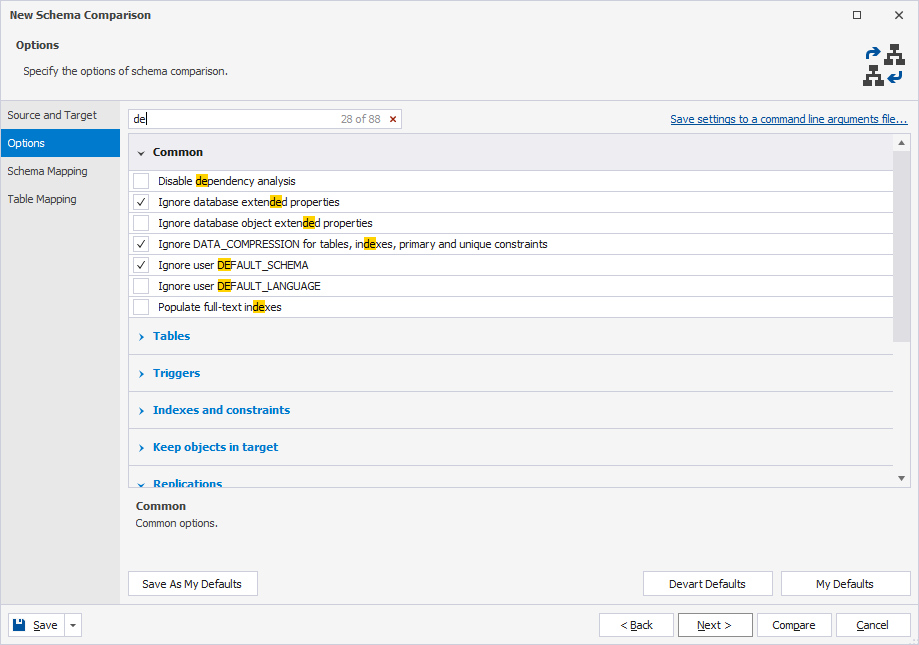
Configure comparison options
You can customize the default behavior of schema comparison on the Options page of the New Schema Comparison wizard.
Open the New Schema Comparison wizard
To open the New Schema Comparison wizard, do one of the following:
- In the top menu, select Comparison > New Schema Comparison.
- On the Start Page, select Database Design > New Schema Comparison.
- In Database Explorer, right-click the server connection or database and select Tasks > New Schema Comparison.
The options are grouped in collapsible categories. Selecting an option displays its description under the options grid.

Set up comparison behavior
Select a checkbox to include an option in schema comparison, or clear it to exclude the option.
Use default options
To save your current selection of options as defaults for all new projects, click Save As My Defaults.
To restore your saved defaults, click My Defaults.
To reset all options to their original state, click Devart Defaults.
Search for options
You can search for comparison options by entering text or symbols (such as a wildcard or underscore) in the search box. The list filters automatically to show only options that contain the search term.
The default search mode is case-insensitive. For example, entering de matches De, de, or DE. Matching text is highlighted, and the search bar shows the number of matches. Multiple words separated by spaces highlight matches for each term.
To clear the search, click ![]() in the search box.
in the search box.
Keyboard shortcuts in the search box
The table describes the keyboard shortcuts you can use in the search box.
