Compare and sync data with a SQL ODBC Linked Server as the source
The guide covers how to compare data between two databases that reside on separate servers - Oracle and SQL Server.
Tip
The example uses Oracle, but you can connect to any other data source, such as a local database server or a cloud source, or services (Salesforce, Snowflake, etc.). For a complete list of ODBC data connectors, see Devart ODBC Drivers.
Note
The linked server must be created on the local SQL Server instance.
The process of comparing those databases includes:
1. Configuring an ODBC Linked Server.
2. Comparing data between the Oracle and SQL Server databases.
What is an ODBC Linked Server?
ODBC (Open Database Connectivity) is a standard interface that enables applications to access data from different database management systems (DBMSs) using SQL queries.
An ODBC Linked Server uses an ODBC driver to connect to a remote database. After the connection is established, you can run SQL queries against the remote database as if it were local. This eliminates the need to export and import data manually; for example, you can configure an ODBC Linked Server in SQL Server to query an Oracle database directly.
Prerequisites
Configure the Linked Server in SQL Server
1. Open SQL Server Management Studio and connect to the SQL Server instance.
2. In Object Explorer, expand the Server Objects node.
3. Right-click the Linked Servers node and select New Linked Server.
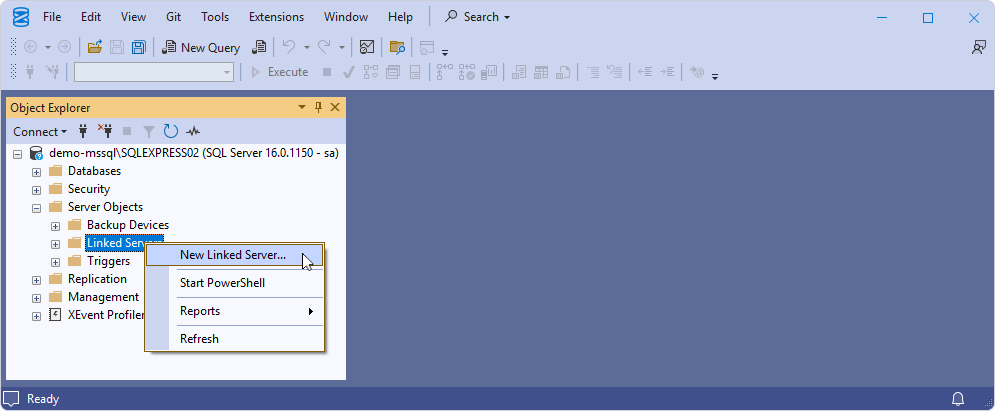
4. In the New Linked Server dialog, provide the linked server configurations:
- In Linked server, enter the linked server name.
- Under Server type, select Other data source.
- In Provider, select Microsoft OLE DB Provider for ODBC Drivers.
- In Data source, enter the Oracle ODBC data source you want to compare with SQL Server.
- In Catalog, enter the Oracle database name.
5. Click OK to save the linked server configurations.
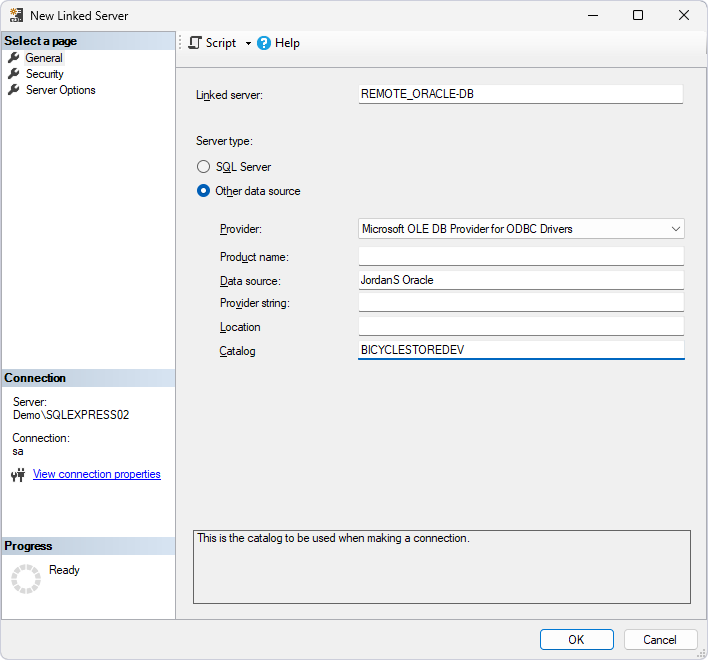
The created linked server with associated database tables appears in Object Explorer.
