Configure the Debugger
Install server-side and client-side T-SQL Debugger components
Server-side tools are included with the SQL Server installation. Client-side tools are not included with SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS) and must be installed separately.
You can install the client-side tools using SQL Server Data Tools (SSDT), which is available through the Visual Studio Installer.
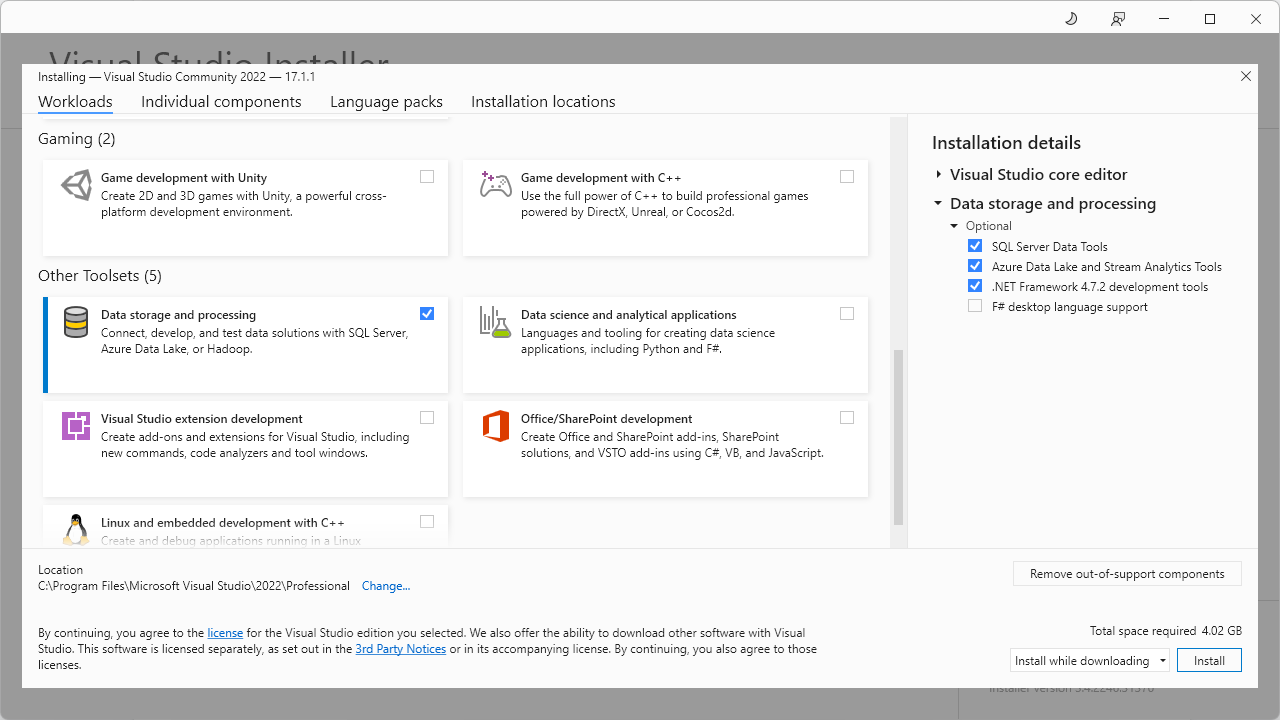
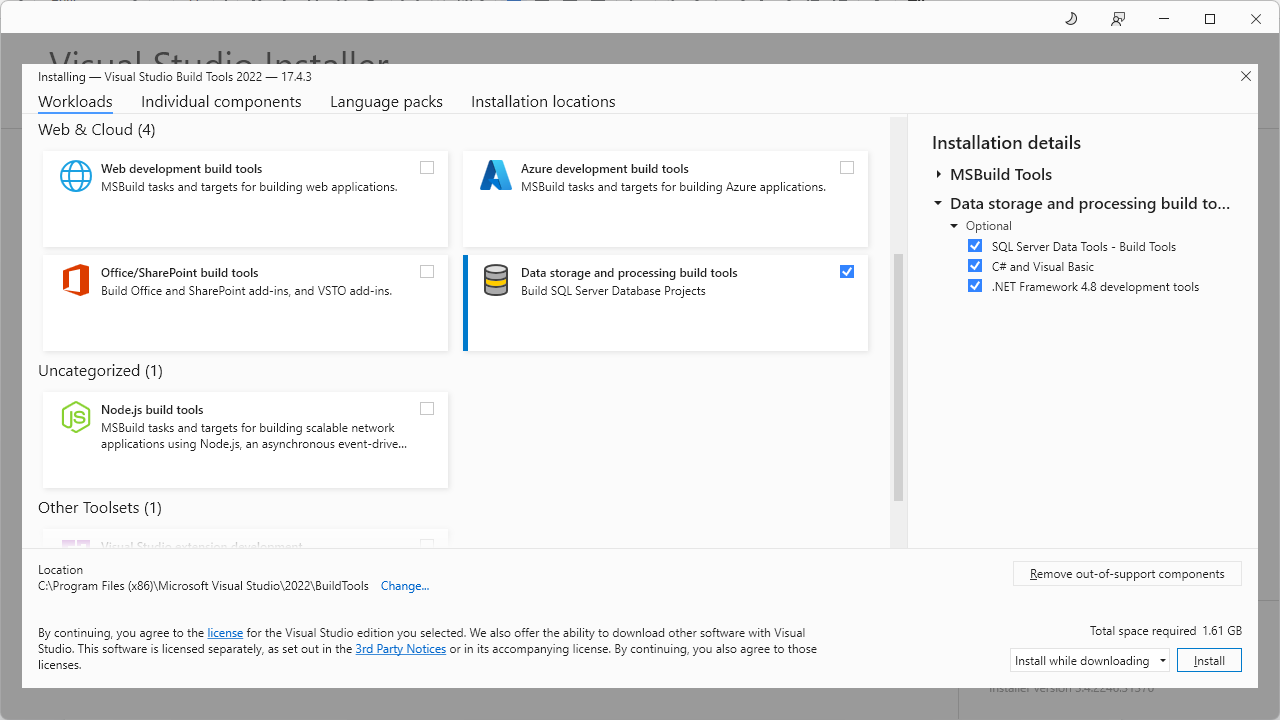
If you don’t use Visual Studio and want to have the minimal installation package, download Build Tools for Visual Studio 2022 to install Data storage and processing build tools.
Enable Firewall exceptions
Enable debugging Firewall exceptions on the server side
1. Open PowerShell by pressing Win+R.
2. Run the following commands but replace C:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\MSSQL13.InstanceName\MSSQL\Binn\sqlservr.exe with your path to sqlservr.exe and 1.1.1.1 with your relevant IP:
New-NetFirewallRule -DisplayName "Allow SQLDebugger" -Direction Inbound -Action Allow -Program "C:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\MSSQL13.InstanceName\MSSQL\Binn\sqlservr.exe" -Profile Any -Protocol TCP -LocalPort RPC
New-NetFirewallRule -DisplayName "Allow SQLDebugger SVCHost" -Direction Inbound -Action Allow -Program "%systemroot%\System32\svchost.exe" -Profile Any -Protocol TCP -LocalPort RPCEPMap
New-NetFirewallRule -DisplayName "Allow Client IP" -Direction Inbound -Action Allow -RemoteAddress 1.1.1.1 -Profile Any -Protocol TCP
Enable debugging Firewall exceptions on the client side
1. Open PowerShell by pressing Win+R.
2. Execute the following commands:
New-NetFirewallRule -DisplayName "Allow SQLDebugger SVCHost" -Direction Inbound -Action Allow -Program "%systemroot%\System32\svchost.exe" -Profile Any -Protocol TCP -LocalPort RPCEPMap
Verify sysadmin role membership
1. On the SQL toolbar, click New SQL to open a SQL document.
2. Enter the following statement:
SELECT name, type_desc, is_disabled
FROM master.sys.server_principals
WHERE IS_SRVROLEMEMBER ('sysadmin',name) = 1
ORDER BY name
3. Click Execute.
If the login is not a member of the sysadmin fixed server role, you can execute the following statement but replace UserName with your actual username:
EXEC sp_addsrvrolemember 'UserName', 'sysadmin';
GO
Ensure the database is in multi‑user mode
1. On the SQL toolbar, click New SQL to open a SQL document.
2. Enter the following statement command but replace YourDb with your database:
if (SELECT user_access_desc FROM sys.databases WHERE name = 'YourDb') = 'SINGLE_USER'
BEGIN
print 'It is in single user mode!'
END
3. Click Execute.
If the database is in single-user mode, switch it to multi-user mode. For this, do the following:
1. Check all active users:
1.1. On the SQL toolbar, click New SQL to open a SQL document.
1.2. Enter the following statement:
sp_who2
This statement returns all session IDs of the users that are required for the next command.
1.3. Click Execute.
2. Disconnect all sessions of the connected users:
2.1. Enter the following command but replace session_id with the session ID of the process you want to end:
KILL <session_id>
2.2. Click Execute.
3. Change the mode for the database but replace YourDB with the required database in the command:
USE [master];
GO
ALTER DATABASE [YourDB] SET MULTI_USER;
GO
4. Execute the command.