| Keyboard shortcut | Description |
|---|---|
| Ctrl+A | Selects all. |
| Ctrl+Left Arrow (←) | Moves the caret to the beginning of the word. |
| Ctrl+Right Arrow (→) | Moves the caret to the end of the word. |
| Ctrl+Shift+Left Arrow (←) | Selects text from the current caret position to the beginning of the current word and moves the caret to the beginning of the word. |
| Ctrl+Shift+Right Arrow (→) | Selects text from the current caret position to the end of the current word and moves the caret to the end of the word. |
| Ctrl+Backspace | Deletes the word to the left of the caret. |
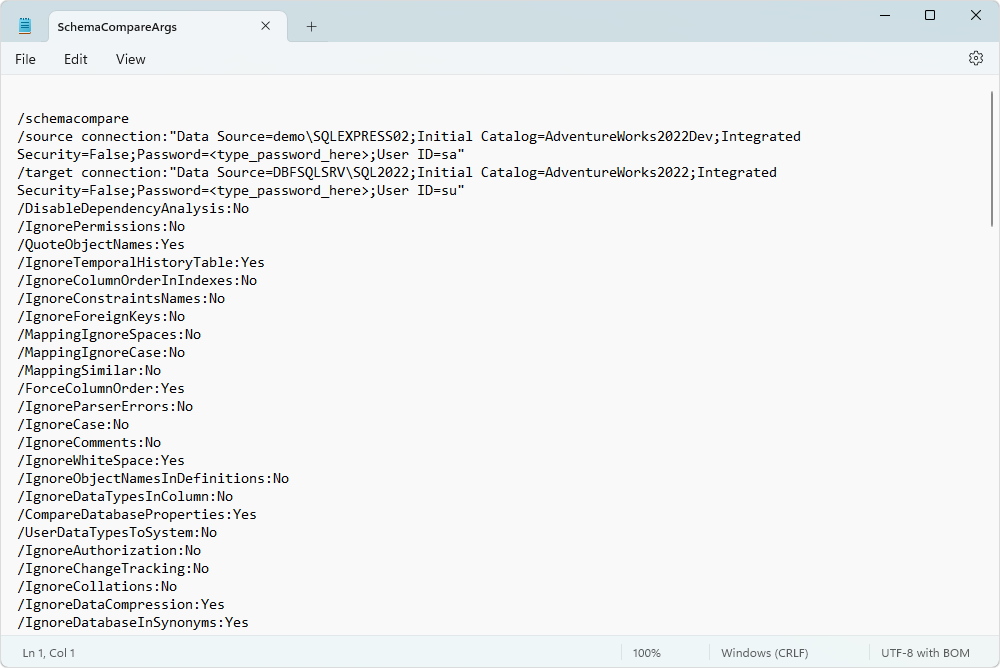
Save settings to a command-line arguments file
To save command-line arguments and settings to a .txt file:
1. In the upper-right corner of the wizard, click Save settings to a command-line arguments file.
2. In the Save As dialog, select the destination folder.
3. Specify the file name.
The default name is SchemaCompareArgs.txt. You can specify a different name.
4. Click Save.
The generated file includes source and target connection details, and a list of comparison options that indicate whether each option is enabled (Yes) or disabled (No):
Note
The command-line arguments file includes both comparison and synchronization options.
Schema comparison options
The table describes a list of schema comparison options.
| Name | Group | Description | Default State |
|---|---|---|---|
| Associate column names having similar name options, 80 % | Auto Mapping | Considers similar column names (for example, column1 and column1a) equal. |
Off |
| Ignore case in object names | Auto Mapping | Ignores cases in object names during mapping and comparison. | Off |
| Ignore spaces in object names | Auto Mapping | Ignores spaces in object names during mapping and comparison. | Off |
| Compare database properties | Common | Includes a database object in comparison and synchronization. Objects that depend on other synchronized objects are synchronized, even when Compare database properties is turned off. |
On |
| Convert user data types into SQL Server system data types | Common | Converts user-defined types to SQL Server system types during comparison and synchronization. | Off |
| Disable dependency analysis | Common | Disables dependency building algorithms and uses object types from the Object Filter dialog. The synchronization script will not be generated. | Off |
| Ignore authorization | Common | Ignores the AUTHORIZATION clauses and statements on contained database objects.Target authorizations will be preserved if possible. |
Off |
| Ignore CHANGE_TRACKING | Common | Ignores the CHANGE_TRACKING clauses when comparing and synchronizing databases. |
Off |
| Ignore CLR datatypes in column | Common | Ignores CLR data types in the column. Column CLR data types in the target tables will be preserved if possible. |
Off |
| Ignore collations | Common | Ignores column collations. Collations are removed if a columns data type is changed to a non-text type, regardless of whether the Ignore collations option is selected. |
Off |
| Ignore database and server names for synonyms | Common | Ignores database and server names for synonyms during comparison and synchronization. | On |
| Ignore database extended properties | Common | Ignores the extended properties of the database. These properties are preserved after synchronization if the database that references them is rebuilt. |
On |
| Ignore database object extended properties | Common | Ignores the extended properties of database objects. These properties are preserved after synchronization if an object that references them is rebuilt. |
Off |
| Ignore datatypes in column | Common | Ignores column data types. Column data types in the target tables will be preserved if possible. |
Off |
| Ignore DATA_COMPRESSION for tables, indexes, primary and unique constraints | Common | Ignores the DATA_COMPRESSION clause for tables, indexes, primary and unique key constraints. It will be preserved in the target. |
On |
| Ignore event notification on queues | Common | Ignores an event notification on queues. | Off |
