Working with Self-Referencing Tables in Master-Detail Browser
This topic explains how to work with self-referencing tables in Master-Detail Browser.
Self-referencing table is a table that is a parent and a dependent in the same referential constraint, i.e. a foreign key constraint can reference columns within the same table in such tables.
The example specified below shows how to view data in a self-referencing table regarding available relations between columns using Master-Detail Browser.
Prerequisites
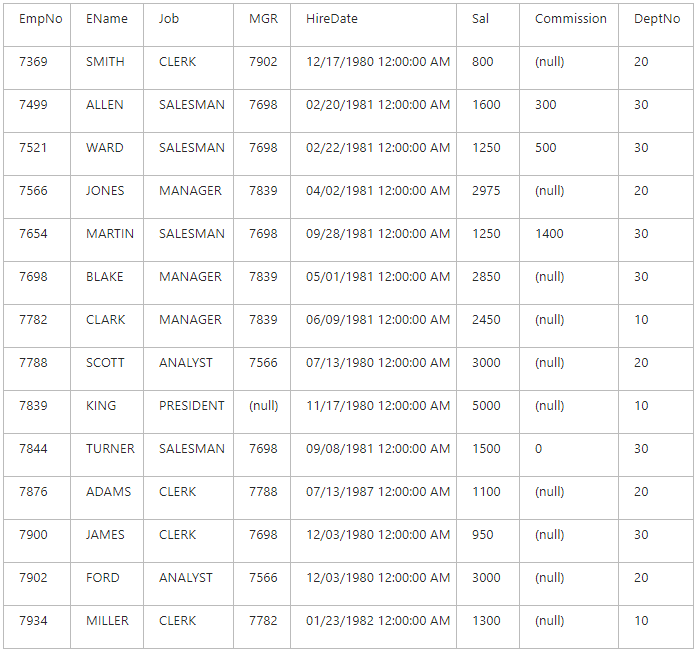
To perform the steps described in the Viewing Data in a Self-Referencing Table part of this topic, you will need a self-referencing table itself. Below is an example of such table (the Employees table) and it will be used in the Viewing Data in a Self-Referencing Table section as a sample table:
Viewing Data in a Self-Referencing Table
Task: it is required to view all employees regarding the levels of company hierarchy using the data available in the sample Employees table.
Solution: because the manager is also an employee, there is a relationship from the MGR column to the EmpNo column. The EmpNo column contains identification number of all employees, and the MGR column contains the identification number of the manager a person subordinates to (you see, the company president has (null) in the MGR column, as he doesn’t subordinate to anyone). Now, as you’ve understood the relationship between these columns, you can perform the following steps to solve the task specified above using Fusion for MySQL Master-Detail Browser:
- On the Fusion menu, click Master-Detail Browser. An empty Master-Detail Browser document will open.
- Drag-and-drop the Employees table you’ve created onto the designer surface.
-
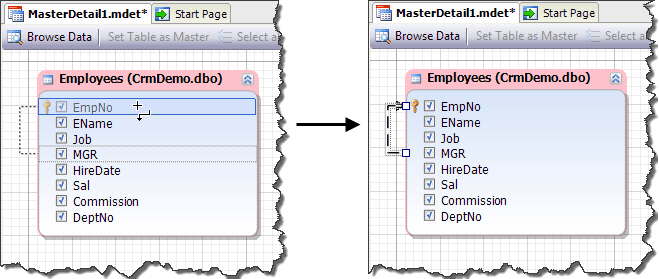
Create a relationship between the MGR and EmpNo columns by selecting the MGR column and dragging it to the EmpNo column. An arrow indicating the relationship will be displayed on the diagram:
Note
There is no foreign key in this table, but if there is one and a relation between columns was established earlier, it’s displayed on the diagram after dropping the table onto it.
- Click the Browse Data button.
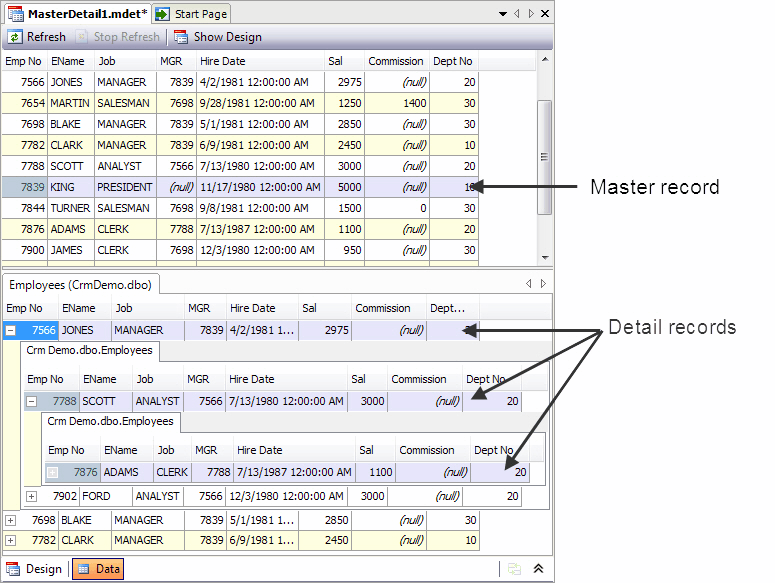
- In the Data view that opened, select the row with PRESIDENT specified in the Job column in the upper part of the view, and click + near each detail record in the lower part of the view to see the next level of company hierarchy and the employees belonging there: