Compare and synchronize scripts folders and static data
A scripts folder is a set of scripts that represent a database schema and table data. It can be utilized for:
- Version-controlling table data by storing the script files in a version-control system to track data modifications
- Comparing table data on an unconnected SQL Server
Note
Scripts folders can only be created and compared using dbForge Data Compare Professional Edition.
A scripts folder stores the following information:
- Database objects that are grouped into folders based on their types in the database, such as Programmability, Security, Storage, Tables, or Views. Each folder contains individual .sql files with creation scripts for each object within that group.
- A folder with static data that contains individual .sql files with INSERT scripts for each table.
- A config.xml file that contains configuration information, including a SQL Server version, the collation of the database from which the scripts folder was created, and the entity, which refers to the database these scripts are associated with.
- A single .sql file with ALTER DATABASE scripts for the whole database.
Static data refers to information that remains constant and unchanged over time. In addition, it does not require regular updates and does not depend on specific instances or contexts. Typically, static data serves for reference purposes and can include a list of countries, time zones, or product categories. It can also be used to populate reference or lookup tables within a database.
With Data Compare, you can create a scripts folder with static data from an existing data source in the New Data Comparison wizard when you set up the comparison.
Note
dbForge Data Compare for SQL Server can read information about tables from scripts folders with different structures, allowing users to further map and compare these tables. It is important to note that scripts folders can be created using the dbForge tool or any third-party tool. In addition, the data must be stored in individual SQL files for each object and not in a single file containing DDL tables. When synchronizing data, dbForge Data Compare will write objects according to the folder structure specified in the dbForge tool.
Create a scripts folder with static data
To create a scripts folder:
1. On the Database menu, select Tasks > Create Scripts Folder to open the Create Scripts Folder or Snapshot dialog:
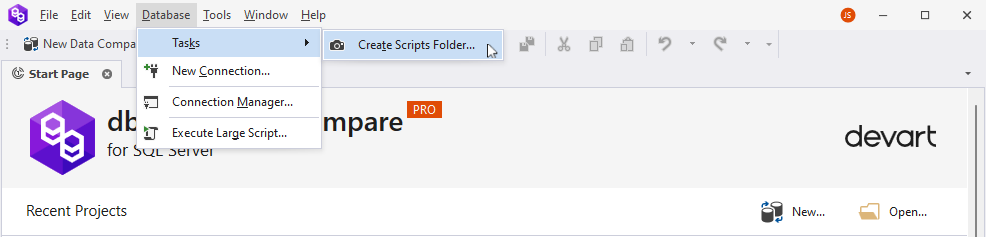
2. In the dialog, specify a database as a source type of the object, a connection, a database name from which a scripts folder will be created, a scripts folder as a destination type, and a path to the output file name to store the scripts folder.
Note
You can create a scripts folder from a database or another scripts folder.
3. The Decrypt encrypted objects option is selected by default. If you do not want Data Compare to automatically decrypt encrypted objects, clear the checkbox next to this option. Turning this option on may result in slower performance.
Note
If you create a scripts folder from another scripts folder, the decryption option is not available.
4. To add static data, select the Include data checkbox.
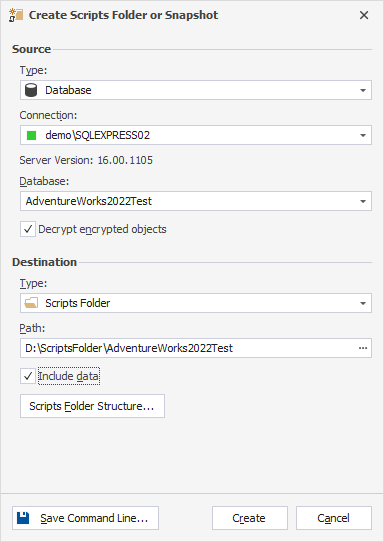
5. To customize the scripts folder structure and file name templates, click Scripts Folder Structure. In the dialog that opens, specify the directories for saving your database objects and click OK.
7. Click Create to create a scripts folder.
How to compare and synchronize scripts folders in SQL Server
When comparing and synchronizing scripts folders either as the Target or the Source, a synchronization script is created. It can be saved to a file or opened in an internal editor.
