Create subqueries visually
A subquery is a SELECT query nested inside another SELECT, INSERT, or UPDATE statement. Subqueries allow you to filter, calculate, or retrieve intermediate results within a larger query.
You can use subqueries in various clauses, including WHERE, FROM, and SELECT. In this article, you’ll learn how to create subqueries visually in Query Builder without writing SQL manually.
To illustrate the process, this guide includes scenarios based on two sample tables: dept and emp. The full script for creating and populating these tables is provided below.
-- Create the dept table
CREATE TABLE dept (
deptno decimal(2, 0) PRIMARY KEY -- "Department ID"
,dname varchar (14) DEFAULT NULL -- "Name of the department"
,loc varchar(13) DEFAULT NULL -- "City where the department is located"
)
-- Create the emp table
CREATE TABLE emp (
empno decimal(4, 0) PRIMARY KEY -- "Employee ID"
,ename varchar(10) DEFAULT NULL -- "Name"
,job varchar(9) DEFAULT NULL -- "Job title"
,mgr decimal(4, 0) DEFAULT NULL -- "Manager ID"
,hiredate date DEFAULT NULL -- "Hire date"
,sal decimal(7, 2) DEFAULT NULL -- "Salary"
,comm decimal(7, 2) DEFAULT NULL -- "Bonus"
,deptno decimal(2, 0) DEFAULT NULL -- "Department ID"
);
-- Create the foreign key for the emp table
ALTER TABLE emp
ADD CONSTRAINT FK_emp_deptno FOREIGN KEY (deptno)
REFERENCES dept (deptno);
-- Populate the dept table with data
INSERT INTO dept VALUES ('10','ACCOUNTING','NEW YORK');
INSERT INTO dept VALUES ('20','RESEARCH','DALLAS');
INSERT INTO dept VALUES ('30','SALES','CHICAGO');
INSERT INTO dept VALUES ('40','OPERATIONS','BOSTON');
-- Populate the emp table with data
INSERT INTO emp VALUES ('7369','SMITH','CLERK','7902','2020-12-17','800.00',NULL,'20');
INSERT INTO emp VALUES ('7499','ALLEN','SALESMAN','7698','2019-02-20','1600.00','300.00','30');
INSERT INTO emp VALUES ('7521','WARD','SALESMAN','7698','2020-02-22','1250.00','500.00','30');
INSERT INTO emp VALUES ('7566','JONES','MANAGER','7839','2021-04-02','2975.00',NULL,'20');
INSERT INTO emp VALUES ('7654','MARTIN','SALESMAN','7698','2018-09-28','1250.00','1400.00','30');
INSERT INTO emp VALUES ('7698','BLAKE','MANAGER','7839','2015-05-01','2850.00',NULL,'30');
INSERT INTO emp VALUES ('7782','CLARK','MANAGER','7839','2017-06-09','2450.00',NULL,'10');
INSERT INTO emp VALUES ('7788','SCOTT','ANALYST','7566','2020-12-09','3000.00',NULL,'20');
INSERT INTO emp VALUES ('7839','KING','PRESIDENT',NULL,'2014-11-17','5000.00',NULL,'10');
INSERT INTO emp VALUES ('7844','TURNER','SALESMAN','7698','2020-09-08','1500.00','0.00','30');
INSERT INTO emp VALUES ('7876','ADAMS','CLERK','7788','2018-01-12','1100.00',NULL,'20');
INSERT INTO emp VALUES ('7900','JAMES','CLERK','7698','2019-12-03','950.00',NULL,'30');
INSERT INTO emp VALUES ('7902','FORD','ANALYST','7566','2020-12-03','3000.00',NULL,'20');
INSERT INTO emp VALUES ('7934','MILLER','CLERK','7782','2021-01-23','1300.00',NULL,'10');
Create a subquery as an unnamed query in the WHERE clause
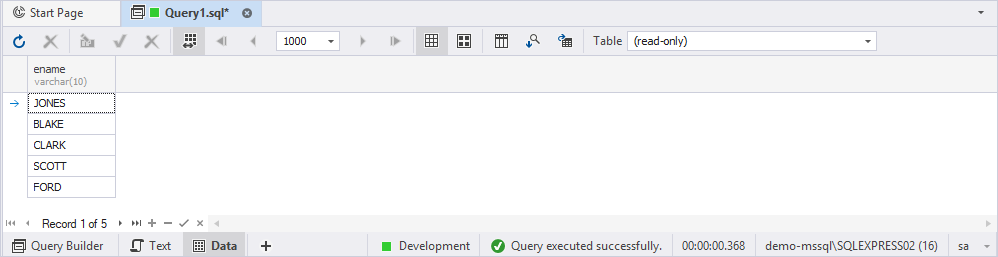
Scenario: Retrieve the names of middle managers from the emp table.
