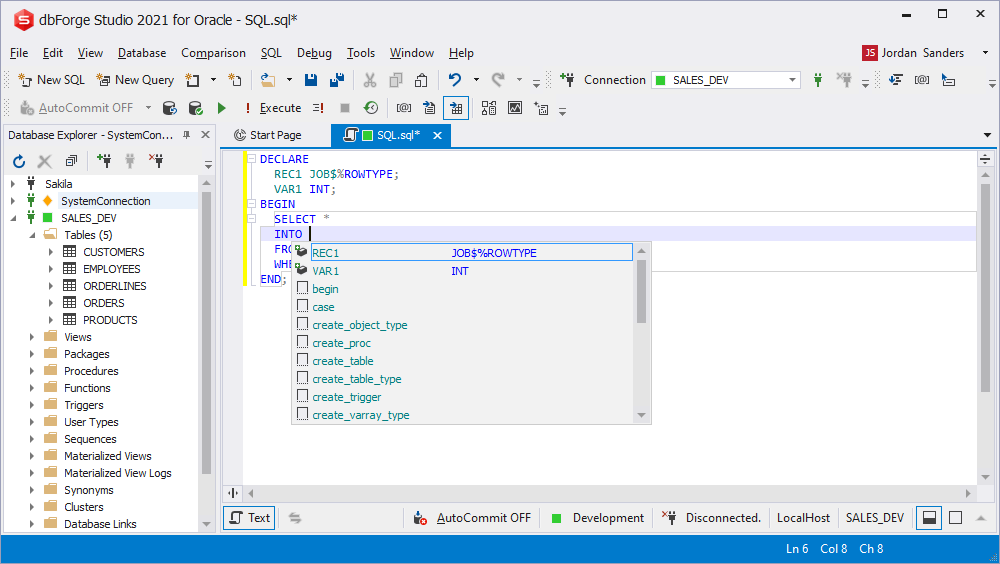
SELECT INTO variables prompt
You can initialize a variable using the SELECT INTO statement.
Assign a value to a variable
You can assign a value to a variable in a number of ways, however the best practice is to use an assignment operator. In this case you can use prompts for all objects that return result.
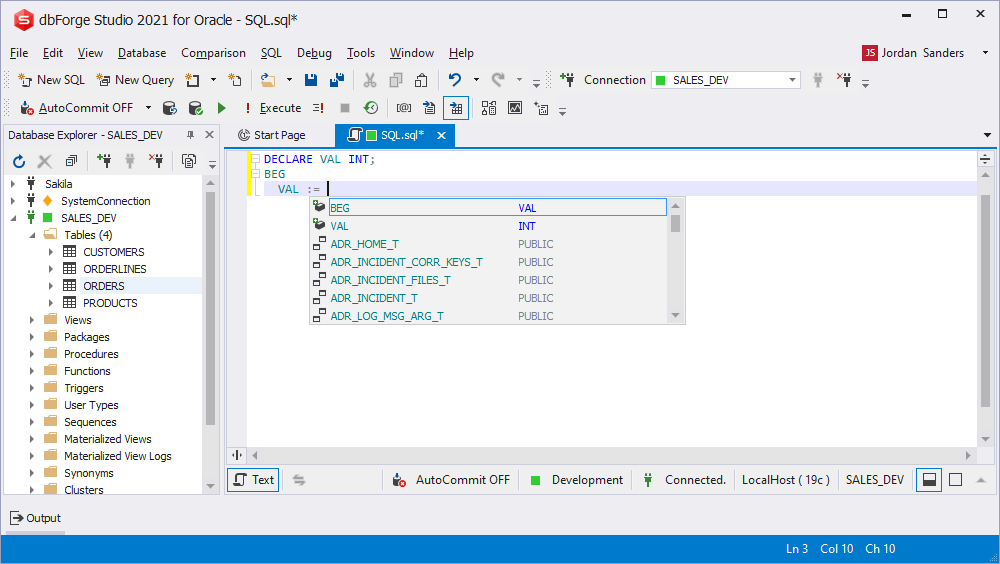
Variable initialization prompt
You can specify an initial value when declaring a variable. The prompt displays objects that can return results. If the current anonymous block is enclosed, the suggestion list displays the cursor variables.
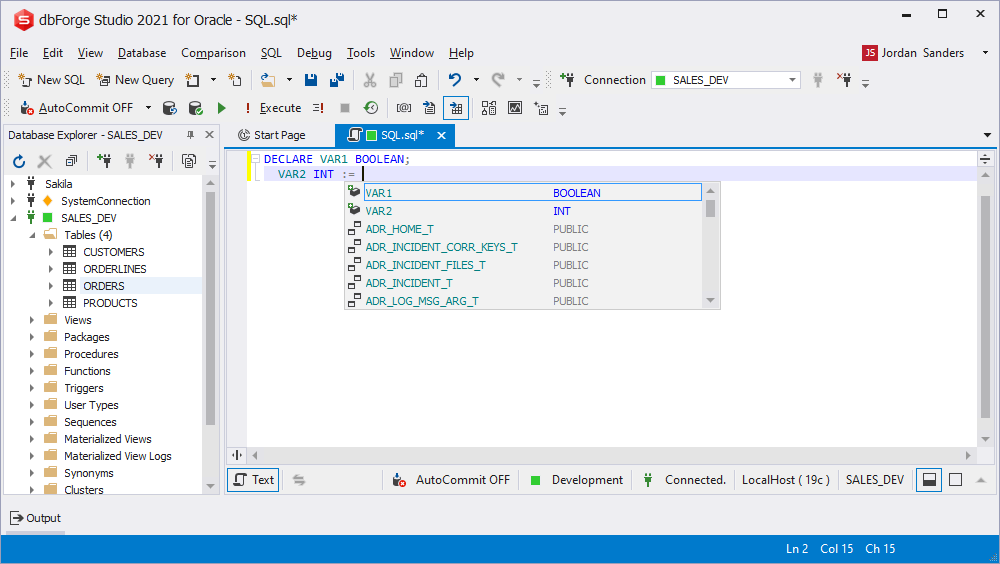
Function parameters prompt
When describing a user-defined function, the application suggests the corresponding function parameters. The prompt also shows all valid objects that include functions.
