Schedule database synchronization
You can schedule or automate a comparison or synchronization with the help of Data Compare, a task scheduler tool, or a PowerShell script.
The scheduling of database synchronization includes the following steps:
- Create a .bat file via dbForge Data Compare
- Create a synchronization task using Windows Task Scheduler
It is possible to automate the synchronization process with a PowerShell script. To do this, follow the steps described in How to automatically synchronize data in two SQL Server databases on a schedule.
Create a .bat file via dbForge Data Compare
First, you need to create a file with the .bat extension for comparing or synchronizing the databases.
To create the .bat file, do the following:
1. On the standard toolbar, click New Data Comparison. The Data Comparison Wizard window opens.
2. On the Source and Target tab, select the source and target connections and databases for comparison and click Next.
3. On the Options tab, select the options for comparison and then click Next.
For more information about options, refer to Set comparison options.
4. Optional: On the Mapping tab, verify the objects to be compared or change the mapping of tables and columns, and then click Compare to run the comparison process.
Note
By default, Data Compare automatically maps tables and views having the same name in the source and target data sources. For more information about mapping settings, see Select tables and views.
5. In the Data Compare window, select the objects you want to synchronize and click  Synchronize objects to the target database.
Synchronize objects to the target database.
6. In the Data Synchronization Wizard that opens, set the synchronization options and then click Save Command Line.
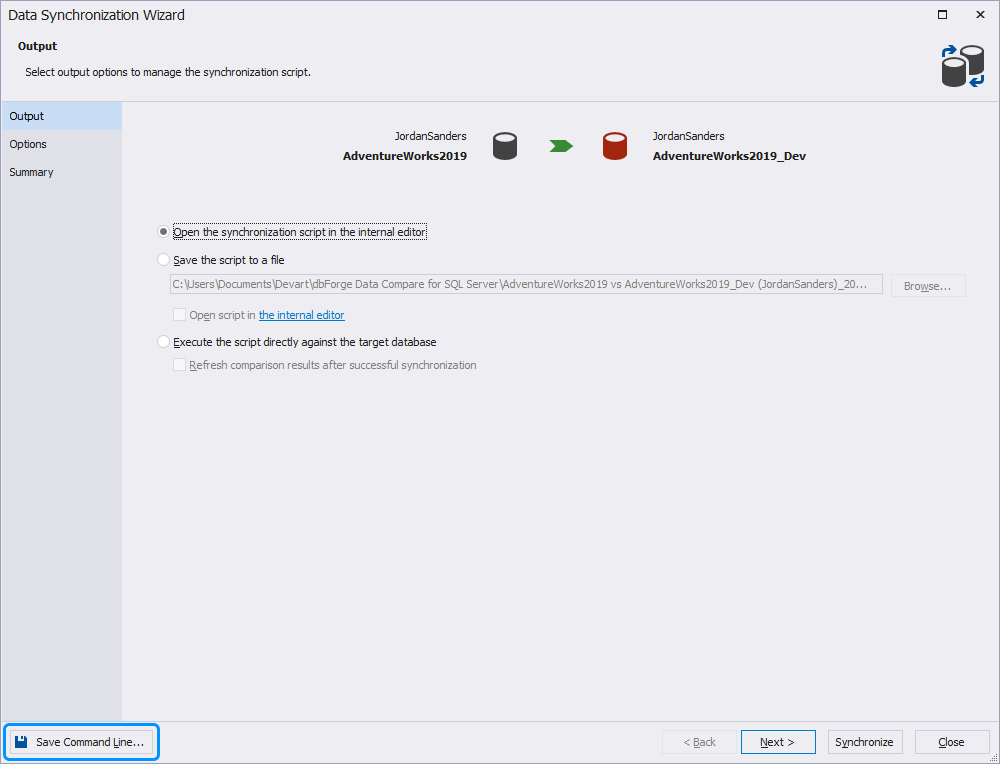
7. In the Command line execution file settings window that opens, verify and configure the settings to manage the *.bat file text.