When a scripts folder is selected as the Source, you can execute the synchronization script directly against the target database or generate a migration script.
When a scripts folder is selected as the Target, you can update the scripts folder after synchronization or generate a migration script.
Note
In addition to comparing data, you can also compare objects within a scripts folder. For more information, see Compare and synchronize scripts folders.
To compare and synchronize a scripts folder in SQL Server as the source
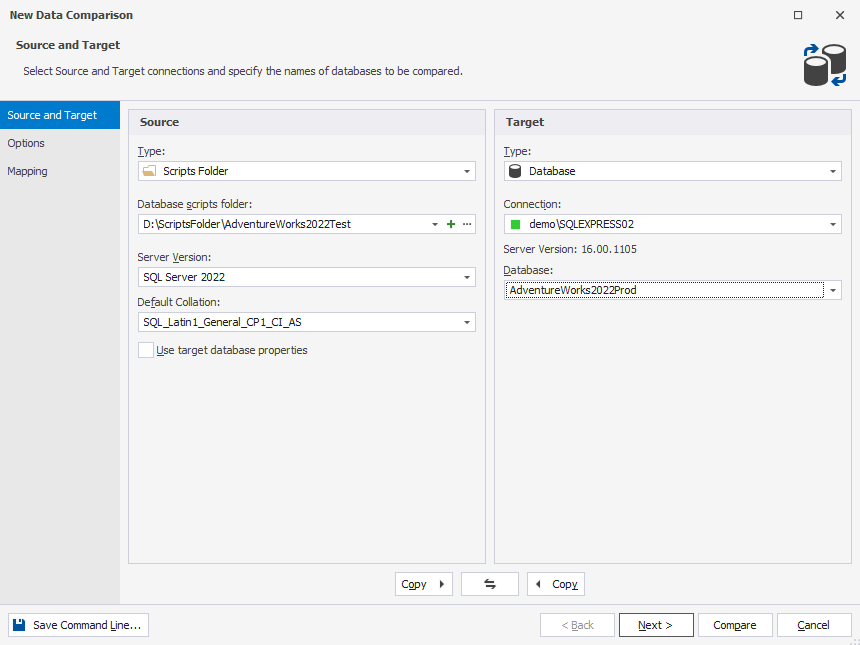
1. On the standard toolbar, click New Data Comparison to open the New Data Comparison wizard.
2. On the Source and Target page of the wizard, choose a scripts folder as a source type and a database as a target type.
3. Under Source:
- In the Database scripts folder field, you can do either of the following:
- From the dropdown list, choose the previously connected scripts folder.
- Click
 New to create a scripts folder.
New to create a scripts folder. - Click
 Browse to select the required scripts folder stored on your machine.
Browse to select the required scripts folder stored on your machine.
- The server version and default collation are automatically inherited from the current server connection.
4. Under Target:
-
From the dropdown list, choose the previously established server connection. Alternatively, select Manage from the dropdown list to open the Connection Manager and create a new connection.
-
Choose a target database to compare.
5. Optional: On the Options page, you can select additional options to customize the default comparison process.
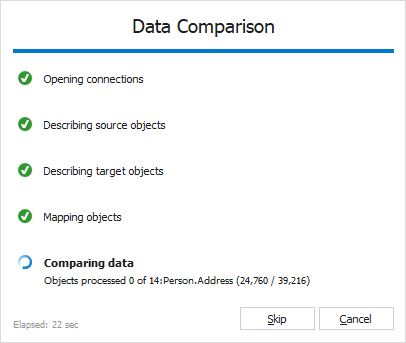
6. Click Compare to run the comparison process. The Data Comparison progress window opens, showing the stages of the comparison process.
