Synchronize data between SQL Server and MySQL databases using ODBC Driver
The method described in this topic comprises an alternative to synchronizing data between different DBMSs using a linked server and custom queries. As custom queries cannot be synchronized, you can not use a database connected via linked server as a target. Below, we offer a practical workaround to help you overcome this limitation.
Prerequisites
- Ensure that you have the Devart ODBC driver for MySQL installed and properly configured.
- The Linked Server should connect to the MySQL database via a user account that has all the necessary permissions to modify data in the tables.
Note
You can learn how to install and configure ODBC Driver for MySQL here.
Step 1: Create an intermediate SQL Server database
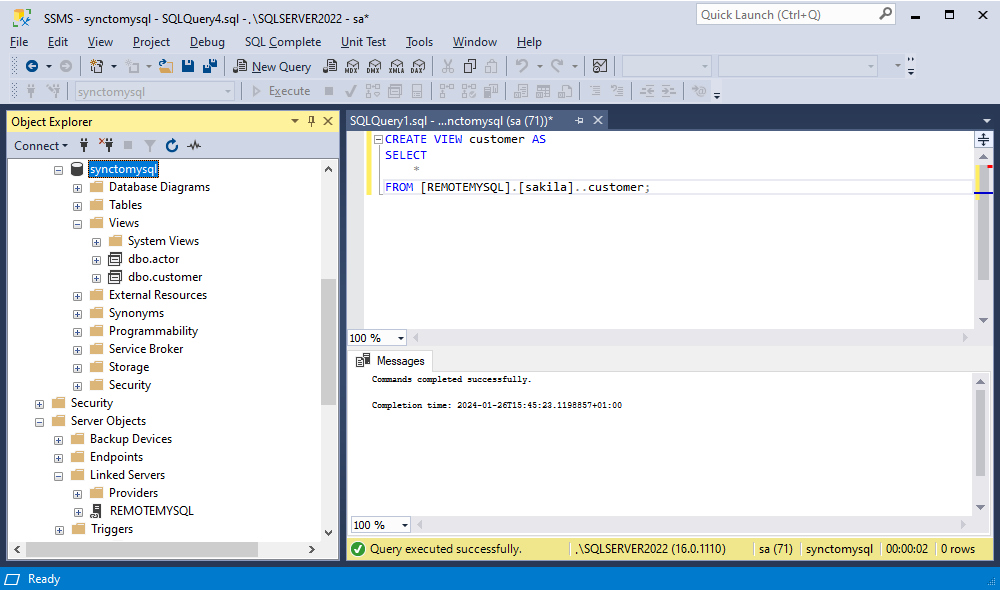
First, on SQL Server, create an intermediate database. Then, in this database, create views that will contain custom queries against the MySQL database.
CREATE VIEW view-name AS
SELECT
*
FROM [linkedserver_name].[database_name]..[table_name];
Step 2: Configure data comparison
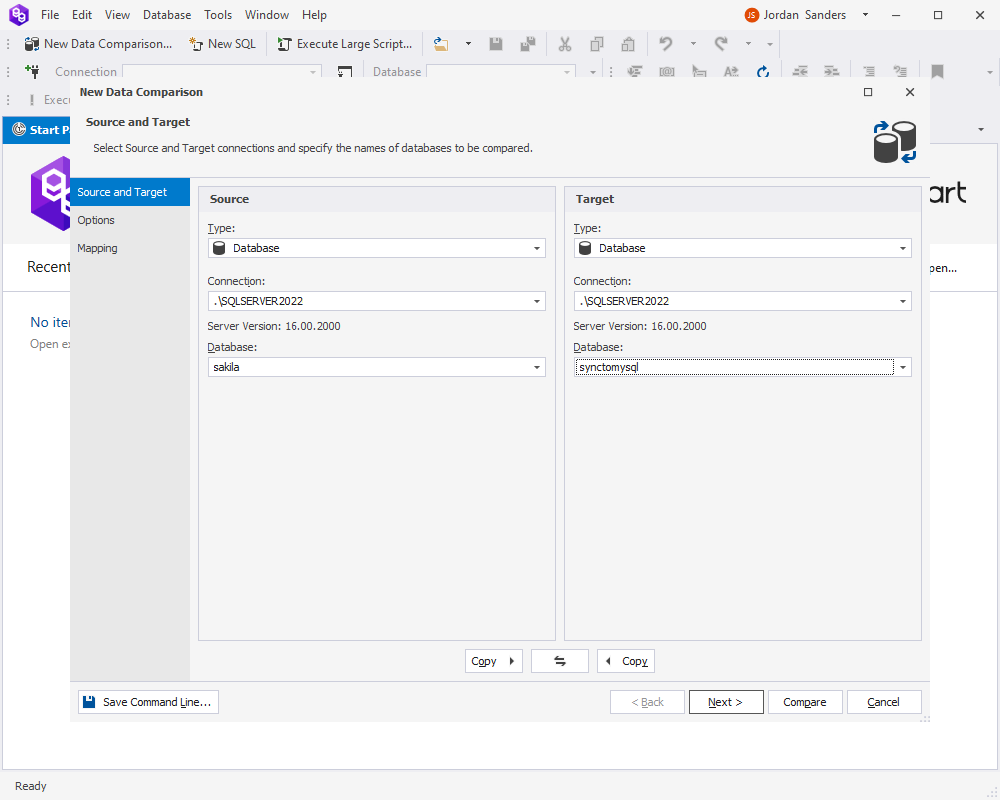
In Data Compare for SQL Server, click New Data Comparison. In the New Data Comparison wizard that will open, as a source, select a database you want to synchronize with a MySQL database. As a target, select the recently created database containing views based on custom queries against that MySQL database. Click Next.