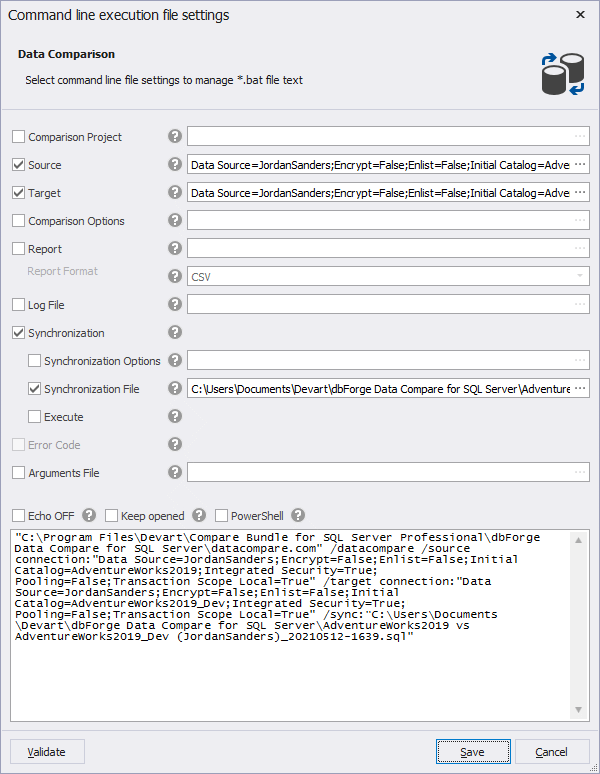
Command-line file settings
| Name | Default State | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Yes | Specify the source options: a server, a connection, a backup, and a scripts folder. |
| Target | Yes | Specify the target options: a server, a connection, a backup, and a scripts folder. |
| Comparison Project | No | Load command-line settings from the previously created comparison project file with the .dcomp extension. |
| Comparison Options | No | Set options to manage the comparison process. |
| Synchronization | Yes | Start database synchronization. If an output file is specified, only synchronization script will be generated. |
| Report | No | Generate a data comparison report file. |
| Report Format | No | Specify the format of the file comparison report: HTML, XLS, and CSV (selected by default). If not specified, the format of the file comparison report takes the exension of the report file. |
| Log File | No | Generate a comparison log file in the specified directory. |
| Synchronization Options | No | Set options to manage the synchronization script. |
| Synchronization File | Yes | Specify a path to the database synchronization script file. |
| Execute | No | Execute the file received in the result of the previous commands execution. |
| Error Code | No | Enable the processing of error levels. |
| Arguments File | No | Specify a command-line arguments file. If a path to the arguments file is specified, a separate command-line file will be generated. |
| Echo OFF | No | Disable echoing all commands in the batch file. All the text in the batch file is enclosed in the @Echo OFF … @Echo ON command. |
| Keep opened | No | Set a pause command at the end of the batch file text. The command window will be opened. |
| PowerShell | No | Generate the & symbol at the beginning of the batch file text. This makes the batch file compatible with PowerShell. |
9. Optional: To verify that the command line settings are valid, click Validate.
10. To save the script as a *.bat file, click Save.
Create a synchronization task using Windows Task Scheduler
After the batch file for database synchronization was created, we can proceed with the creation of the synchronization task using the Windows Task Scheduler so that the computer can carry out the task automatically.