To create a subquery inside the WHERE clause:
1. In Database Explorer, right-click the emp table and select Send to > Query Builder.
2. Rename the table alias to e1.
3. Select the checkbox for the ename column.
The ename column is now displayed on the Selection tab.
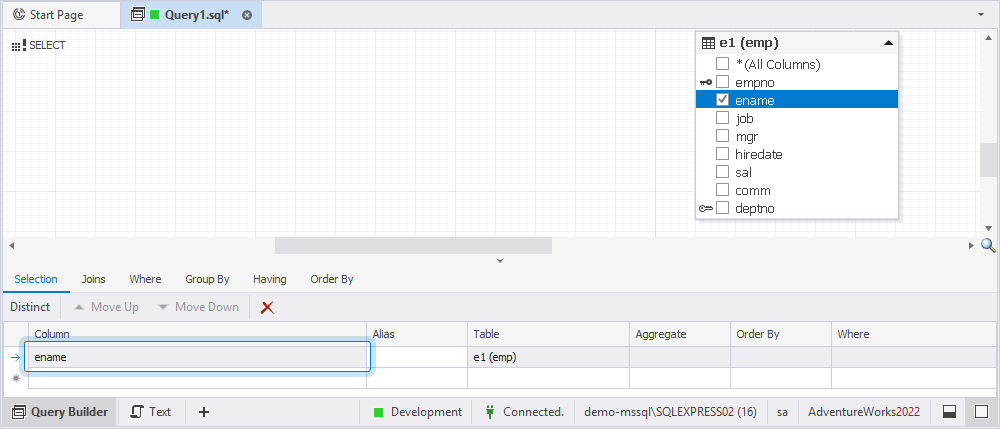
4. Switch to the Where tab to specify the filter condition.
5. Click ![]() and complete the following:
and complete the following:
-
Click the enter table name placeholder and select the mgr column from the e1 table.
-
Choose the
INoperator. -
Click the enter a value placeholder and click
 to define a subquery as a filter.
to define a subquery as a filter.
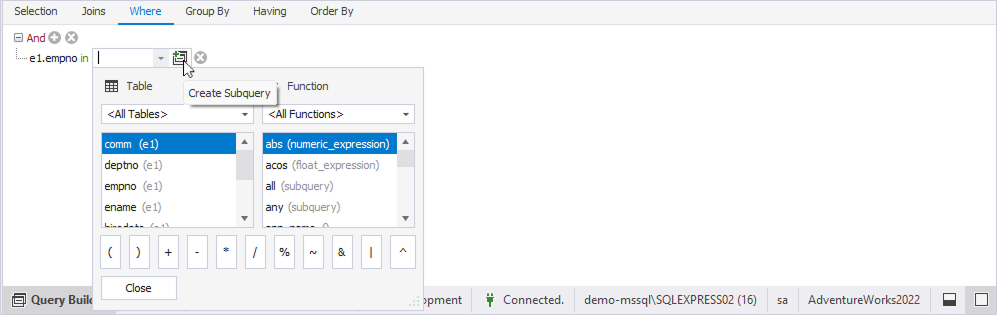
The Query Builder diagram now shows two tabs:
- Root Query – Represents the main query.
- Unnamed Query – Represents the subquery.
