How to export data from the command line
You can automate the data export process using the command line. This can be useful for scenarios that require frequent data exports from the same table or view.
First, create a template file using the Data Export Wizard. Then, run the export operation from the command line using the /dataexport command,
referencing the template file that saves all export settings. This eliminates the need to navigate through the wizard pages. In addition,
you can specify parameters, such as connection details and output file locations, directly in the command line.
Note
Parameters specified in the command line will override the corresponding values in the template file.
Export data from the command line
The workflow will be as follows:
- Step 1: Create a template file
- Step 2: Export data from the command line
A template file is a .det file that stores settings to export data from tables.
Step 1: Create a template file
1. Open the Data Export Wizard using one of the following ways:
- On the ribbon, select Database > Tasks > Export Data.
- In Database Explorer, right-click the database whose data you want to export and select Tasks > Export Data.
2. On the Export format page of the wizard, choose an export format and select Next.
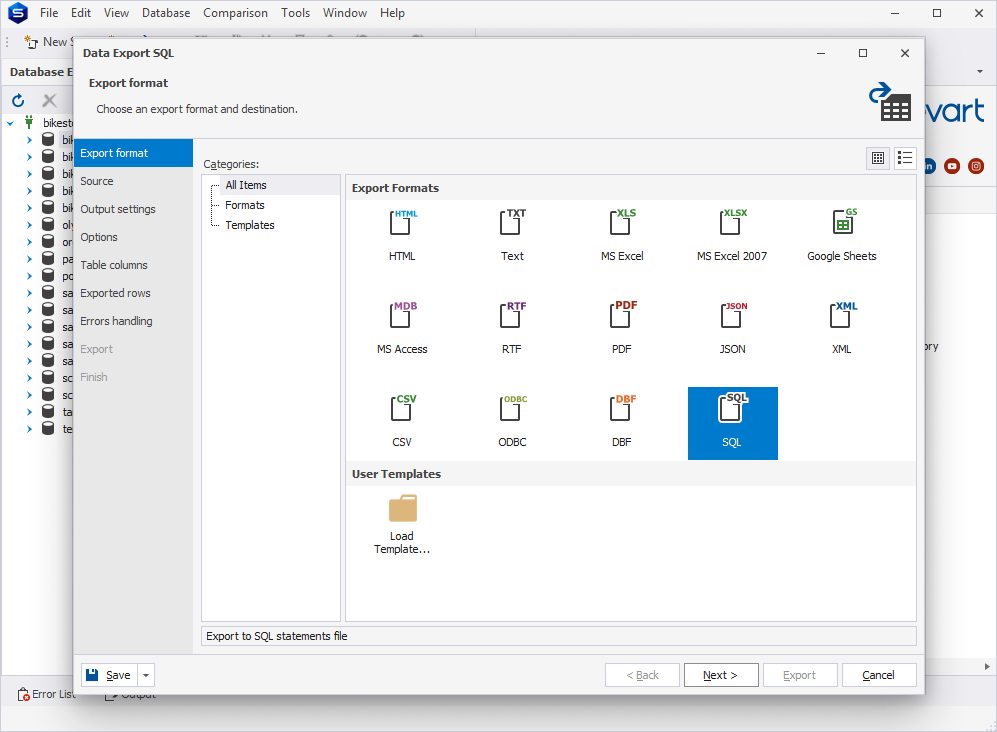
Note
The screenshot illustrates data export in a SQL format. The procedure is identical for exporting data to other formats.
3. On the Source page, select the source connection, database, schema, and table for data export.
4. On the Output settings page, select the path to store the output file:
- Export data into separated files: Select this option to store each table to be exported as an individual file within a folder.
- Export data into a single file: Select this option to store all the tables to be exported in a single file.