To create a Windows synchronization task, do the following:
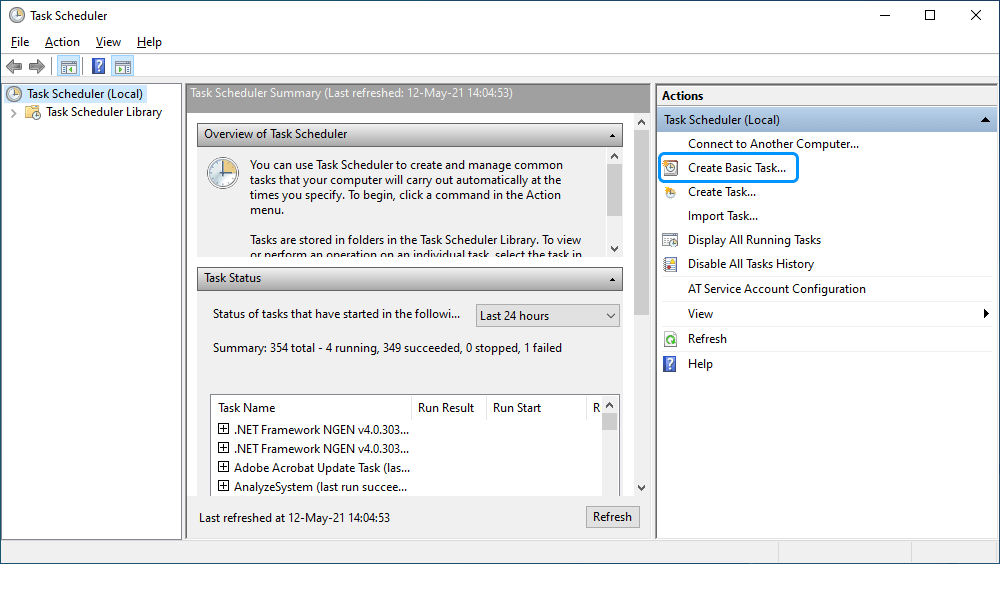
1. Open the Control Panel > Administrative Tools and select Task Scheduler.
2. In the Task Scheduler window that opens, navigate to the Actions pane and click Create Basic Task to create a scheduled task.
Note
For quick access to the Task Scheduler, just start typing task in the Windows 10 search bar. Once you see the Task Scheduler in the list, click it to open.