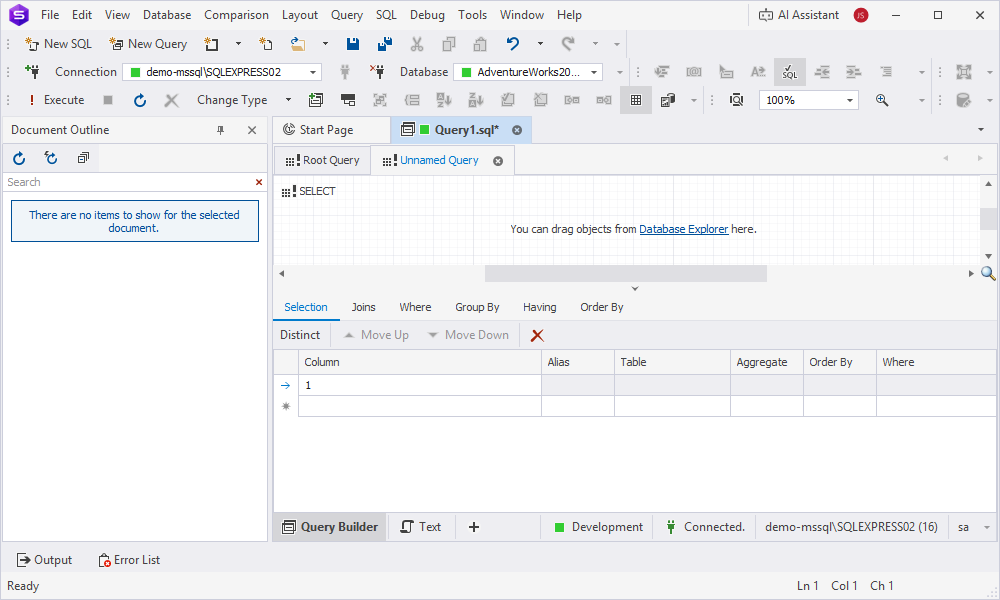
6. Switch to the Unnamed Query tab and drag the emp table from Database Explorer to the diagram.
7. On the Unnamed Query tab:
- Drag the emp table from Database Explorer.
- Rename the alias to e2.
- Select the checkbox next to the mgr column.
Note
Clear the checkbox next to the empno column. Subqueries that are not introduced with
EXISTSmust return only one column. Otherwise, the database engine returns the following error:Only one expression can be specified in the select list when the subquery is not introduced with EXISTS.
8. Optional: To preview the query, click Text in the bottom panel of the Query Builder document.
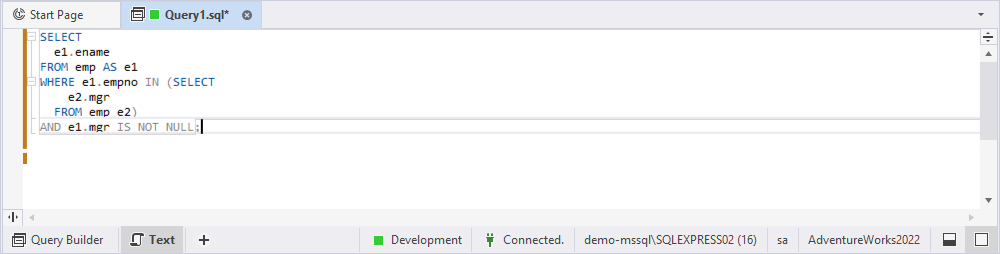
9. Click Execute or press F5 to run the query.
Create a subquery using Wrap to Subquery
You can use the Wrap to Subquery command to include a table along with its JOINs, conditions, and subqueries into a subquery. To do this, ensure you select the entire diagram area – not just an individual table.
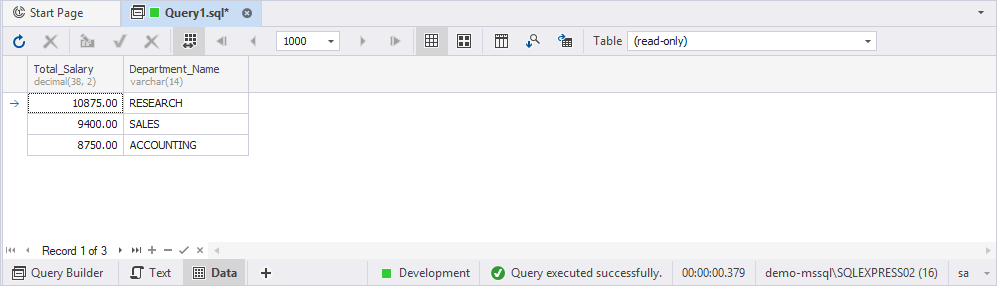
Scenario: Calculate the total salary for each department, filter for departments where the total exceeds 8000, and sort the results in descending order. The output should include the department name and the total salary.
To solve this scenario, use a subquery in the FROM clause. The subquery should include JOIN, GROUP BY, HAVING, and ORDER BY clauses.