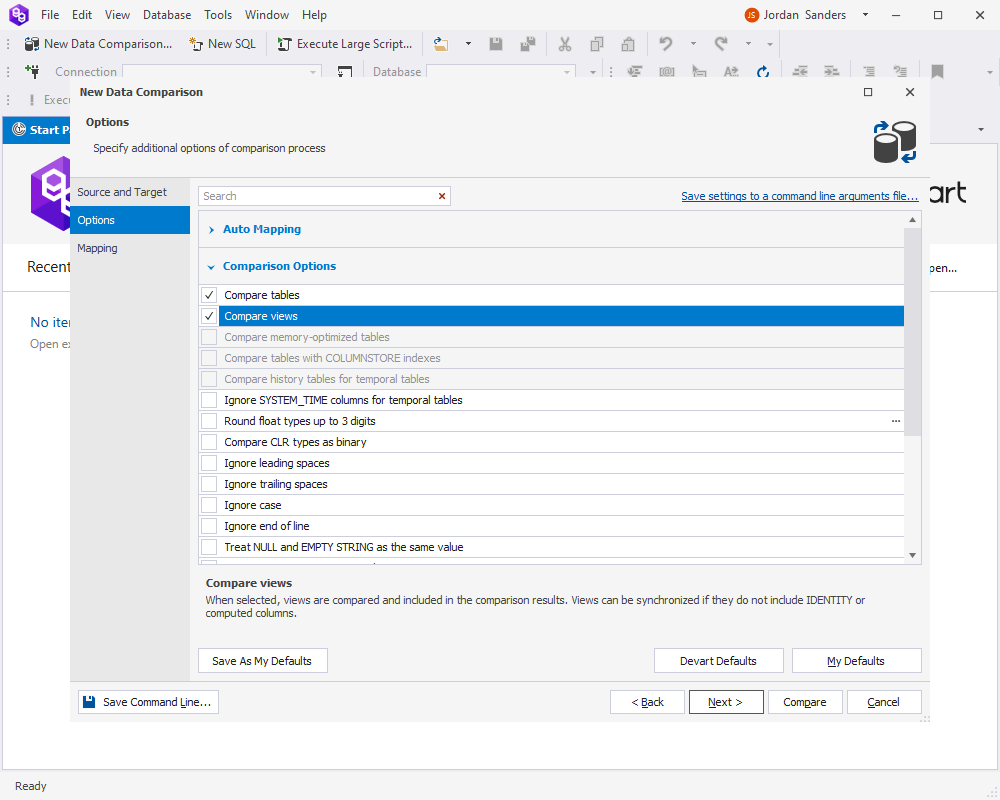
On the Options page of the wizard, select the Compare views option. Click Next.