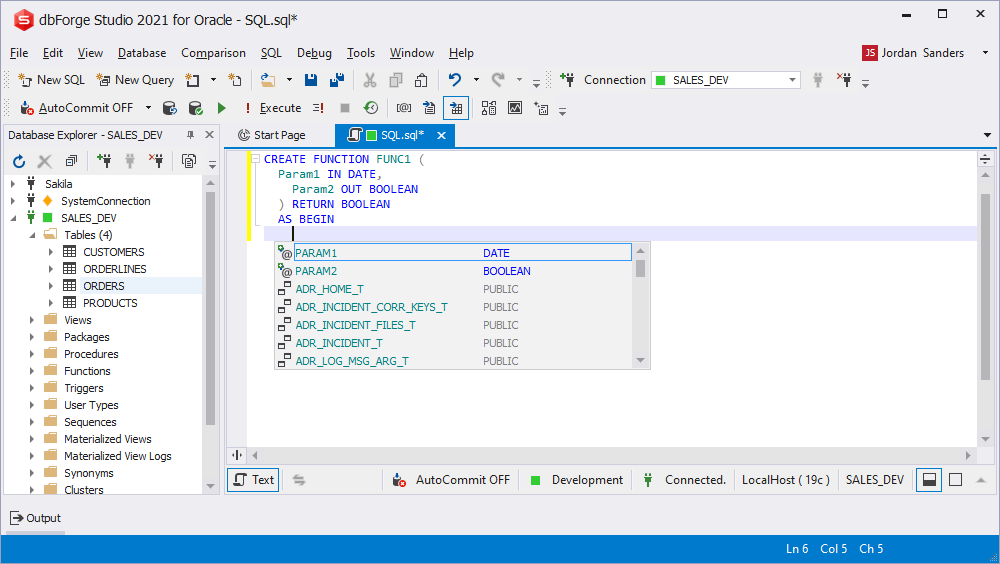
Stored procedures parameters prompt
Like a function, a procedure supports the prompt on its parameters. When analyzing the parameters, you can divide them into input and output ones.
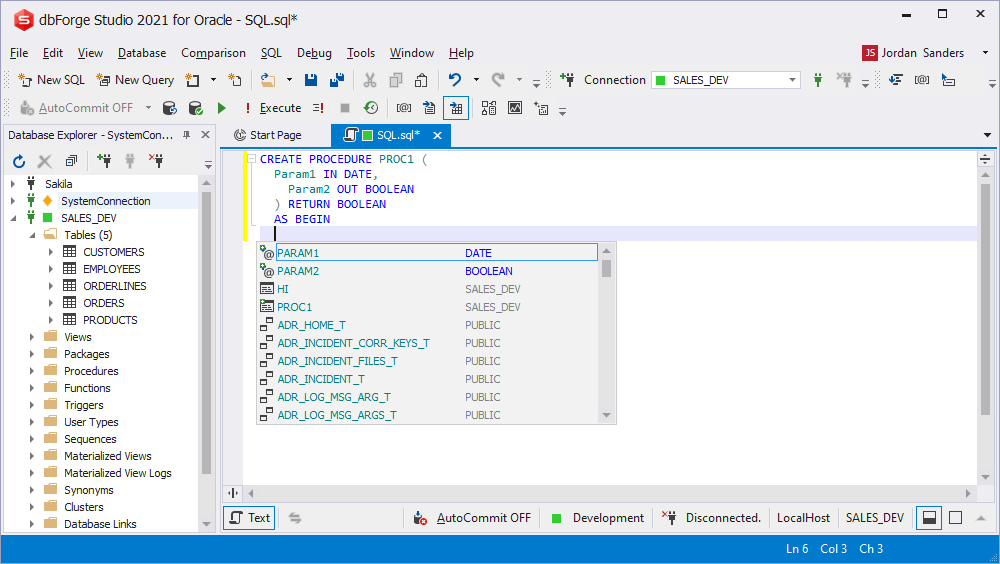
Recursive calls prompt
Similar objects are listed as script objects, while calling a function or a procedure recursively.
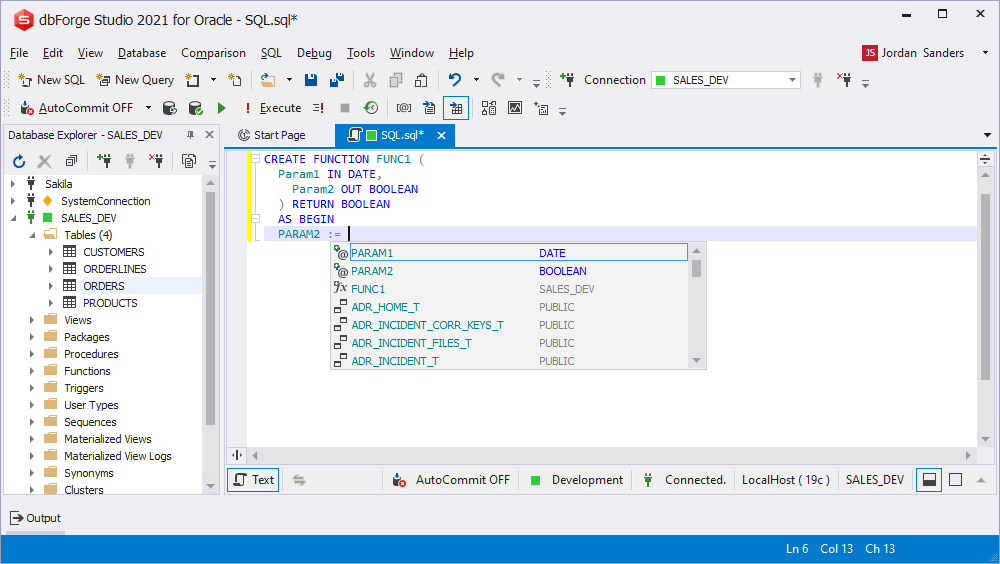
Prompting procedures declared in packages
When a statement waits for a call that does not return a result, the prompt on procedures described in the call is supported for packages.