To create a subquery:
1. In Database Explorer, press and hold Ctrl, then select the dept and emp tables.
2. Right-click the selection and select Send to > Query Builder.
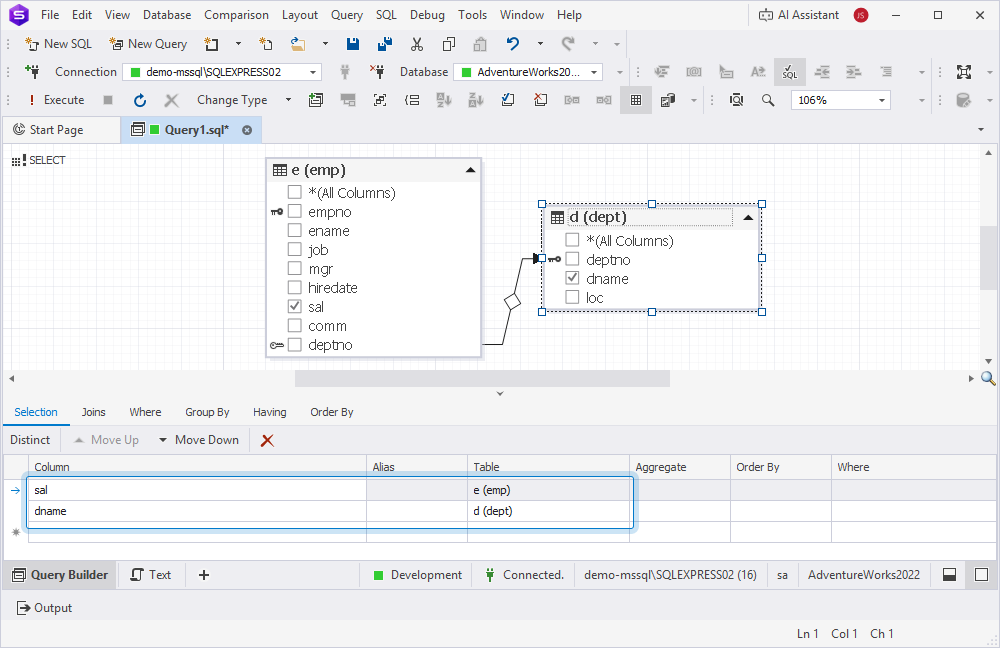
3. On the Query Builder diagram:
- Rename the table aliases:
- For the emp table, enter e.
- For the dept table, enter d.
- Select the checkboxes next to the following columns:
d.dname(department name)e.sal(salary)
The selected columns appear on the Selection tab.
4. On the Query Builder toolbar, click ![]() to convert the diagram into a subquery.
to convert the diagram into a subquery.
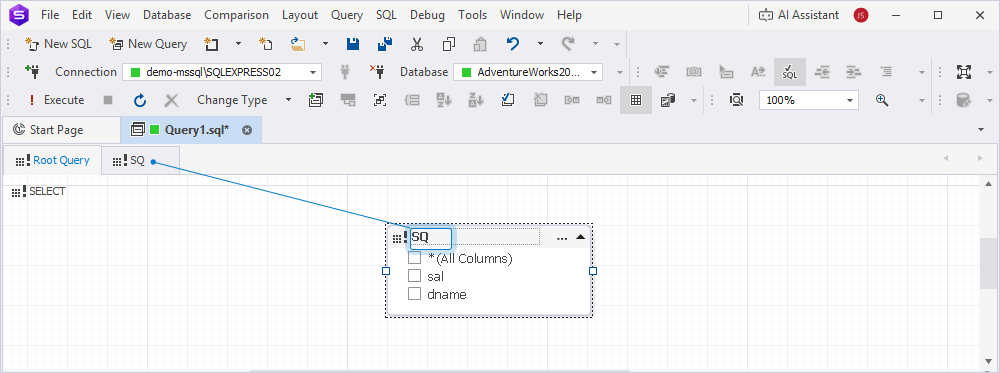
The Query Builder now displays two tabs:
- Root Query – Represents the main query.
- SubQuery – Represents the subquery.
On the Root Query tab, the icon on the table header will change to ![]() indicating that the subquery was added to the query.
indicating that the subquery was added to the query.
5. On the Root Query tab:
- Double-click the subquery header and rename the alias (for example,
salary_summary). - Select the checkboxes next to the dname and sal columns.
