Link a database to a Git repository in GitLab
GitLab is a free and open-source web-based platform designed for Git repositories, providing a collaborative space for web developers to work on code, plan projects, perform testing, deploy applications, and monitor changes — all within a single tool. Some of the main features offered by GitLab include built-in CI/CD pipelines, container registry, and code review tools. GitLab also allows users to host their own GitLab instance on-premises or on a private cloud, making it an attractive option for organizations that require complete control over their source code management tools.
Prerequisites
- Install Git for a Windows client on the machine you’ll be version-controlling a database
- Have a GitLab account
Step 1: Create a repository on Gitlab
You can create a repository by creating a project or forking an existing project.
1. Sign in to your GitLab account.
2. On the top bar, click Create new > New project/repository.
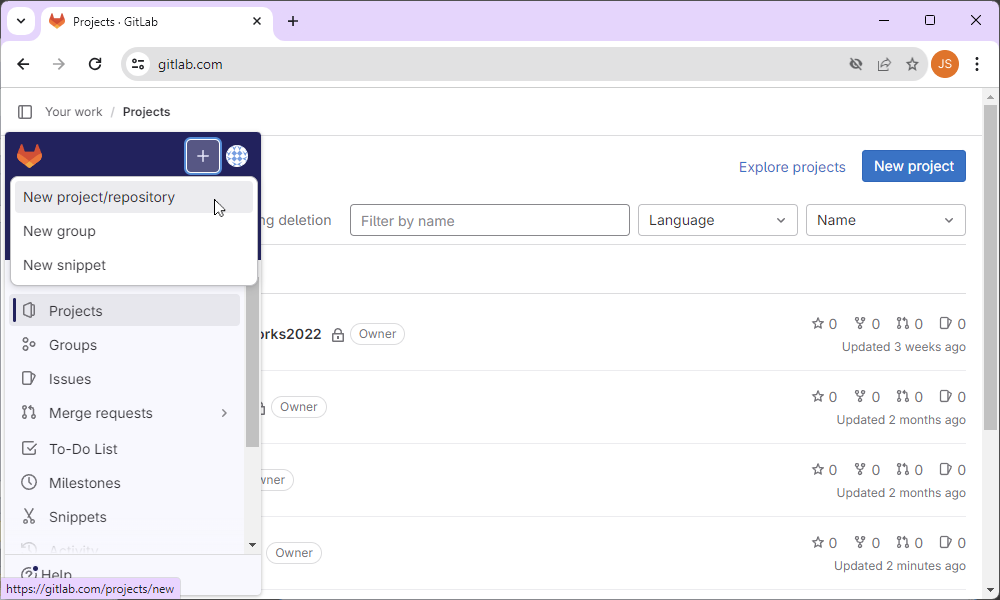
3. Click Create blank project to create a repository.
4. On the Create blank repository page, add the repository details:
- In the Project name field, specify a project name. The project name must start with a lowercase or uppercase letter, digit, emoji, or underscore. It can also contain dots, plus or dash signs, or spaces. Adding the project name will automatically create the project slug.
- In the Project slug field, enter the path to your project.
- Optional: In the Project deployment target field, select your project’s deployment target.
- Select a visibility level:
- Private (the default option) to grant access to specific users.
- Public to provide access to all users without any authentication.
- Select Initialize repository with a README (the default option) to initialize the repository and set it up properly. It will also create a README file for the repository and the default branch (main). If you want to push an existing repository, clear the checkbox.
- Optional: Select Enable Static Application Security Testing (SAST) to check the source code for known security vulnerabilities.
4. Click Create project to create the new repository on GitLab.
Step 2: Clone a repository using the command line
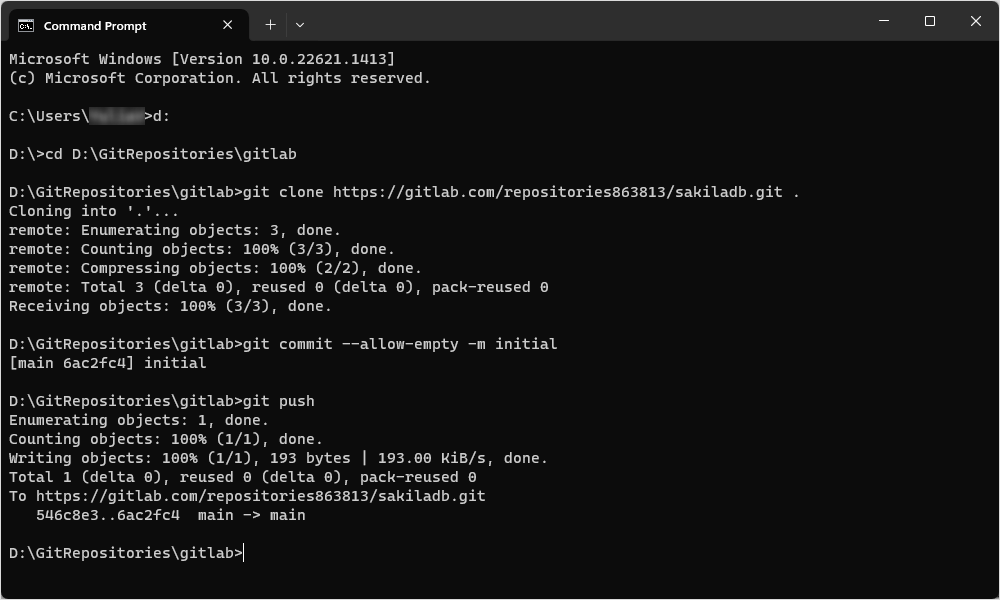
1. Create an empty folder on the drive of your computer to store the local repository. For example, you can create a folder - gitlab - on the drive D.