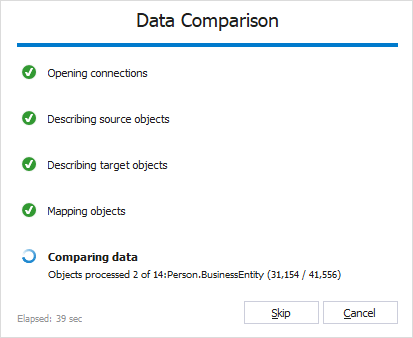
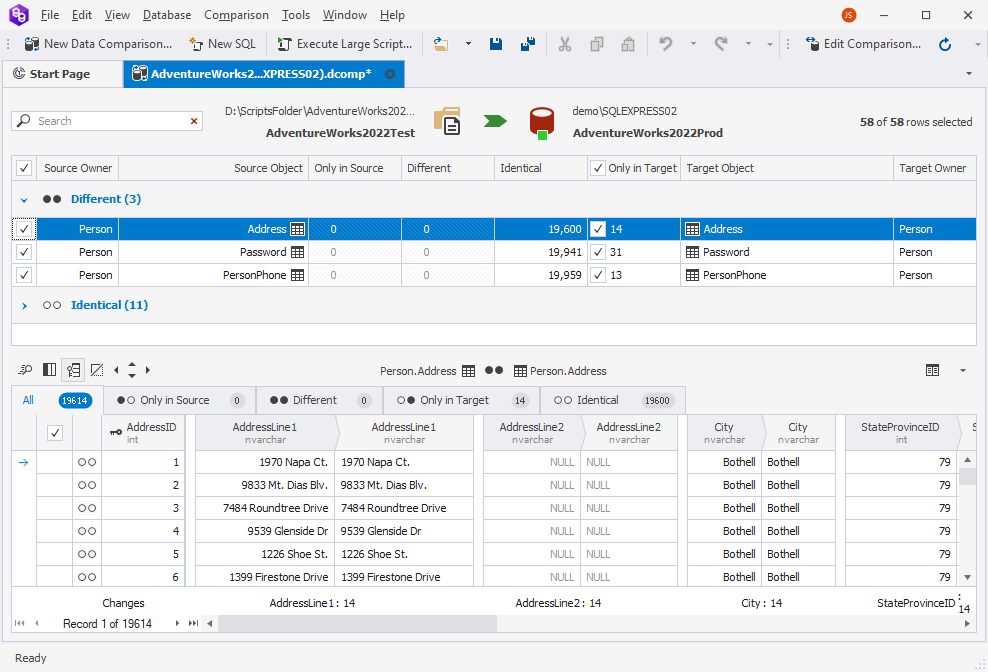
7. In the Data Comparison document that opens, select the objects to compare and click ![]() Synchronize data to the target database to open the Data Synchronization Wizard.
Synchronize data to the target database to open the Data Synchronization Wizard.
