Export SQL Server data to Microsoft Excel
The XLS format is designed to organize spreadsheet data, enabling users to work with rows, columns, and multiple worksheets in a single file.
Note
If Microsoft Office is not installed on your computer, install the Open XML SDK 2.5 for Microsoft Office to export data to Excel spreadsheets.
To export data to XLS:
1. Open the Data Export wizard in one of these ways:
-
In the Data Editor grid, select the specific data or the entire grid you want to export.
-
On the top toolbar, click
 .
.
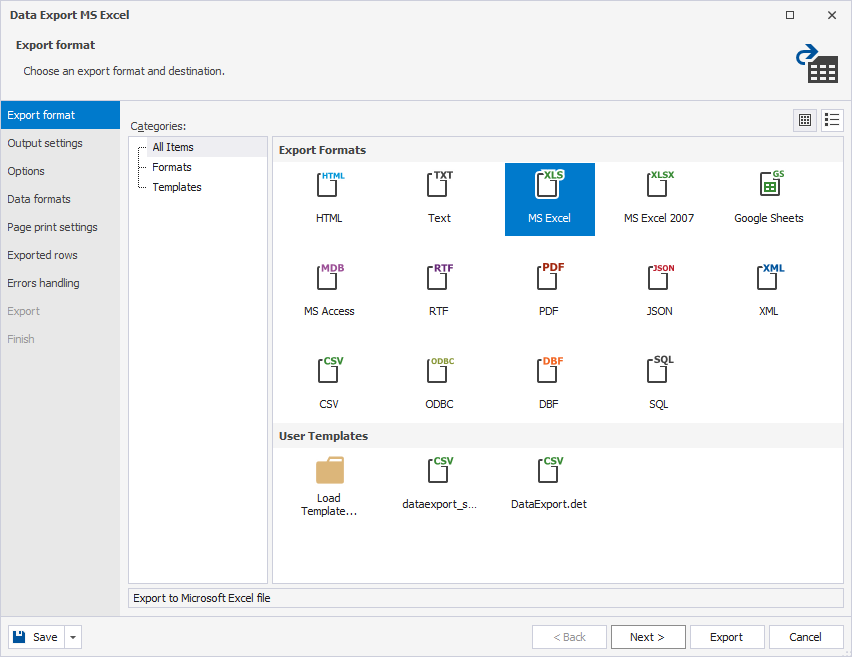
2. On the Export format page of the Data Export wizard, do one of the following:
- Under Export Formats, select MS Excel.
- Under User Templates, load export options from a template file if you saved it previously.
Note
The export of data to Microsoft Excel 2003 using an ODBC provider is limited to 65,536 rows.
If you export data to Excel without using an ODBC provider, the only limitation is the available disk space.
3. On the Output settings page, configure how the exported data will be saved:
-
Export data into separated files – Create a separate output file for each selected table or view. You’ll need to specify the full path to the destination folder where the files will be saved. If the folder does not exist, dbForge Studio will prompt you to create it. Click Yes to continue.
-
Export data into single file – Combine all selected tables or views into one output file. You’ll need to specify the full path to the file and its name.
Note
When you export data from a single table, the Export data into single file option is selected by default, and the Export data into separated files option is unavailable.
When you export data from multiple tables, the Export data into separated files option is selected by default. If needed, switch to the Export data into single file option.
Additional options
-
Append timestamp to the file name (selected by default) – Add the current date and time to the file name. To exclude the timestamp, clear the checkbox.
-
Auto delete old files – Remove exported files older than a specified number of days. Set the number of days, and define the maximum number of files to keep–files exceeding this limit will also be deleted.
-
Use compression (Zip) – Create a compressed archive of the exported files. Then, choose a compression level: No Compression, Best Speed, Fast, Default, Good, or Maximum. You can also add a comment and protect the archive with AES128 or AES256 encryption by setting a decryption password.
-
Exported files preview – Review the files that will be generated.
4. On the Options page, configure the table grid settings for the exported data, including text and background colors, fonts for Headers and Rows, and the width and color of Borders.
A live preview of your settings appears in the Preview section.
5. On the Data formats page, configure the export settings:
- On the Columns tab, select the columns to export. If needed, review or edit their aliases and data types.
- On the Formats tab, customize the default export format for the following data types: Date, Time, Date Time, Currency, Float, Integer, Boolean, and Null String.
6. On the Page print settings page, configure the page size, orientation, margins, header and footer text, including the option to repeat the table header.
A live preview of your settings appears in the Preview section.
7. On the Exported rows page, specify the data range to be exported:
-
Export all rows – Export the entire dataset.
-
Export only the selected rows – Export the rows currently selected in the data grid.
-
Export a specified range of rows – Specify the starting and ending row numbers to export a custom range.
Note
The Export only the selected rows option is available only when you export rows directly from the results grid in Data Editor.
8. On the Errors handling page, define how the export process should respond to errors and how they should be logged:
-
Abort at the first error – Stop the export immediately when the first error occurs.
-
Prompt a user for an action – Pause the export and prompt the user to choose how to proceed when an error occurs.
-
Ignore all errors – Continue the export process, skipping any errors without interruption.
Tip
To reuse your export configuration, click Save Template in the bottom-left corner of the wizard.
9. Click Export.
The Finish page appears, indicating whether the data export completed successfully or failed. From this page, you can:
- Open the exported file or folder.
- Start another export operation.
- View the log file.
- Click Finish to close the wizard.