2. Log in to your GitLab account. In the sidebar, click Projects and select the repository you want to clone.
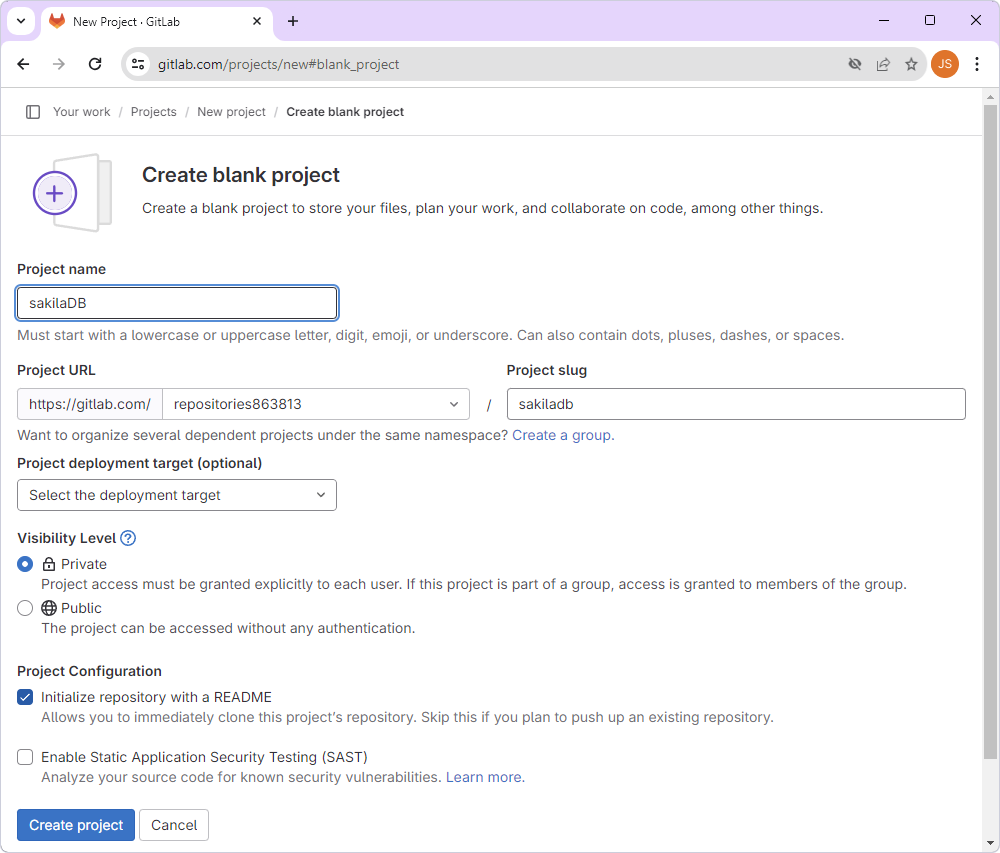
3. In the upper-right corner of the repository page, click Clone and select the connection protocol to copy the repository URL:
- Clone with HTTPS to authenticate with user and password each time you perform an operation between your computer and GitLab. In the example, HTTPS protocol connection is used.
- Clone with SSH to authenticate once using an SSH key pair - a public and a private key.
4. Start Windows Command Prompt (CMD). If you need to change the disk drive and navigate to the empty folder you created in Step 1, use the cd command.
5. Execute the git clone command for the repository URL you have created on GitLab.
Note
Specify a dot at the end of the command to clone the repository to the folder you have created. Otherwise, another subfolder will be created.
git clone <repository URL> .
where <repository URL> is the URL directory of the remote repository.
If you didn’t add any files to the repository when you created it for the first time, execute the following commands:
-
git commit --allow-empty -m initial -
git push
Step 3: Link a MySQL database to source control
You can link the database to source control using the Source Control tool available in dbForge Studio for MySQL.
1. In Database Explorer, right-click the database you want to link to source control and select Source Control > Link Database to Source Control.