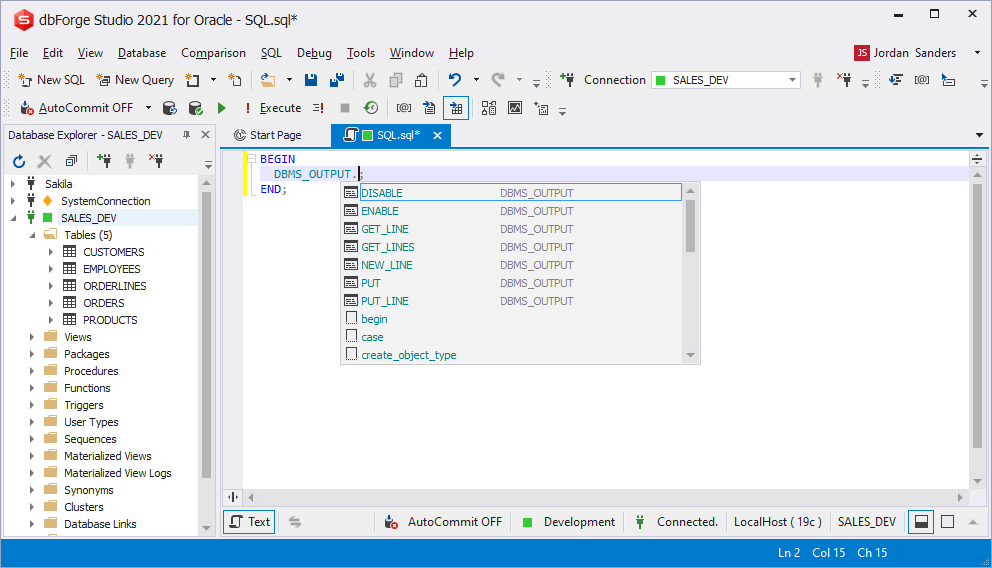
Prompting package functions and variables
Prompting for internal functions and variables is available for packages.
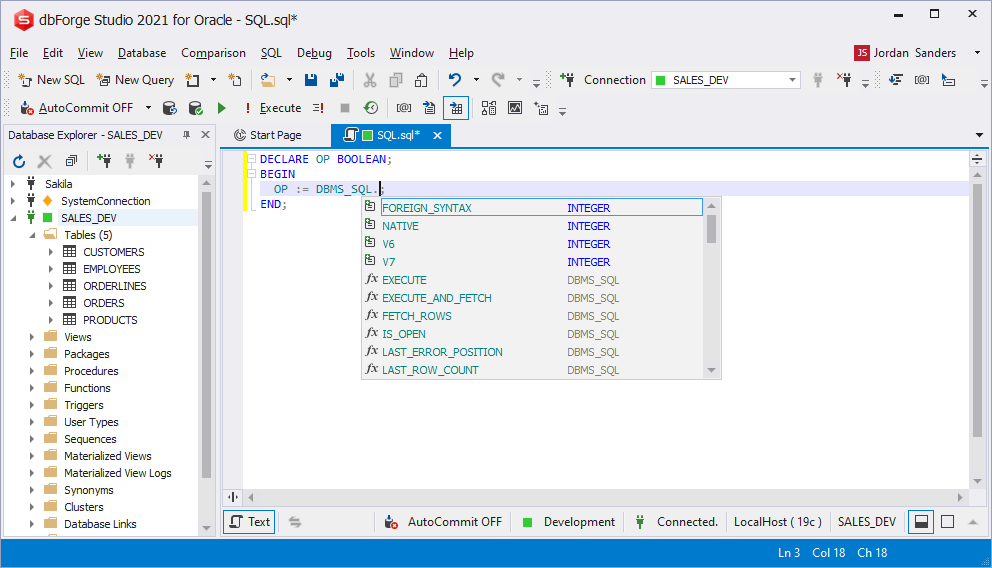
SEQUENCE built-in functions prompt
Prompt on all built-in SEQUENCE functions is supported. Select one of them, and the context prompt will be displayed automatically.
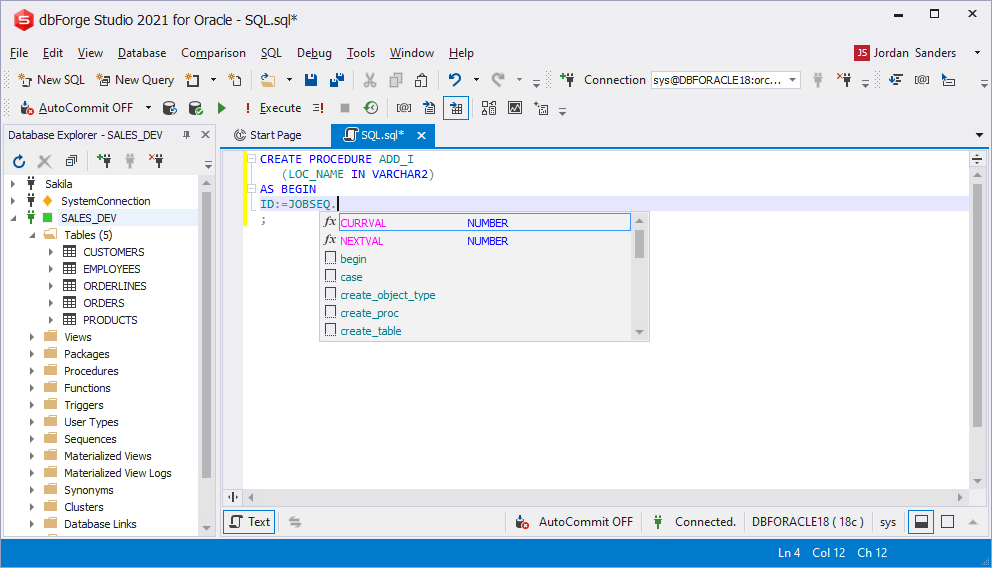
Prompting built-in methods of the table type
When working with the table types, the prompt on built-in functions is supported. The prompt for each built-in function is integrated.
