Integrate SQL Formatter into DevOps
SQL Formatter built into dbForge Studio for SQL Server can be integrated in the DevOps process using the PowerShell cmdlets. They can help format scripts for creating and updating a database before they get into a NuGet package.
Format scripts in the CI process
In database development, Continuous Integration (CI) automates the building and testing process each time the development team modifies the database project scripts. This helps quickly detect defects and instantly notify developers about the changes made.
The Database CI involves the following stages:
- Development: Changes are made to the database project schema.
- Version Control: Developers commit the changes to the version control system.
- Build: The database is created from .sql scripts.
- Unit Test: The database is tested using unit tests.
- Publish: An artifact with the database changes, such as a NuGet package, is published.
dbForge Studio for SQL Server can be involved in the automated Continuous Integration (CI) process at the development stage. The PowerShell Invoke-DevartFormatScript cmdlet is required to automate the formatting of scripts to update or create a database according to company standards before sending the scripts into a NuGet package. The script invokes the Invoke-DevartFormatScript cmdlet, which initiates the formatting functionality of dbForge Studio. You can format the entire folder with multiple .sql files or a single .sql file using predefined or custom formatting profiles.
In this PowerShell script, you need to specify only a path to the .sql file or folder with .sql files you want to format and a formatting profile you want to use.
Prerequisites
- Install PowerShell version 3.0 or later.
- Install dbForge DevOps Automation for SQL Server.
- Prepare SQL files you want to format.
Note
PowerShell is installed on Windows 8, 8.1, 10, and 11 by default. For other versions, download PowerShell from the official Microsoft Download Center.
Tip
To check the current version of PowerShell, open WindowsPowerShell ISE and run the
$PSVersionTable.PSVersioncommand. The Major column will display the version installed on your computer.
Install dbForge DevOps Automation PowerShell for SQL Server
dbForge DevOps Automation for SQL Server is supplied as a part of dbForge SQL Tools (Professional version) and includes dbForge DevOps Automation PowerShell for SQL Server.
To install dbForge DevOps Automation PowerShell for SQL Server:
1. Download the product from the Devart website.
2. Run the installer and follow the instructions in the Setup wizard.
After the installation is complete, the Devart.DbForge.DevOpsAutomation.SqlServer module appears in the Commands > Modules list in Windows PowerShell ISE.
Use predefined formatting profiles
dbForge Studio for SQL Server supports the following predefined formatting profiles:
- Collapsed
- Commas before
- Compact
- Default
- Extended
- Indented
- MSDN SQL
- Right aligned
- Stack compact
You can also create a custom formatting profile for later use.
Format an entire folder with files
1. Run Windows PowerShell ISE as an administrator.
2. In Windows PowerShell ISE, run the following script:
# Defining variables
$ScriptFolder = "D:\ScriptFolder\"
$FormattedFiles = "D:\FormattedFiles\"
$FormatProfile = "C:\Users\Username\AppData\Roaming\Devart\dbForge Studio for SQL Server\FormatProfiles\Custom profile.xml"
# Formatting scripts
Write-Host "Formatting a script folder..." -ForegroundColor Cyan
$Result = Invoke-DevartFormatScript -Source $ScriptFolder -FileExtension *.sql -IncludeSubfolders -Output $FormattedFiles -Profile $FormatProfile
where:
D:\ScriptFolder\is the path to the folder that stores the files you want to format.D:\FormattedFiles\is the path to the folder that will store the formatted files.C:\Users\Username\AppData\Roaming\Devart\dbForge Studio for SQL Server\FormatProfiles\Custom profile.xmlis the default path to the file with formatting settings. To use a different location, specify the correct file path.