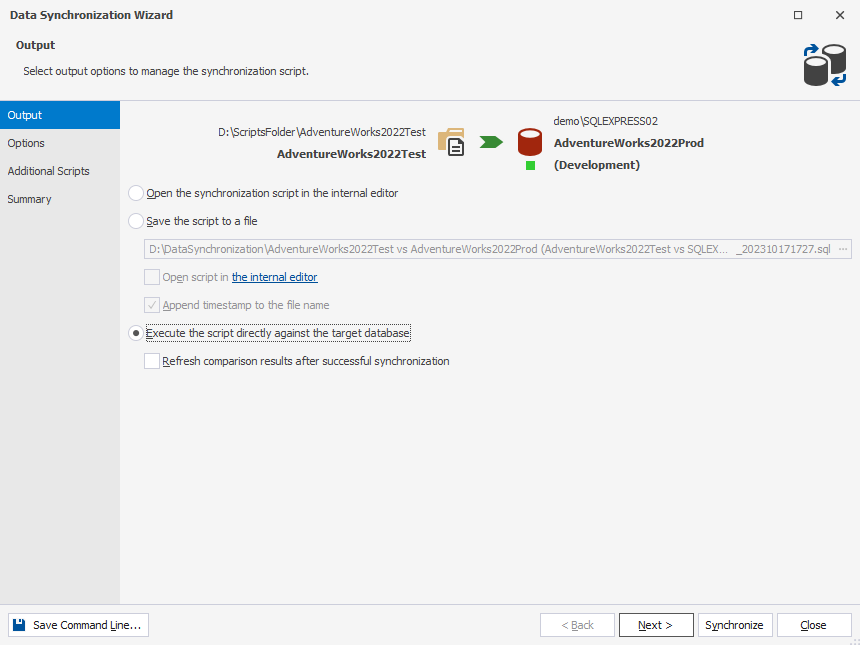
8. In the wizard, select the way you want to manage a synchronization script and click Synchronize.
To compare and synchronize a scripts folder in SQL Server as the target
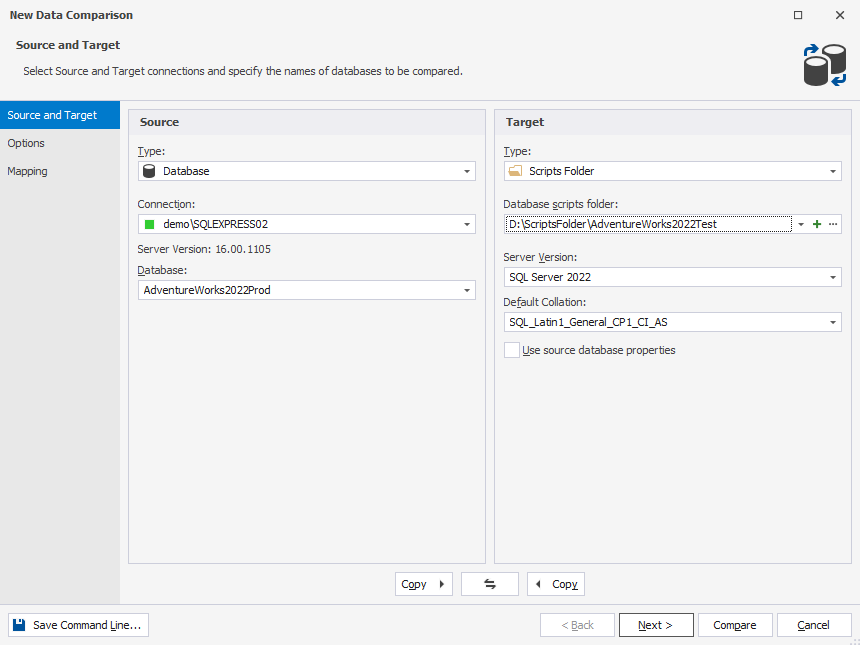
1. On the standard toolbar, click New Data Comparison to open the New Data Comparison wizard.
2. On the Source and Target page of the wizard, choose a database as a source type and a scripts folder as a target type.
3. Under Source:
-
From the dropdown list, choose the previously established server connection. Alternatively, select Manage from the dropdown list to open the Connection Manager and create a new connection.
-
Choose a source database to be compared.
4. Under Target:
- In the Database scripts folder field, you can do either of the following:
- From the dropdown list, choose the previously connected scripts folder.
- Click
 New to create a scripts folder.
New to create a scripts folder. - Click
 Browse to select the required scripts folder stored on your machine.
Browse to select the required scripts folder stored on your machine.
- The server version and default collation are automatically inherited from the current server connection.
5. Optional: On the Options page, you can select additional options to customize the default comparison process.
6. Click Compare to run the comparison process. The Data Comparison progress window opens, showing the stages of the comparison process.