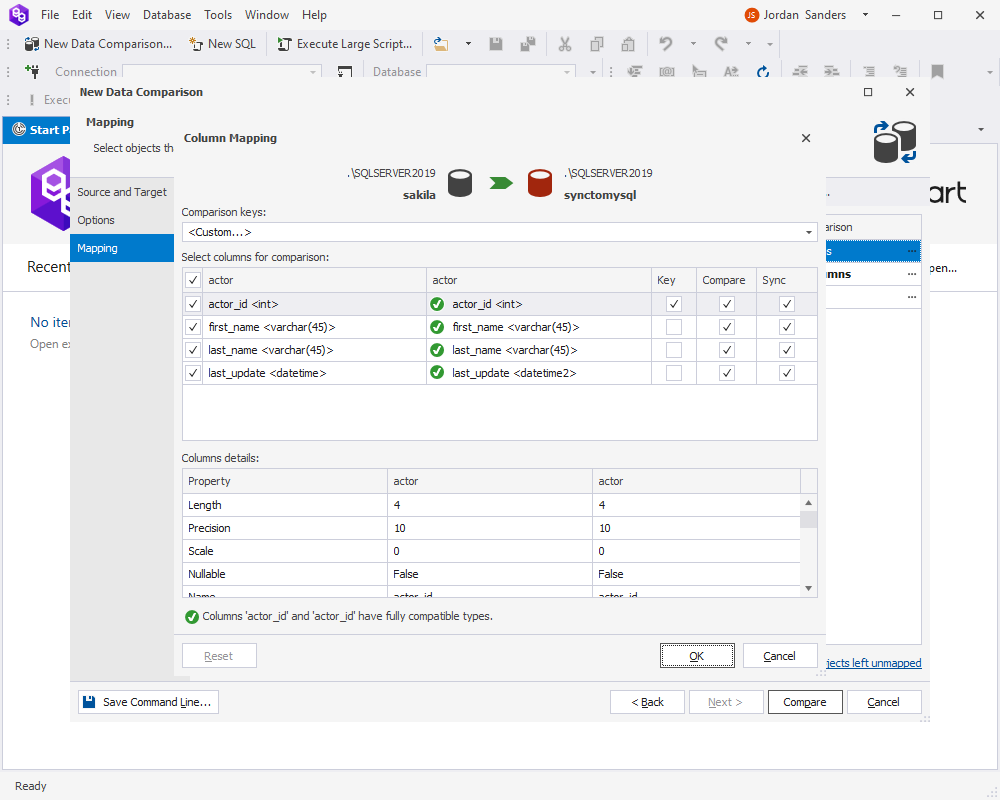
On the Mapping page, map source columns to the columns in the target’s views. Click Compare.
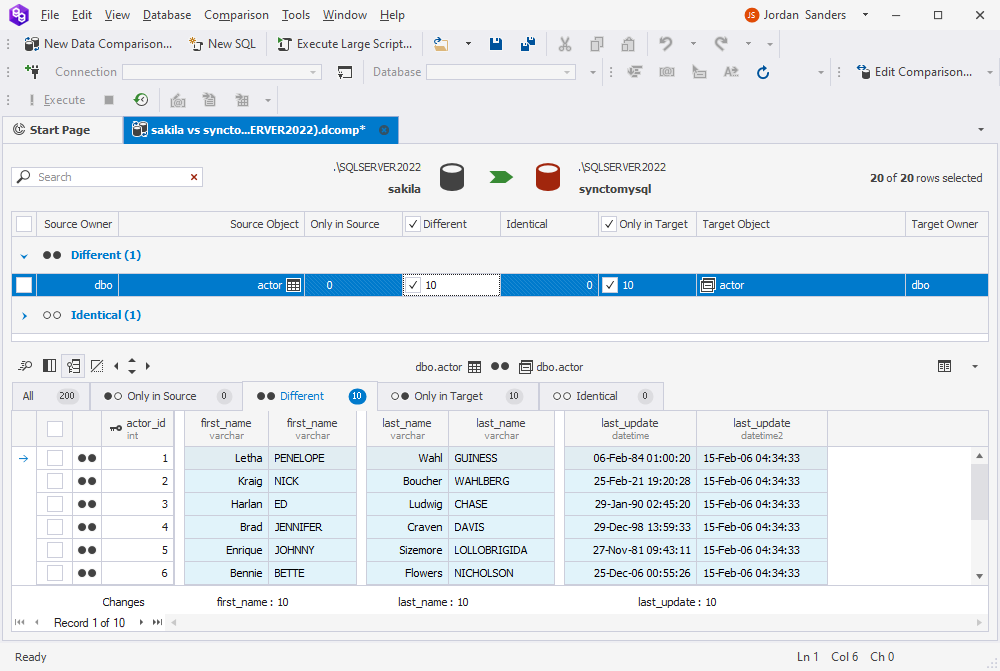
Data Compare will display the comparison results. Select the objects you want to synchronize and click Synchronize.