2. In the Link Database to Source Control dialog that opens, click + in the Source control repository field.
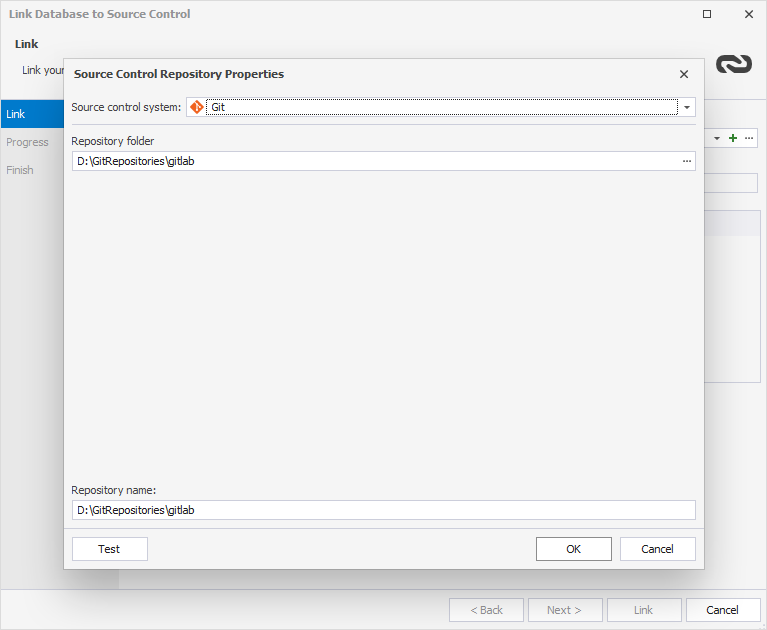
3. In the Source Control Repository Properties dialog that opens, do the following:
- From the Source control system dropdown list, select Git as a source control system.
- In the Repository folder field, click
 More to add the repository folder. In the Select Folder window that opens, select the folder, which is a local copy of your GitLab remote repository, and then click Select Folder.
More to add the repository folder. In the Select Folder window that opens, select the folder, which is a local copy of your GitLab remote repository, and then click Select Folder.
Note
The repository folder name represents a path to the local copy of the remote repository and must not contain the URL of the remote repository.
- Optional: In the Repository name field, you can change the name of the repository folder.
- Optional: Click Test to verify that the database has successfully been connected to source control.
- Click OK to close the Source Control Repository Properties dialog.
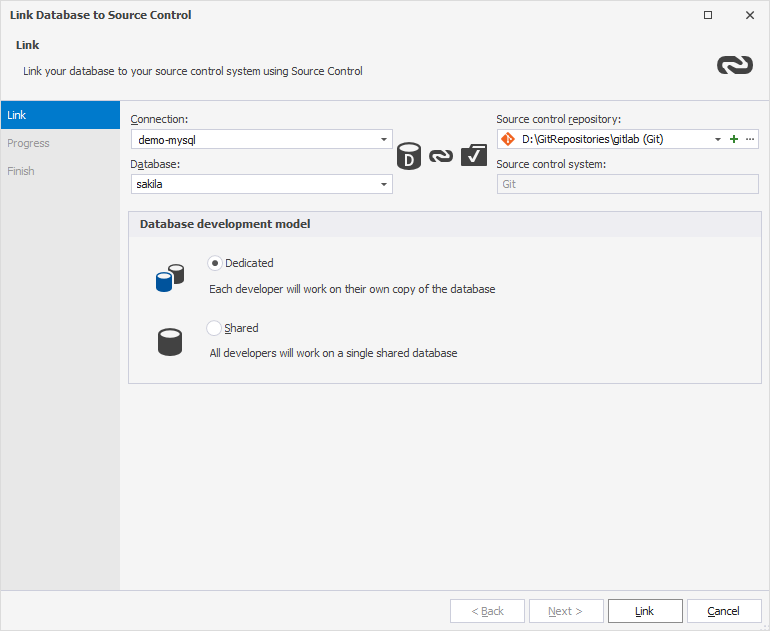
4. In the Link Database to Source Control dialog, select a database development model:shared or dedicated.
5. Click Link to establish the connection between the database and repository.
The Refresh progress window opens automatically, showing the stages of the refresh operation.
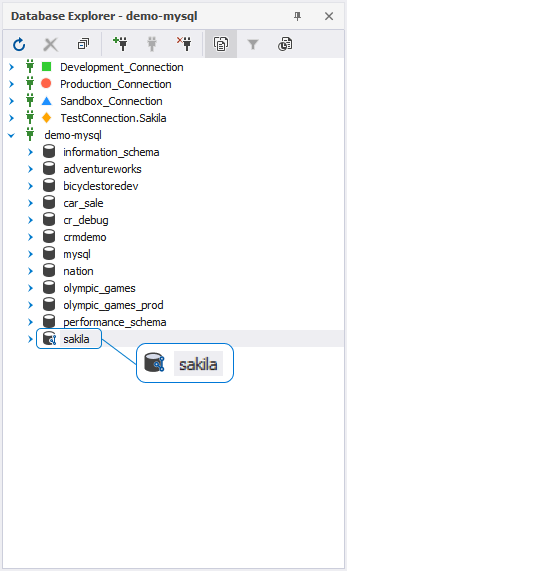
The linked database gets the following icon in Database Explorer:
Step 4: After linking a database to the GitLab repository
If you are the first person to link this database, add the database objects to source control in an ‘initial commit’: go to the Local changes section, select the objects, and click Commit. For more information, see Commit changes.
If you linked a database that is already in source control, update your database to the latest version: go to the Remote changes section, select the objects, and click Get Latest, which is available only in the dedicated model. For more details, see Get the latest version.