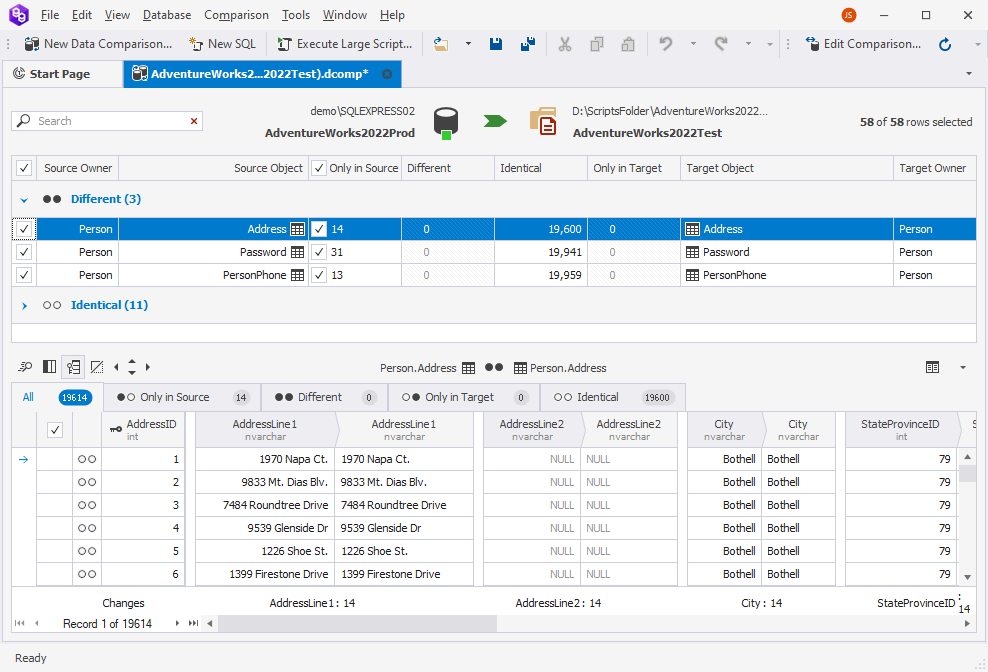
8. In the Data Comparison document that opens, select the objects you want to compare and click ![]() Synchronize data to the target database to open the Data Synchronization Wizard.
Synchronize data to the target database to open the Data Synchronization Wizard.
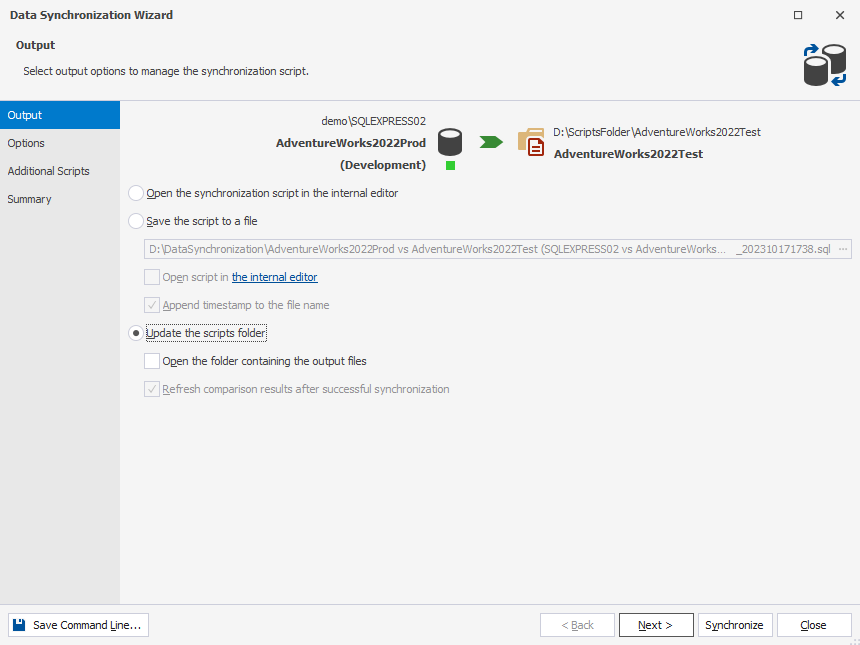
9. In the wizard, select the way you want to manage a synchronization script and click Synchronize.
Scripts folders synchronization issues
-
We recommend you select the Ignore spaces in object names and Ignore trailing spaces options when using a scripts folder as a data source. That should be done because SQL Server doesn’t always handle white space and comments correctly in object definitions for objects such as views, stored procedures, and rules.
-
When you select a scripts folder as a target data source, comments that are part of a table definition will be lost when the table is modified and the object creation script is updated.
-
You can use the scripts folder comparison feature to copy or transfer database data. Before moving data, ensure that the structure of the scripts folder and target database is identical. To learn how to do it with dbForge Schema Compare, see Compare and synchronize scripts folders.