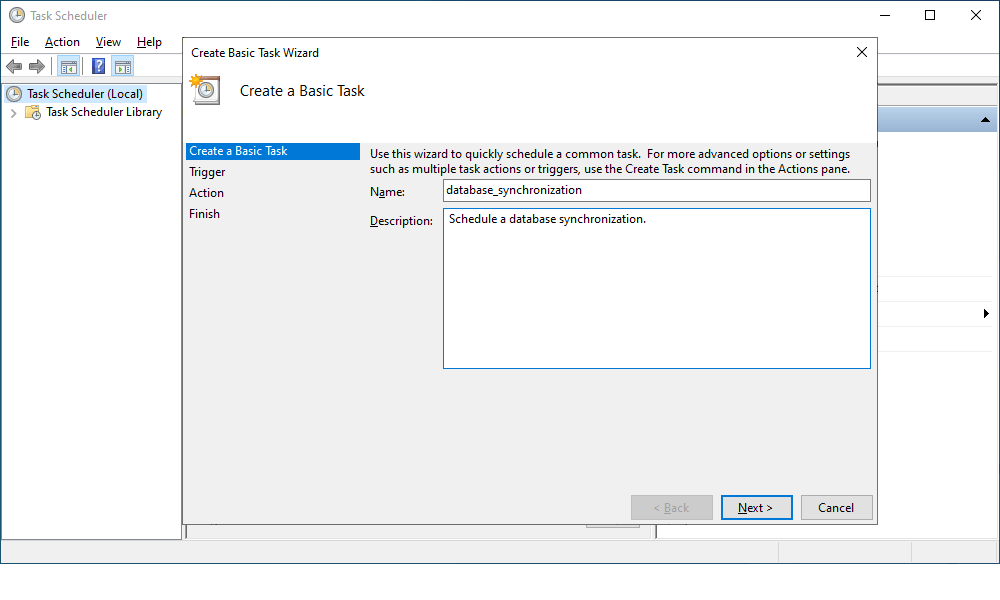
3. In the Create Basic Task Wizard window that opens, specify the name and description of the task and click Next.
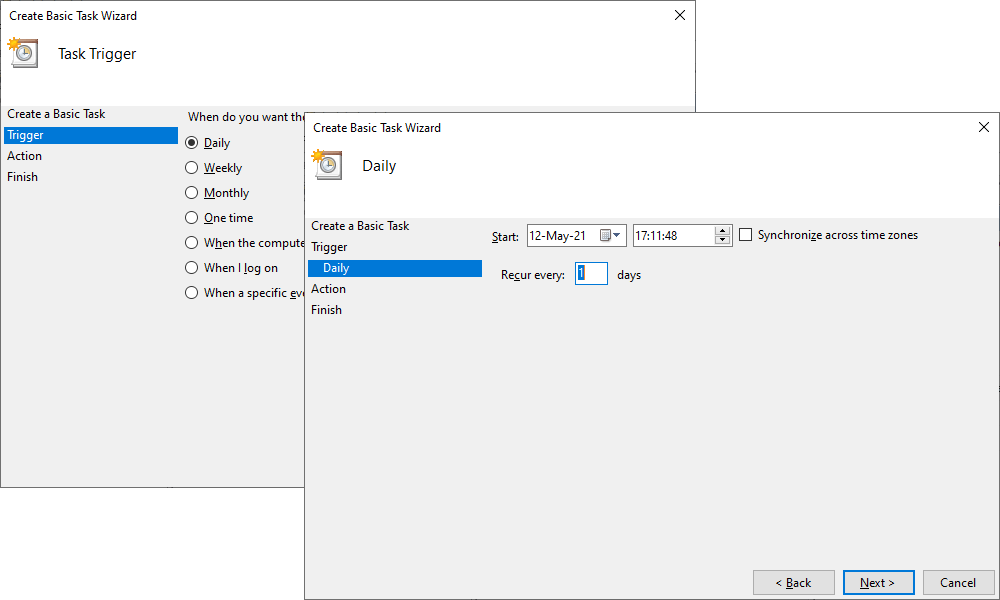
4. On the Trigger tab, choose when to launch the task and then click Next.
- Schedule based on the calendar: Daily, Weekly, Monthly, or One time. For this, specify the schedule you want to use.
- Schedule based on common recurring events: When the computer starts or When I log on.
- Schedule based on specific events: When a specific event is logged. For this, specify the event log, source, and even ID using the drop-down lists.