| Ignore filegroups and partition schemes/functions | Common | Ignores filegroups, partition schemes, and partition functions. It is selected by default as the tool doesn’t synchronize the aforementioned clauses but synchronizes the corresponding properties of tables, indexes, primary keys, and unique constraints. |
Off |
| Ignore full-text catalog path | Common | Ignores the path in the full-text catalog. | Off |
| Ignore full-text search | Common | Ignores full-text stoplists, full-text catalogs, and full-text indexes. If these objects are altered or deleted during synchronization, they will be restored if possible. |
Off |
| Ignore next filegroups | Common | Ignores next filegroups. Next filegroups in the target partition scheme will be preserved if possible. |
Off |
| Ignore semicolons | Common | Ignores semicolons at the end of statements. | Off |
| Ignore tSQLt framework and unit tests | Common | Excludes tSQLt framework objects and unit tests from comparison and synchronization. | Off |
| Ignore user DEFAULT_SCHEMA | Common | Ignores the DEFAULT_SCHEMA setting for users. |
On |
| Ignore permissions | Common | Ignores security permissions. Target database permissions will be preserved if possible. |
Off |
| Ignore users’ permissions | Common | Ignores users’ permissions and roles memberships. | Off |
| Ignore user DEFAULT_LANGUAGE | Common | Ignores the DEFAULT_LANGUAGE setting for users. |
Off |
| Ignore logins, certificates, asymmetric keys for users | Common | Ignores logins, certificates, and asymmetric keys, and synchronizes the corresponding user properties. Logins for users that exist in the target database will be preserved. |
On |
| Populate full-text indexes | Common | Populates full-text indexes. It is not selected by default because creating full-text indexes with population is time-consuming. |
Off |
| Quote object names with square brackets | Common | Quotes object names with square brackets during script generation. | On |
| Force column order | Tables | Causes table re-creation when new columns are added. Column order will be preserved. Otherwise, difference in column order will be ignored, and objects will be equal. |
On |
| Ignore bound rules and defaults | Tables | Ignores bound rules and defaults to a column, set with sp_bindrule or sp_bindefault. |
Off |
| Ignore default column collations | Tables | Ignores default column collations. If a column data type is changed to non-numeric, column collations will be canceled. |
On |
| Ignore history table | Tables | Ignores history tables. | On |
| Ignore history table names | Tables | Ignores history tables names. They will be preserved in the target. |
On |
| Ignore identity on columns | Tables | Ignores identity on columns. When selected, the Ignore identity seed and increment values option is applied too. Identity and its seed and increment values will be restored in the target. |
Off |
| Ignore identity seed and increment values | Tables | Ignores identity seed and increment values. They will be preserved after synchronization. If a target column doesn’t have the IDENTITY property, after synchronization it will get this property but with default seed and increment values. |
Off |
| Ignore LOCK_ESCALATION | Tables | Ignores the LOCK_ESCALATION setting for tables. It will be preserved in the target. |
On |
| Ignore SENSITIVITY COLLATION | Tables | Ignores metadata about the sensitivity classification of source columns. Target column sensitivity classification metadata will be preserved if possible. |
Off |
| Ignore table DML triggers | Triggers | Ignores DML triggers for tables. If they prevent the synchronization, triggers will be dropped and then restored. If a table is dropped, its triggers will be dropped regardless of whether the Ignore table DML triggers option is selected. |
Off |
| Ignore INSTEAD OF triggers | Triggers | Ignores INSTEAD OF triggers for tables.If a view is dropped, its triggers will be dropped in both cases regardless of whether the Ignore INSTEAD OF triggers option is selected. |
Off |
| Ignore state of DML triggers | Triggers | Ignores the state of DML triggers. State of DML triggers in the target database will be preserved if possible. |
Off |
| Ignore state of DDL triggers | Triggers | Ignores the state of DDL triggers. State of DDL triggers in the target database will be preserved if possible. |
Off |
| Ignore firing order for triggers | Triggers | Ignores the firing order for DDL and DML triggers. | Off |
| Ignore check constraints | Indexes and constraints | Ignores check constraints. Check constraints won’t be restored if, for example, the data type of the column it is related to was changed. In this case, the check constraint condition may become invalid. |
Off |
| Ignore column order in indexes | Indexes and constraints | Ignores the column order for the included columns. | Off |
| Ignore constraint names | Indexes and constraints | Ignores constraint names. Check constraints will be preserved in the target. |
Off |
| Ignore constraints’ system names | Indexes and constraints | Ignores system-generated constraint names, for example FK_Table1_Table2_1B1EE1BE. |
On |
| Ignore default constraints | Indexes and constraints | Ignores default constraints and schema defaults. Default constraints and schema defaults won’t be restored after synchronization, for example, if the IDENTITY property has appeared in a column to which they are related. |
Off |
| Ignore foreign key | Indexes and constraints | Ignores foreign keys. Foreign keys won’t be restored after synchronization, for example, if a referenced column has no primary key. |
Off |
| Ignore foreign key actions ON UPDATE and ON DELETE | Indexes and constraints | Ignores cascading referential integrity constraints for foreign keys. | Off |
| Ignore indexes | Indexes and constraints | Ignores indexes in tables and views. Indexes won’t be restored after synchronization, for example, if one of their columns will be dropped. |
Off |
| Ignore indexes’ names | Indexes and constraints | Ignores index names in tables and views. Names of indexes will be preserved in the target. |
Off |
| Ignore NOCHECK state on constraints | Indexes and constraints | Ignores the NOCHECK clause for foreign keys and check constraints.It will be preserved in the target. |
Off |
| Ignore NOT NULL constraint for a column | Indexes and constraints | Ignores the NOT NULL constraint for a column.The option is not applied to columns defined as a PRIMARY KEY constraint. |
Off |
| Ignore PAD_INDEX and FILLFACTOR for indexes and constraints | Indexes and constraints | Ignores the PAD_INDEX and FILLFACTOR settings for indexes and constraints.The options will be preserved in the target. |
Off |
| Ignore PAGE_LOCK and ROW_LOCK for indexes and constraints | Indexes and constraints | Ignores the ALLOW_PAGE_LOCK and ALLOW_ROW_LOCK settings for indexes and constraints.The options will be preserved in the target. |
Off |
| Ignore primary keys | Indexes and constraints | Ignores differences in primary keys. | Off |
| Ignore sort direction (ASC/DESC) for index columns | Indexes and constraints | Ignores sort direction for index columns. It will be preserved in the target. |
Off |
| Ignore statistics | Indexes and constraints | Ignores column statistics. If it prevents synchronization, it will be dropped and then restored with default options. Statistics won’t be restored after synchronization, for example, if its column is dropped. |
Off |
| Ignore STATISTICS_NORECOMPUTE for indexes and constraints | Indexes and constraints | Ignores the STATISTICS_NORECOMPUTE setting for indexes and constraints.It will be preserved in the target. |
Off |
| Ignore unique keys | Indexes and constraints | Ignores differences in unique keys. Unique keys won’t be restored after synchronization, for example, one of their columns was dropped. |
Off |
| Ignore WITH NOCHECK state on constraints | Indexes and constraints | Ignores the WITH NOCHECK setting for constraints.It will be preserved in the target. |
Off |
| Ignore CACHE | Sequences | Ignores the CACHE setting in sequences. |
Off |
| Ignore CYCLE | Sequences | Ignores the CYCLE setting in sequences. |
Off |
| Ignore INCREMENT BY | Sequences | Ignores the INCREMENT BY setting in sequences. |
Off |
| Ignore MAXVALUE | Sequences | Ignores the MAX VALUE setting in sequences. |
Off |