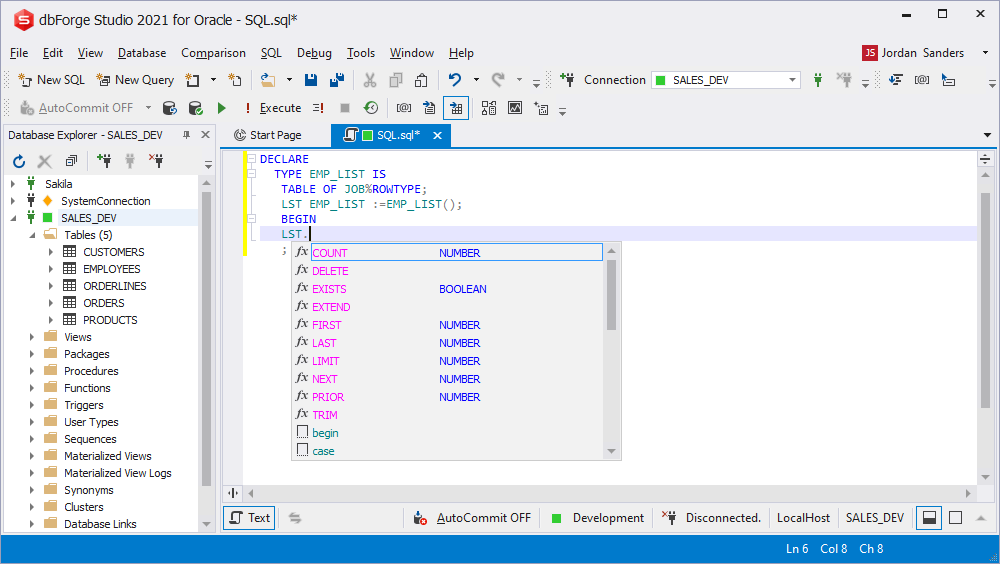
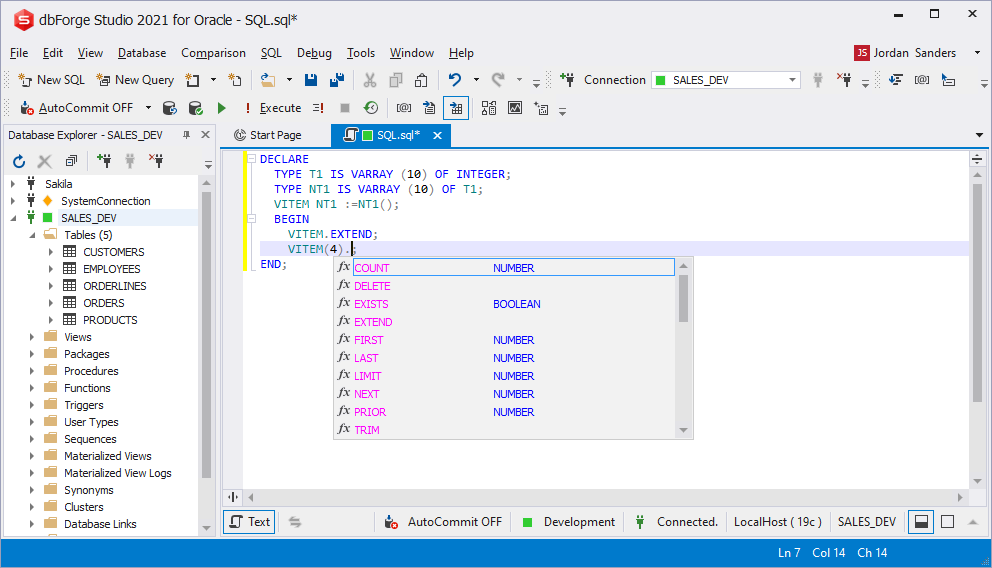
Prompting built-in array methods
In spite of the user type declaration, the prompt on built-in functions is suggested for efficient work with an array.
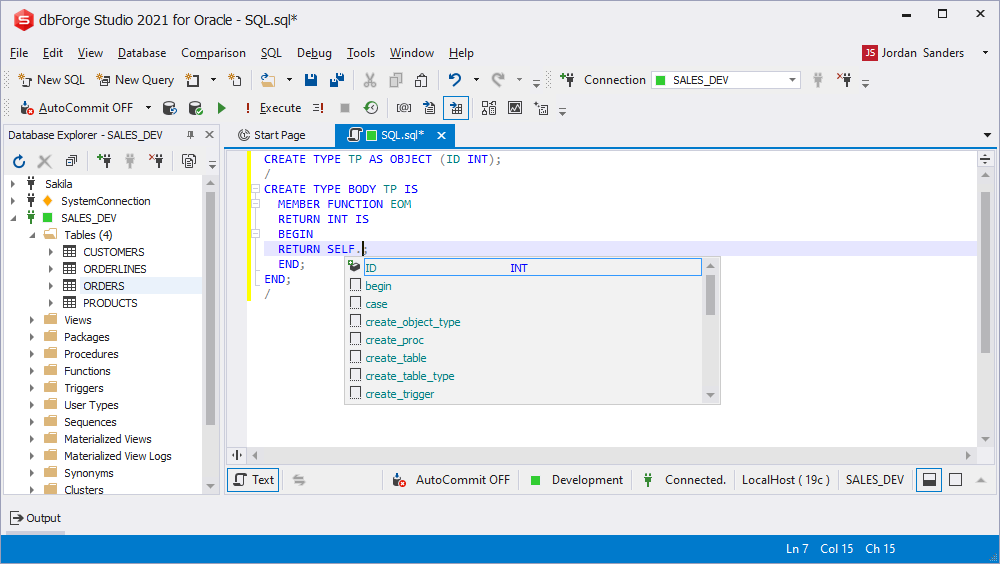
SELF-type variables prompt
When using the SELF-type variable, the application displays the context prompt on object variables and methods.
