Create an encrypted database backup
This topic describes how to create a database backup with encryption in SQL Server using the Backup wizard.
Overview
You can encrypt the data while creating a database backup. To do this, specify:
- An encryption algorithm. The supported algorithms are: AES 128, AES 192, AES 256, and Triple DES.
- An encryptor, a certificate, or an asymmetric key, to protect the encryption key.
Note
It is recommended that you back up your certificate or asymmetric key and store them in a different location from the backup you encrypted.
If the certificate or asymmetric key is unavailable or you don’t have access to it, you can’t restore the backup.
Limitations
The following limitations apply to backups with encryption.
- Backup encryption is supported starting with SQL Server 2014.
- SQL Server Express doesn’t support encryption during backups.
- Encrypted backups are not readable by SQL Server versions earlier than 2014.
- Encrypted backups can be restored only on the server that has the same certificate or asymmetric key used for encryption.
- The certificate used for encryption must be stored in the master database.
- Encrypted backups cannot be appended to an existing backup set.
Permissions
The account must have specific permissions to use the certificates or keys for encryption and to perform backup operations.
| Object | Permissions |
|---|---|
| Database backup | The db_backupoperator database-level role. |
| Certificate or asymmetric key |
|
| Database master key (DMK) | The CONTROL permission on the database that owns the master key (usually it is the master database). |
Prerequisites
- Create a database master key (DMK) in the master database.
- Create a certificate or asymmetric key.
Back up a database with encryption
You can back up a database by using the Backup wizard or T-SQL.
Use the Backup wizard
To back up a database with encryption:
1. Follow the steps described in Create a full database backup.
2. On the Backup options page, select Encrypt backup, then specify encryption options:
- Algorithm: Select an encryption algorithm. The supported encryption algorithms are: AES 128, AES 192, AES 256, and Triple DES.
- Certificate or Asymmetric key: Select a certificate or asymmetric key to protect the encryption key.
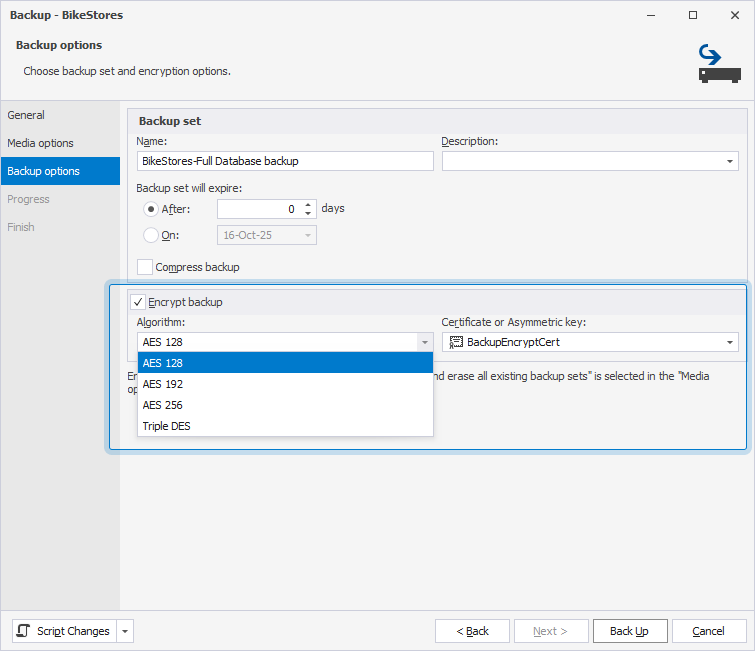
3. Click Back Up.
Use T-SQL
To back up a database with encryption:
1. Open the SQL Editor.
2. Enter the following BACKUP DATABASE statement, and replace the parameters with your actual values.
BACKUP DATABASE { database_name }
TO DISK = N'C:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\<instance_name>\MSSQL\Backup\file_name.bak'
WITH
COMPRESSION,
ENCRYPTION
(
ALGORITHM = { encryption },
SERVER CERTIFICATE = Encryptor_Name | SERVER ASYMMETRIC KEY = Encryptor_Name
),
STATS [= percentage]
GO
where:
database_name– The name of the database you want to back up.C:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\<instance_name>\MSSQL\Backup\file_name.bak– The default path to store the backup file.encryption– The encryption algorithm. The available algorithms are: AES_128, AES_192, AES_256, and TRIPLE_DES_3KEY.Encryptor_Name– The certificate (SERVER CERTIFICATE) and an asymmetric key (SERVER ASYMMETRIC KEY) created in the master database.= percentage– The percentage value indicating the progress of a backup operation. When you specifySTATS = 10, SQL Server prints a message each time 10% of the backup completes. If you omit the percentage value, SQL Server defaults toSTATS = 10.
Note
Starting with SQL Server 2016 (13.x), the TRIPLE_DES_3KEY encryption algorithm is deprecated. For older algorithms (not recommended), set the database compatibility level to 120 or lower.
3. On the SQL toolbar, click Execute or press F5 to run the statement.
Backup wizard options
Media options
The table describes the options available on the Media options page of the Backup wizard.
Overwrite Media
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Back up to the existing media set | Adds your backup to an existing media set, which can contain multiple backup sets. |
| Append to the existing backup set | Adds the new backup to the end of the current backup set. Existing backups are preserved. |
| Overwrite all existing backup sets | Replaces the current contents of the media set with new data. All previous backups on this set will be lost. |
| Check media set name and backup set expiration (checkbox) | Verifies the name and the expiration date of the backup sets. |
| Back up to a new media set and erase all existing backup sets | Creates a new media set, removing all existing backup sets on the media. |
| Media set name and Media set description | Specifies the name and description for the current media set. |
Reliability
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Verify backup when finished | Verifies the backup to ensure it can be read and restored correctly. |
| Perform checksum before writing to media | Adds a checksum for each page to detect corruption during the write operation. |
| Continue on error | Continues a backup operation if an error is encountered. |
Backup options
The table describes the options available on the Backup options page of the Backup wizard.
Backup set
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | Specifies a backup name. |
| Description | Specifies a backup description. |
| Backup set expiration | Specifies when the backup set can be overwritten:
|
| Compress backup | Reduces the size of the backup file, regardless of the server-level default. When selected, new backups are compressed by default. |
For more information on configuring SQL Server backups on a Windows system, see How to Set Up Daily Database Auto Backup in SQL Server.