6. On the Selection tab:
- For the dname column:
- Double-click the Alias field and enter Department_Name.
- For the sal column:
- Double-click the Alias field and enter Total_Salary.
- Double-click the Aggregate field and select sum.
- Double-click the Order By field and choose Descending.
- Double-click the Where field and enter >8000.
These settings are also reflected in the column boxes on the diagram.
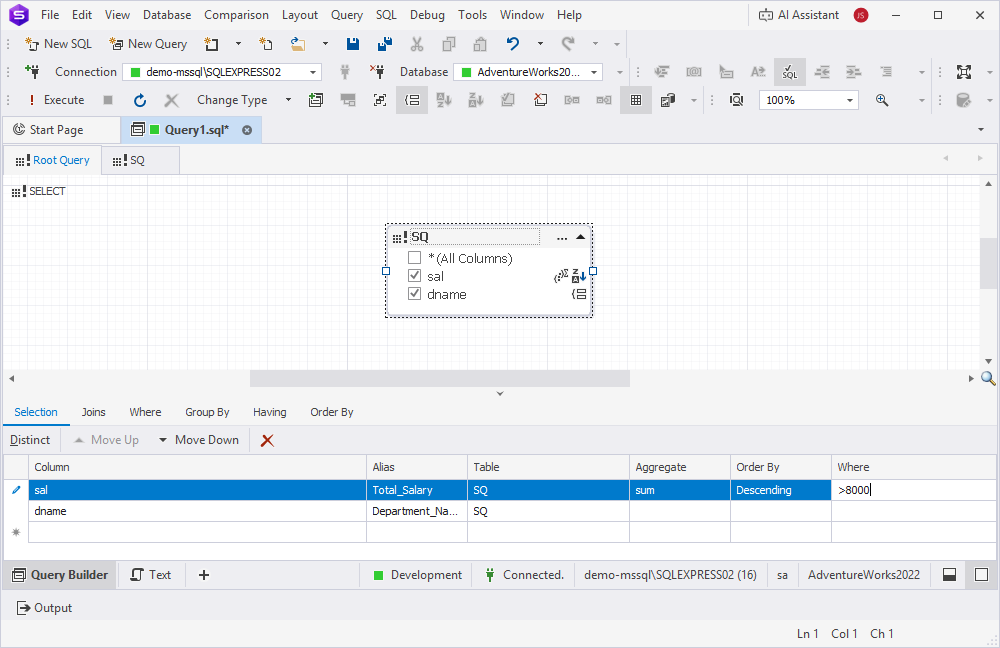
7. Optional: To preview the query, click Text in the bottom panel of the Query Builder document.
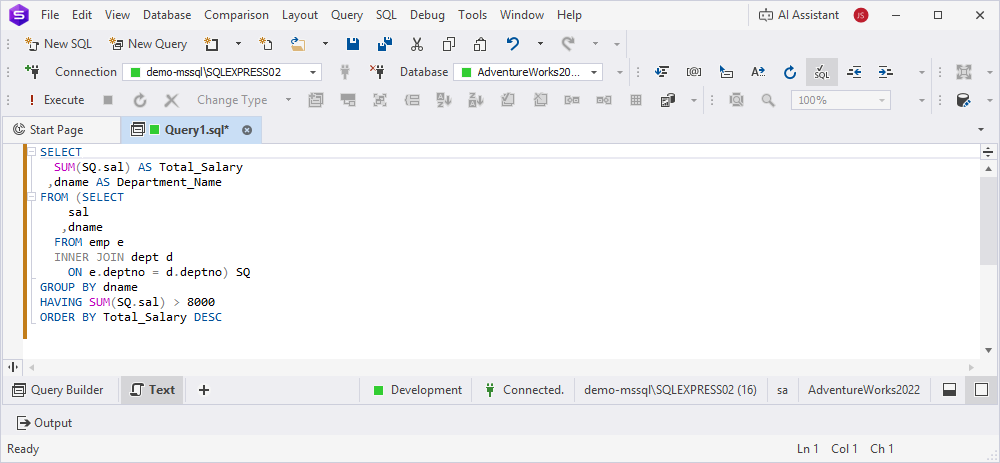
8. Click Execute or press F5 to run the query.
This retrieves the data about departments where the total salary is higher than 8000 and sort it in descending order.