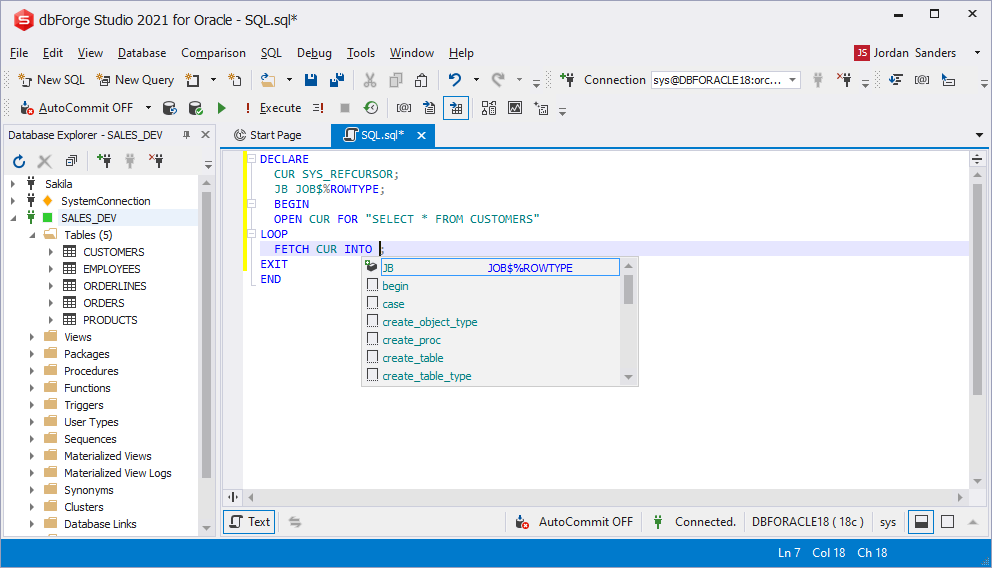
Prompting objects inside FETCH INTO
While processing the cursor records, try out the variables prompt and transfer the current row value to a variable.
User-defined types prompt
The prompts on built-in and user-defined variables are similar. When displaying variables, their types are specified, even if a type and a variable are specified in the same block.
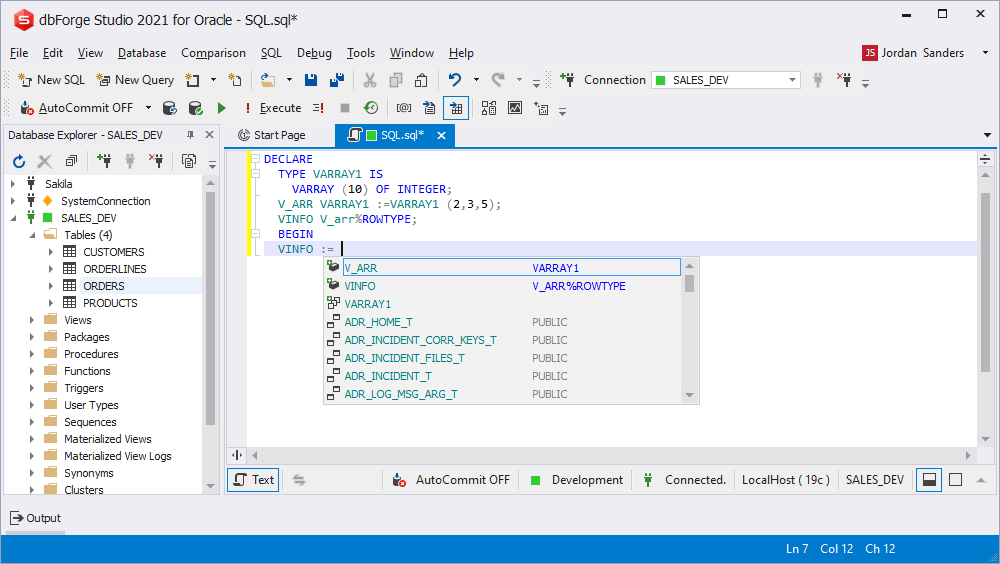
Prompting objects inside FOR IN
While iterating records in the FOR IN statement, you can specify lower and upper limits. The prompt for all objects that can return the results is available.