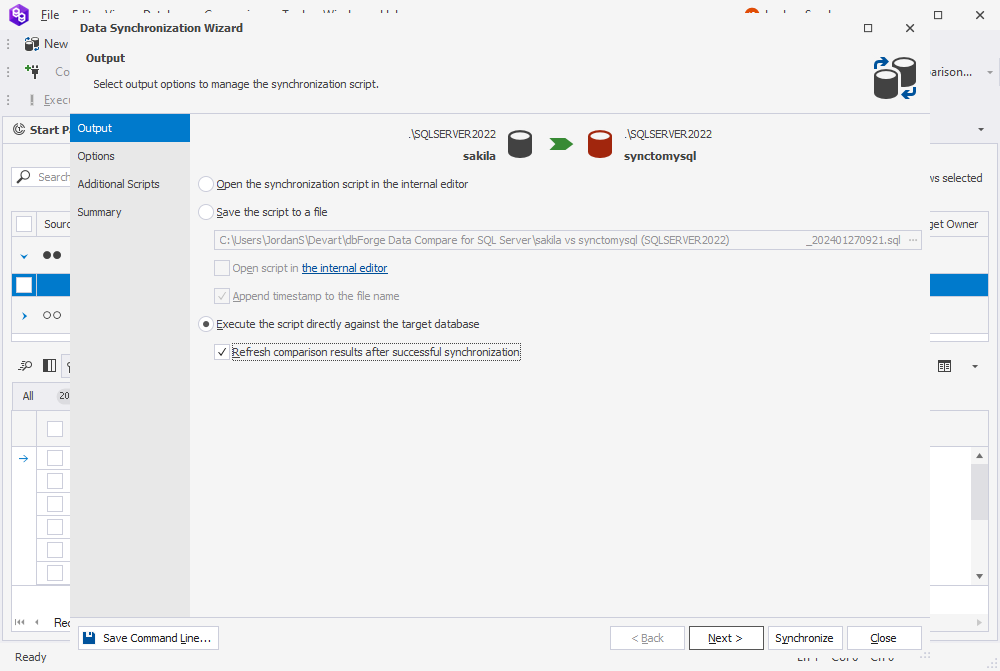
Data Compare for SQL Server allows you to open the synchronization script in the internal editor for further modifications, save it to a file, or execute it directly against the target database.
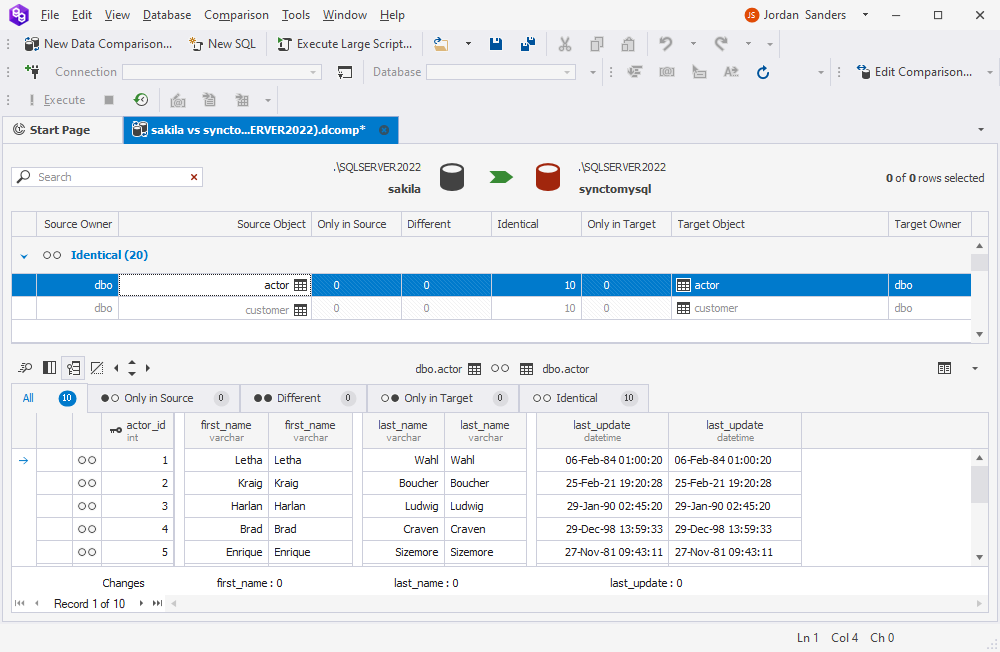
If you refresh the comparison results after synchronization, you’ll find that the data in the source and target databases is now identical.
Note
If a MySQL database contains foreign keys, data synchronization may fail. In such cases, you may need to manually disable and then re-enable foreign keys.