If formatting completes successfully, the result may be as follows:
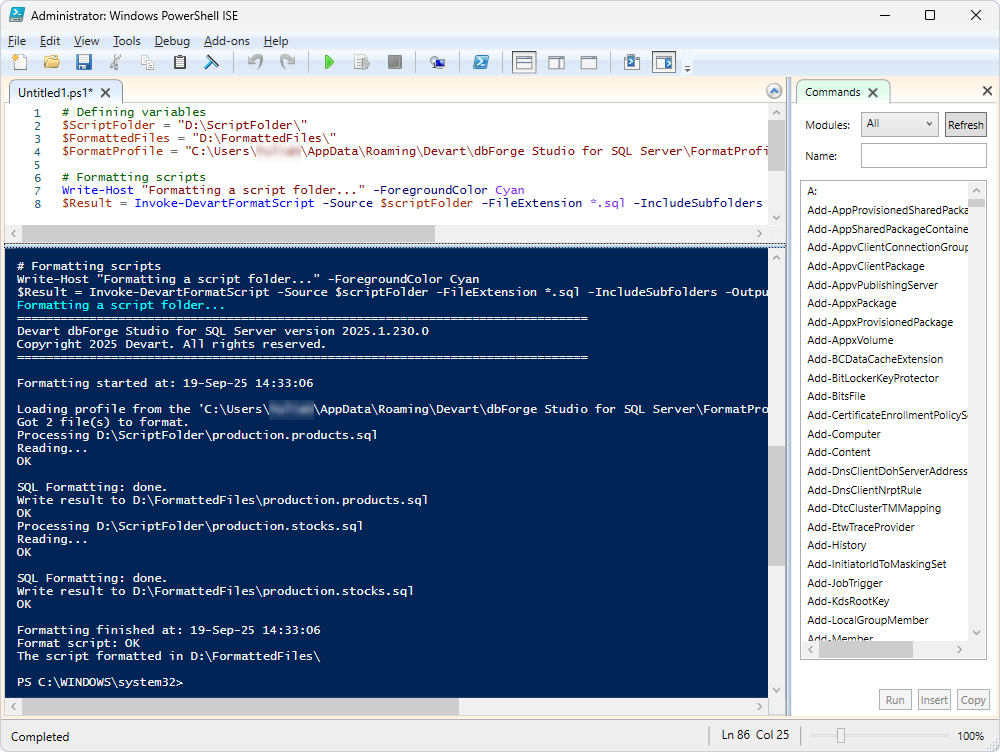
Format a single file
1. Run Windows PowerShell ISE as an administrator.
2. In Windows PowerShell ISE, run the following script:
# Defining variables
$File = "D:\FormatSQL\uspGetBillOfMaterials.sql"
$FormattedFiles = "D:\FormattedFiles\formatted_uspGetBillOfMaterials.sql"
$FormatProfile = "C:\Users\Username\AppData\Roaming\Devart\dbForge Studio for SQL Server\FormatProfiles\Custom profile.xml"
# Formatting script
Write-Host "Formatting a script ..." -ForegroundColor Cyan
$Result = Invoke-DevartFormatScript -Source $File -FileExtension *.sql -IncludeSubfolders -Output $FormattedFiles -Profile $FormatProfile
where:
D:\FormatSQL\uspGetBillOfMaterials.sqlis the path to the file you want to format.D:\FormattedFiles\formatted_uspGetBillOfMaterials.sqlis the path to the formatted file.C:\Users\Username\AppData\Roaming\Devart\dbForge Studio for SQL Server\FormatProfiles\Custom profile.xmlis the default path to the file with formatting settings. To use a different location, specify the correct file path.
Note
You must specify the name of the formatted file in the script.
Parameters used in the scripts
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
-Source |
Specifies the SQL file or folder containing the files to be formatted. |
-FileExtension |
Defines the file extension of the source files to be formatted. |
-IncludeSubfolders |
Includes the current directory and all subdirectories when searching for files. |
-Output |
Specifies the output file or folder where formatted results will be saved. If omitted, results overwrite the source files. |
-Profile |
Specifies the path to a configuration file containing formatting settings. |
Note
If the
-Profileparameter is not specified, the active formatting profile is used. You can check which formatting profile is active in the Options dialog under Text Editor > Formatting > Profiles.