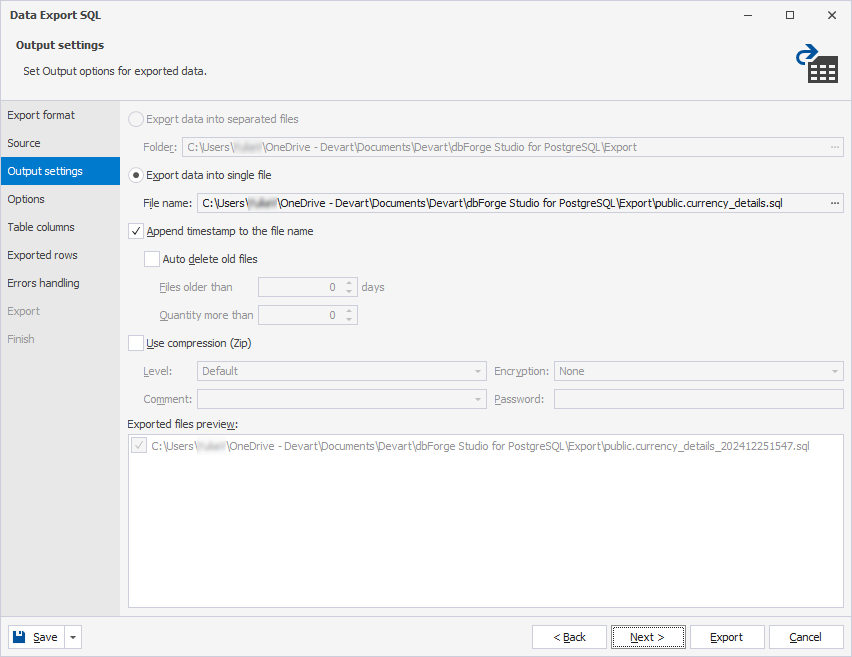
5. Optional: Configure the data export through other wizard pages.
6. In the lower-left corner of the wizard, select Save > Save Template.
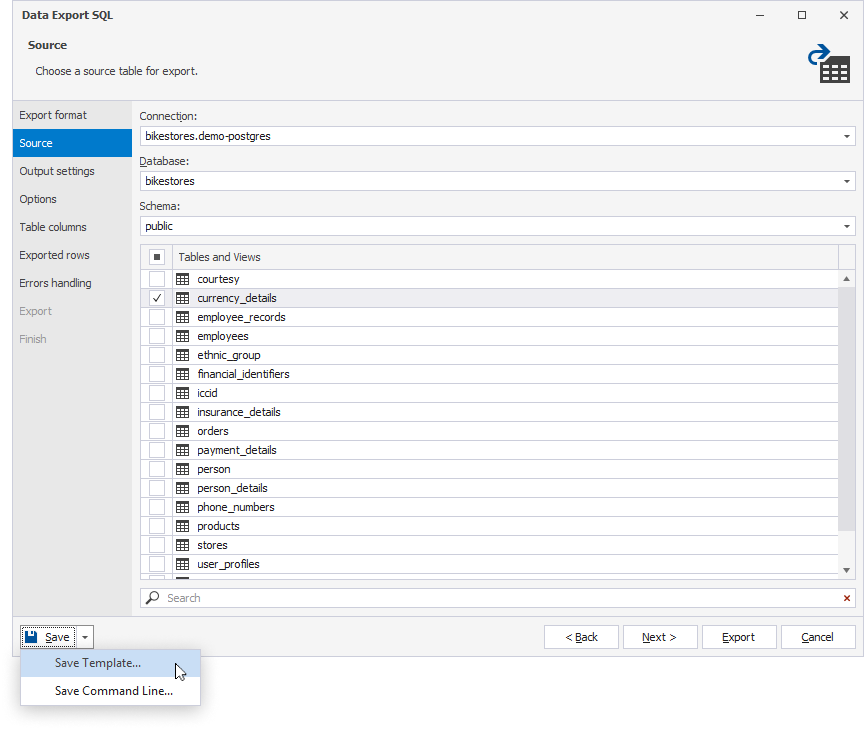
7. In the Save As window that opens, specify the file name and path to save the template file, and select Save to save the file.
Note
For security reasons, the generated file does not contain password information. If the Allow saving password option is selected for the connection in the Database Connection Properties dialog, no additional action is required for the password. However, if the option is not selected, the password must be specified using the
/passwordoption.
8. In the upper-right corner of the wizard, click the cross icon to close the wizard. Alternatively, select Cancel to close the wizard.
Note
You do not need to select Export in the wizard to create a template file.
Step 2: Export data from the command line
1. In the Command Prompt, navigate to the installation folder of dbForge Studio for PostgreSQL.
Note
The installation folder may vary depending on whether dbForge Studio was installed as a standalone tool or as part of the dbForge Edge bundle.
If the Studio was installed as part of dbForge Edge, the installation folder path is as follows:
C:\Program Files\Devart\dbForge Edge\dbForge Studio for PostgreSQLIf the Studio was installed as a standalone tool, the installation folder path is as follows:
C:\Program Files\Devart\dbForge Studio for PostgreSQL
2. Specify the following command-line script to export data:
dbforgepostgresql.com /dataexport /templatefile:"path_to_template_file"
where:
/dataexportis the command to perform the data export operation./templatefileis the command-line parameter to specify the path to a .det file that saves export settings, such as the source table, output file to store exported data, and data format."path_to_template_file"is the path to the previously generated .det template file.
3. Press ENTER to execute the command.
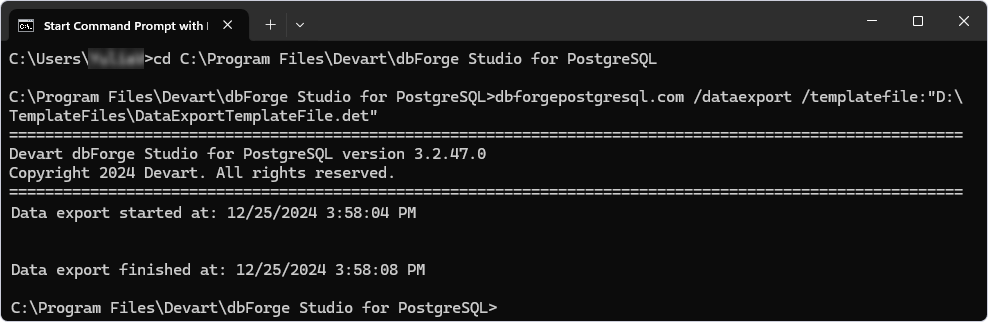
The file with the exported data is stored at the specified path:
Switches used in the command line
To get more information on switches related to data export using the command line, execute the following command:
dbforgepostgresql.com /dataexport /?
Command line usage
The usage of options available for /dataexport in the command line is as follows:
dbforgepostgresql.com /dataexport [/option_name1[:value | [parameter1:value parameter2:value ..]] /option_name2 ..]
The table provides arguments and their usage available for the /dataexport command.
| Argument | Usage and Action |
|---|---|
/connection |
Usage: /connection:<connection_string>Specifies the connection string. |
/errormode |
Usage: /errormode:<ignore|abort>Specifies the application behavior when encountering an error: Ignore: Ignore all errors and continue execution. Abort: Cancel execution if an error occurs. |
/exitcodes |
Usage: /exitcodesDisplays the list of exit codes that can be returned by the command-line process. |
/outputfile |
Usage: /outputfile:<filepath>Specifies a destination file or directory for multiple export. The option is inaccessible for the ODBC format. |
/outputtable |
Usage: /outputtable:<tablename>Specifies a destination table name. The option is available for SQL, ODBC and Access formats. |
/password |
Usage: /password:<pw>Specifies the server password that overrides the values specified in the /connection parameter. |
/range |
Usage: /range all|<start:<startfrom> length:<count>> Specifies the range of exported rows. all: Allows exporting all rows.start:<startfrom>: Allows specifying the row’s number to start exporting data from.length:<count>: Allows specifying the quantity of rows for export. |
/singlefile |
Usage: /singlefile:file nameSpecifies that all data has to be exported into a single file, even if there are several source tables. |
/table |
Usage: /table <tablename> [<tablename>]Specifies a source table name. Multiple tables can also be specified if needed. |
/templatefile |
Usage: /templatefile:<filepath>Specifies a path to the template file. |
/treatWarningAsError |
Usage: /treatWarningAsError:[Yes|No]Specifies the behavior for treating warnings: Yes: Treats all warnings as errors, and the subsequent behavior will be determined by the errormode option.No: Ignores warnings and continue the command line execution. |
Examples of using switches
- Export data using settings specified in the template file:
/dataexport /templatefile:"D:\Export_CSV.det"
- Export data from multiple tables into a single file, with overridden connection and table settings:
/dataexport /templatefile:"D:\Export_CSV.det" /connection:"User Id=postgres;Password=pass;Host=localhost;Port=5432;Database=db;Unicode=True;Integrated Security=False" /table HumanResources.Employee HumanResources.Mapping /singlefile:"D:\expdata.csv"
- Export 10 records while overriding the file save path. The error processing mode is set to ‘Ignore all errors’:
/dataexport /templatefile:"D:\Export_CSV.det" /range start:100 length:10 /outputfile:"D:\Sales_OrderTracking.csv" /errormode:ignore
Exit codes used in the command line
An exit code is a status code that a command-line script returns. It indicates whether the execution was successful or failed.
The table provides exit codes and their descriptions for the /dataexport command.
| Exit Code | Description |
|---|---|
| 0 | Success. |
| 2 | Execution terminated with Ctrl+Break. |
| 3 | Failed. |
| 10 | Command line usage error. |
| 11 | Illegal argument duplication. |
| 20 | Trial expired. |
| 30 | Project file corrupted. |
| 40 | Server connection fail. |
| 103 | Script executed with errors. |
| 105 | Resource unavailable. |
| 107 | Failed to create report. |
| 108 | There are no objects to perform the specified operation. |