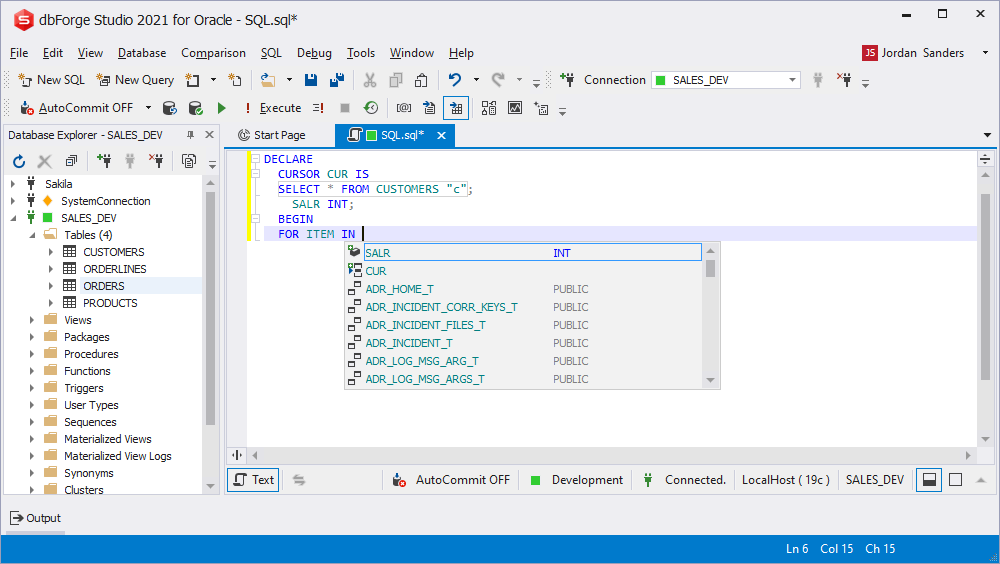
Variables prompt in the VALUES block
The VALUES statement displays the suggestion list of variables with the RECORD type priority on the top of the list.
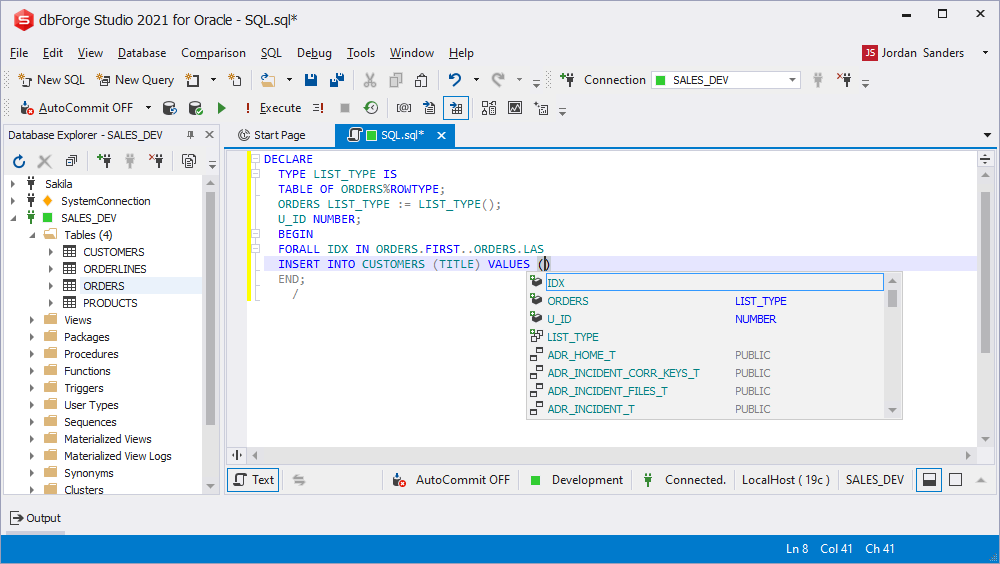
Objects prompt in the user-defined package
User-defined packages support a complete prompt on objects. Due to supported work with an object script description, it is not necessary to create an object in a database.
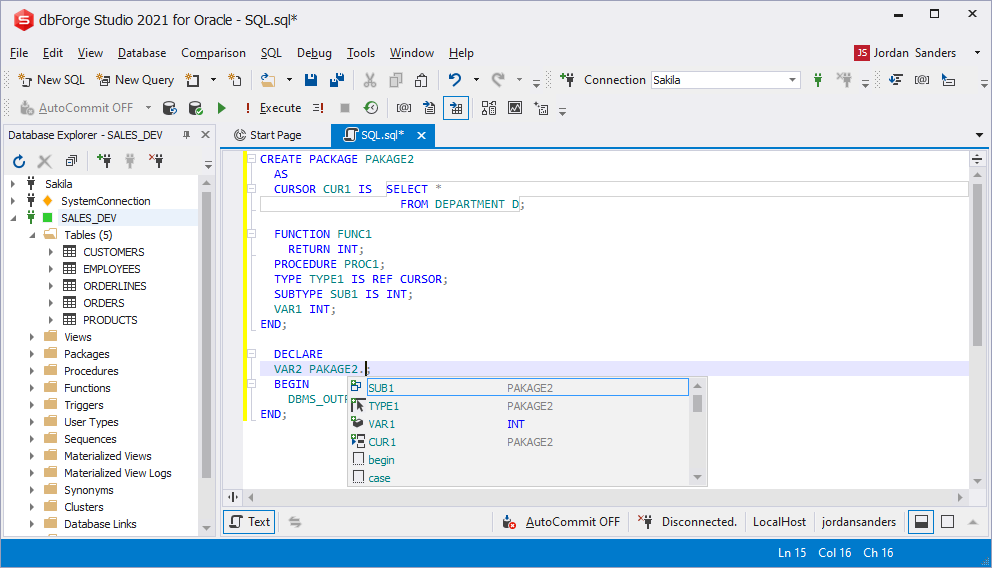
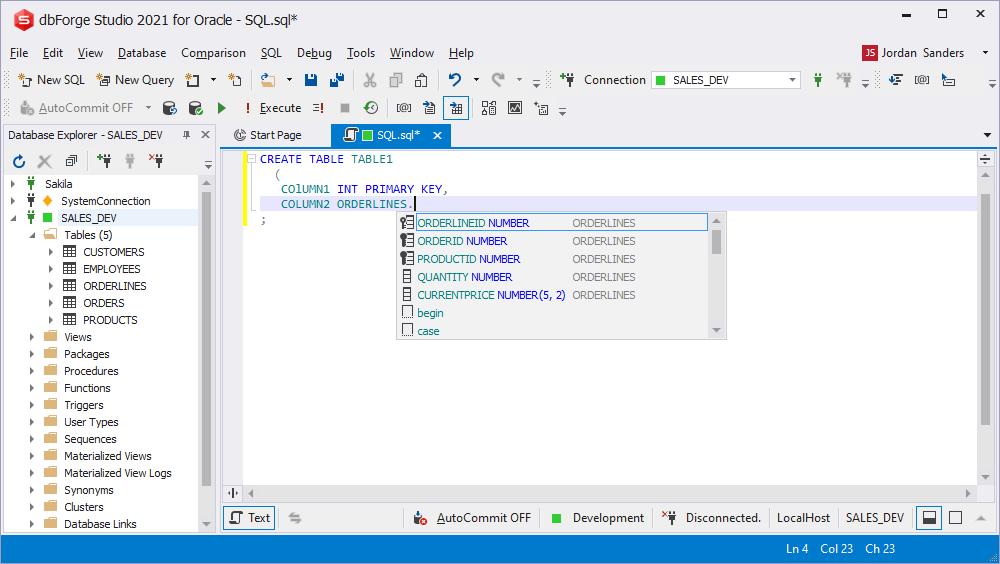
CREATE TABLE prompt
The CREATE TABLE statement is completely supported. All possible objects are prompted.