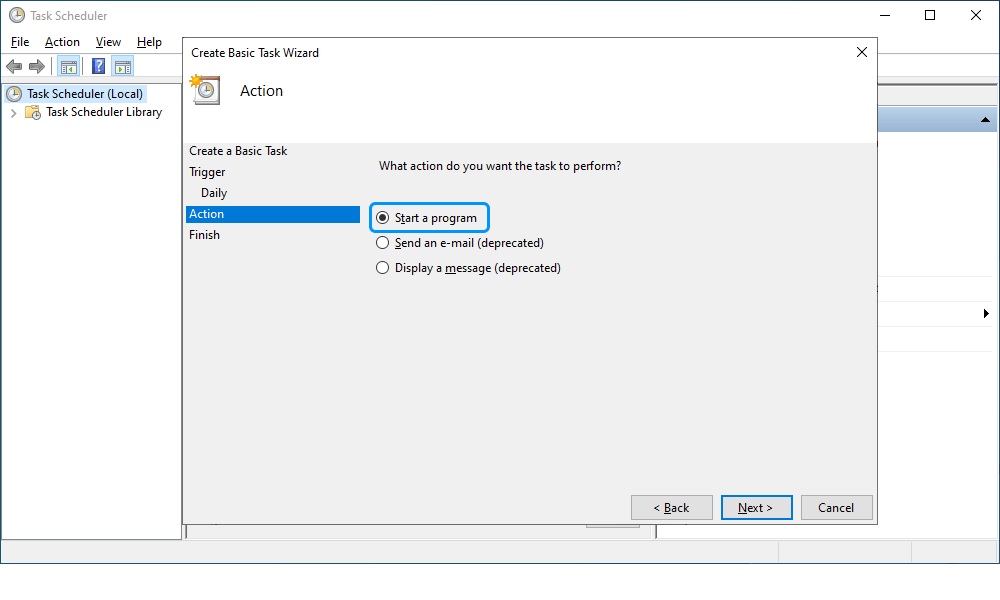
5. On the Action tab, click Start a program to schedule a program to start automatically and then click Next.
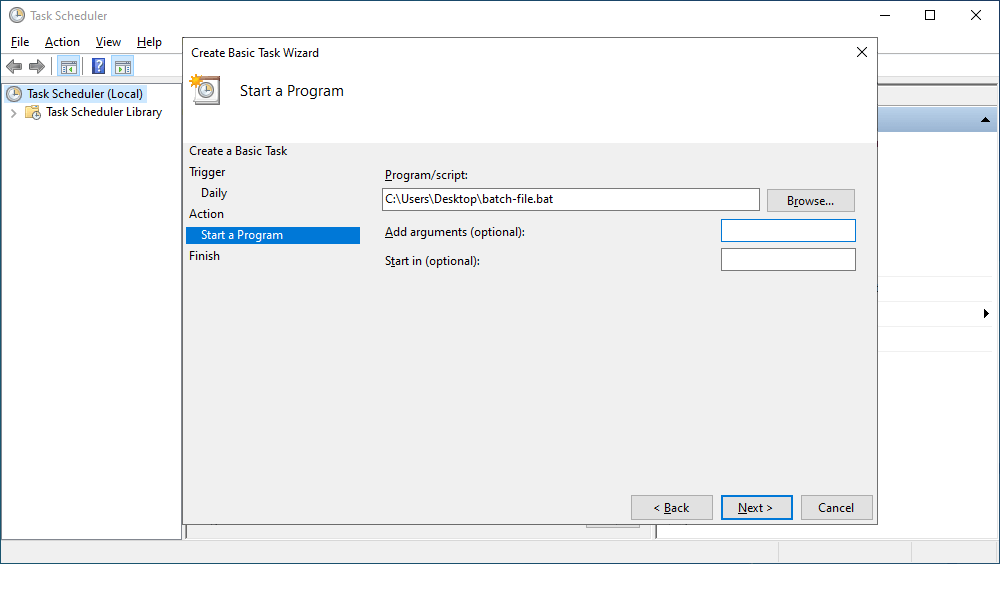
6. On the Start a Program subtab, click Browse to select the .bat file you have created in the Data Synchronization Wizard and then click Next.
There are optional fields that you can set:
- Add arguments: Specify the arguments to run the task with specific instructions.
- Start in: Specify the folder in which the program will start.
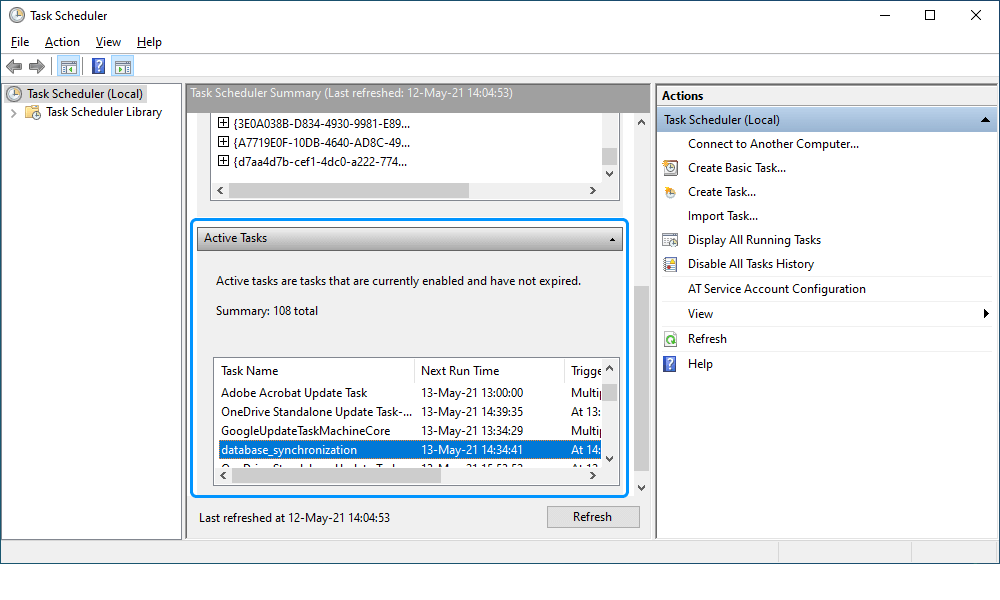
7. On the Finish tab, verify the settings and click Finish.
The task will be displayed in the Active Tasks section.
See also: How to set up email delivery for data comparison logs
Also, you may be interested in the How to automatically synchronize data in two SQL Server databases on a schedule article.