| Ignore MINVALUE | Sequences | Ignores the MIN VALUE setting in sequences. |
Off |
| Ignore START WITH | Sequences | Ignores the START WITH setting in sequences. |
On |
| Ignore DML and INSTEAD OF triggers present only in Target | Keep objects in target | Ignores DML triggers that exist only in the target when comparing and synchronizing tables or views. | Off |
| Ignore indexes present only in target | Keep objects in target | Ignores dropped indexes that exist only in the target when comparing and synchronizing tables or views. | Off |
| Ignore NOT FOR REPLICATION for indexes, constraints and triggers | Replications | Ignores the NOT FOR REPLICATION setting for indexes, constraints, and triggers.They will be preserved in the target. |
Off |
| Ignore replicated tables | Replications | Ignores replication tables during comparison. | On |
| Ignore replication procedures | Replications | Ignores replication procedures. Procedures with names starting with “sp_MSupd_…”, “sp_MSins_…”, “sp_MSdel_…” will be ignored. |
Off |
| Ignore replication roles | Replications | Ignores replication roles. Roles with names starting with “MSmerge_…” will be ignored. |
Off |
| Ignore replication schemas | Replications | Ignores replication schemas. Schemas with names starting with “MSmerge_…” will be ignored. |
Off |
| Ignore replication triggers | Replications | Ignores replication triggers. Triggers with names starting with “MSmerge_…” and “tr_MStran_…” will be ignored. |
Off |
| Compare the original scripts of stored objects | Script Objects | Compares and synchronizes the original scripts of stored objects. This setting applies to the following types of objects: procedures, functions, views, and DDL and DML triggers. |
On |
| Decrypt encrypted objects | Script Objects | Decrypts the bodies of encrypted objects for database comparison and synchronization. They are shown in the comparison results as usual script objects. If you compare encrypted objects in database with large bulks of data, selecting this option will slightly slow down comparison. |
On |
| Ignore case | Script Objects | Ignores case differences in object definitions during database comparison. For example, objects with case differences will have the Equal status in the comparison results. |
Off |
| Ignore comments | Script Objects | Ignores comments while comparing stored procedures, views, functions, etc. During synchronization, comments will be preserved in the body of the script object. |
Off |
| Ignore keyword reduction | Script Objects | Ignores differences between full and short keyword names during database comparison. For example, PROC/PROCEDURE, EXEC/EXECUTE, TRAN/TRANSACTION, etc. |
On |
| Ignore object names in definitions | Script Objects | Ignores object names in definitions during comparison. | Off |
| Ignore QUOTED_IDENTIFIER and ANSI_NULLS | Script Objects | Ignores the QUOTED_IDENTIFIER and ANSI_NULLS settings for stored procedures, functions, triggers, etc. They will be preserved in the target. |
Off |
| Ignore signatures | Script Objects | Ignores signatures when comparing and synchronizing stored procedures, functions, triggers, and assemblies. | Off |
| Ignore white spaces | Script Objects | Ignores white spaces (new lines, tabs, spaces, etc.). Original white spaces in the scripts for database objects and computed columns are preserved. | On |
| Ignore WITH ENCRYPTION | Script Objects | Ignores differences in the WITH ENCRYPTION attribute. |
Off |
| Ignore WITH option order | Script Objects | Ignores the order of elements in the WITH clause when comparing and synchronizing stored procedures, views, triggers, functions, and similar objects. |
On |
Note
When comparing database objects, such as procedures, views, triggers, and functions, dbForge Studio for SQL Server formats the SQL code according to the active formatting profile. This affects only how scripts appear in Text Compare.
To view only DDL differences without formatting applied, on the Text Compare toolbar, turn on Format Database Object Script . This option is available when Format Database Object Script in Text Compare is enabled. For more information, see Compare objects that differ only in formatting.