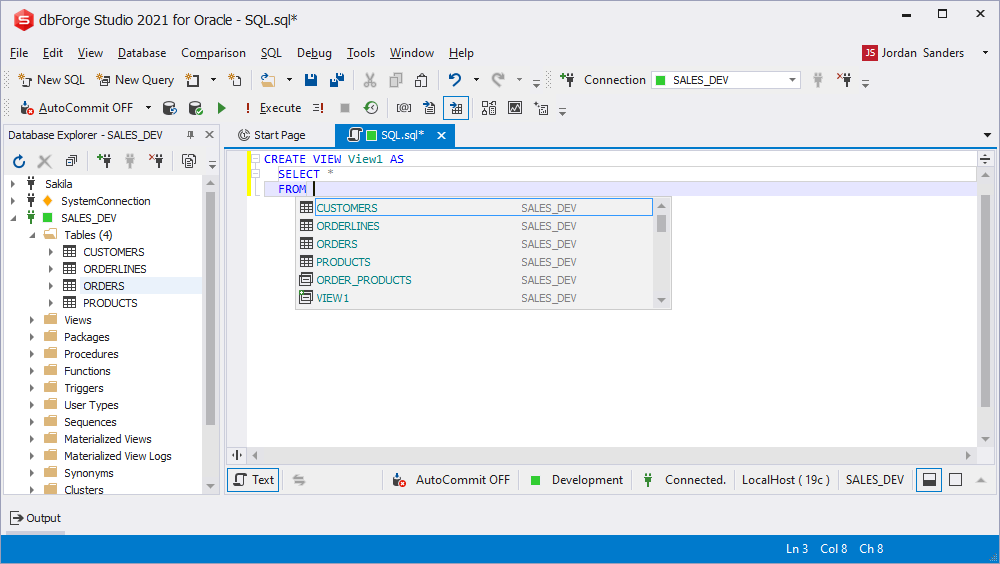
CREATE VIEW prompt
The context objects prompt depends on a block where the user creates a script object.
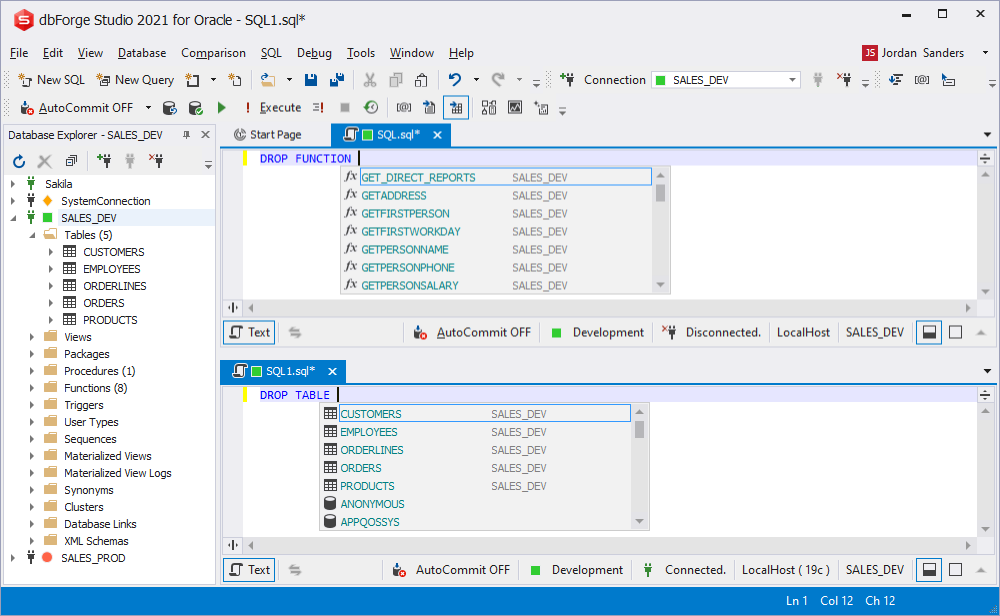
Prompting objects in the DROP statement
Commonly the DROP statements support the prompt list on objects and schemas names. The types of deleting objects define the items order in the suggestion list.
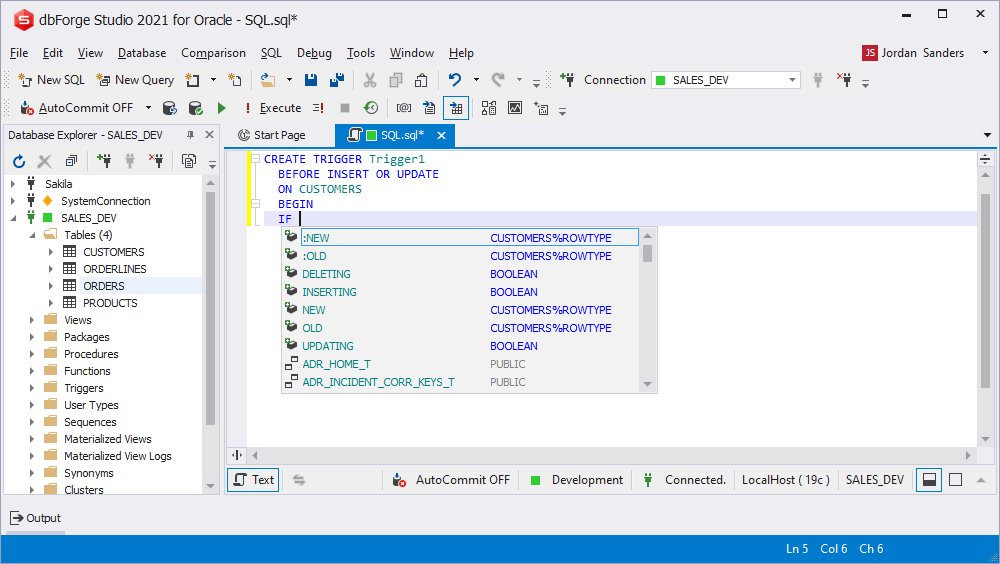
Prompting NEW/OLD variables columns
When you create a trigger in a table, the prompt on NEW/OLD variables columns is shown.
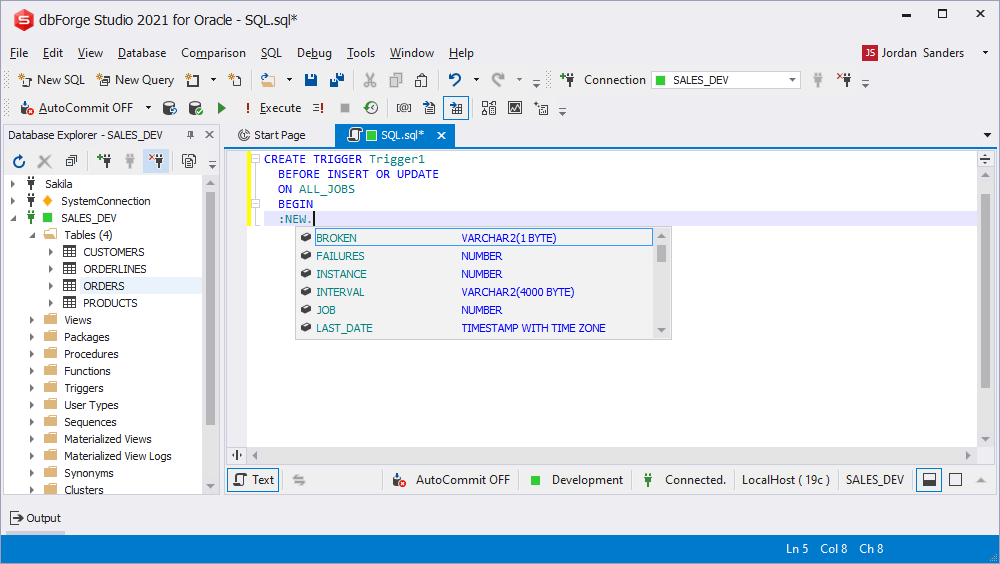
Triggers prompt
When coding a trigger body, the suggestion list displays objects and trigger variables of the corresponding statement.
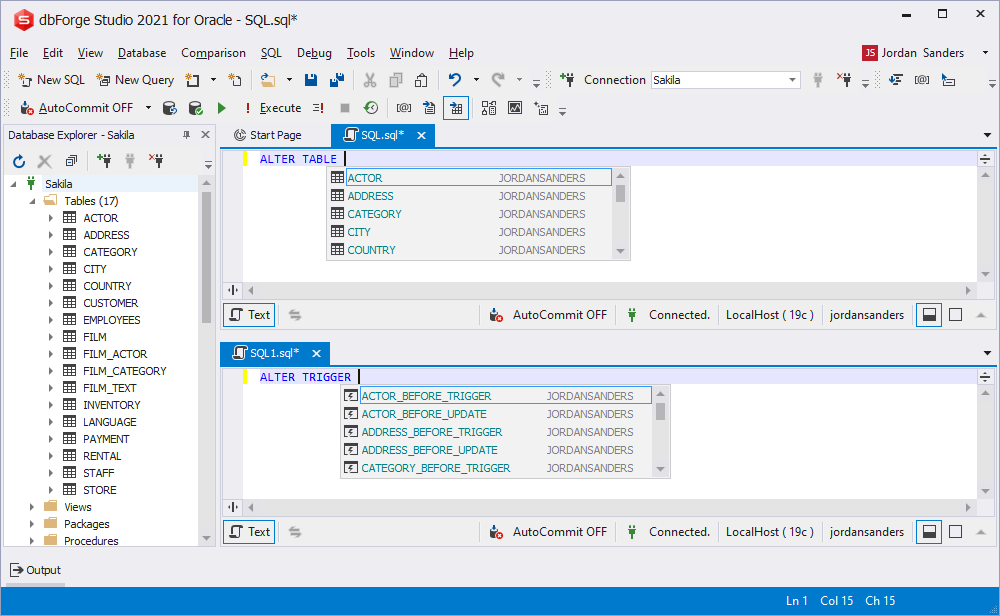
Objects prompt inside the ALTER statement
To display the objects suggestion list, specify a type of the ALTER statement.
Clauses prompt of the MERGE statement
The prompt suggests clauses of the MERGE statement, that determine whether to update or insert into the target table or view.