Compare data between the SQL Server and Oracle databases
Note
A linked server cannot be used as a target because the source cannot be synchronized with the results of a custom query. However, if you create a view that selects data from the linked server source, you can synchronize the data.
Work with linked servers in SQL Server
You can use standard T-SQL statements to query the data from the linked server. Here’s an example of how to retrieve data from a table in the linked database.
SELECT * FROM [<linked_server_name>].[<database_name>].[<schema_name>].[<table_name>];
In SQL Server, object names can include up to four parts.
- The linked server name (
<linked_server_name>) and the table name (<table_name>) are obligatory. - The database name (
<database_name>) and the schema name (<schema_name>) are optional.
Oracle does not have a traditional database concept. To query data from an Oracle table using a linked server in SQL Server, use the following syntax:
SELECT * FROM [<linked_server_name>]..[<schema_name>].[<table_name>];
MySQL uses a different schema concept. To query data from a MySQL table using a linked server in SQL Server, use the following syntax:
SELECT * FROM [<linked_server_name>].[<database_name>]..[<table_name>];
Compare data between databases using a linked server as the source
1. Open dbForge Studio for SQL Server.
2. Run the data comparison.
3. In the New Data Comparison wizard, select the SQL Server database for both the source and target.
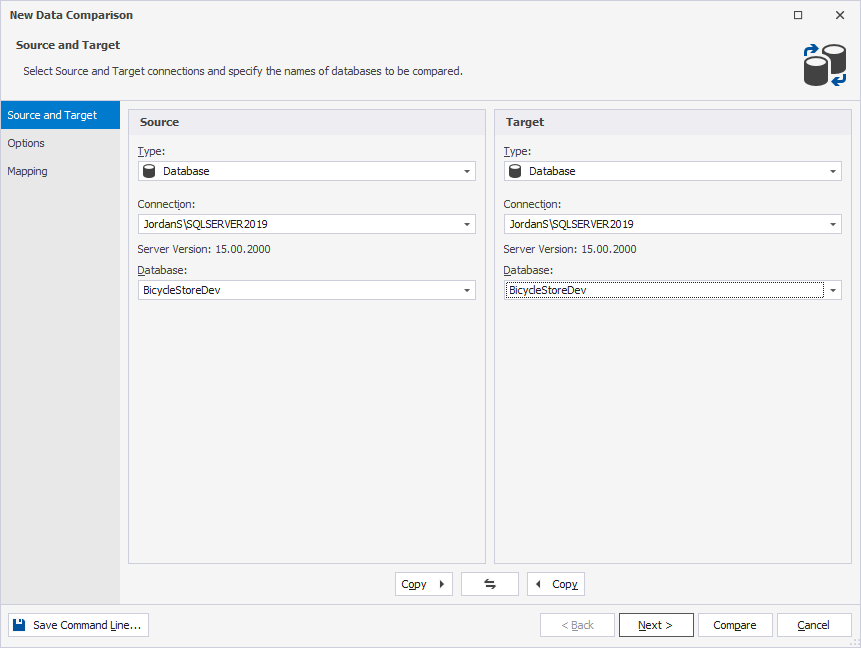
4. On the Mapping page, unmap all the tables.
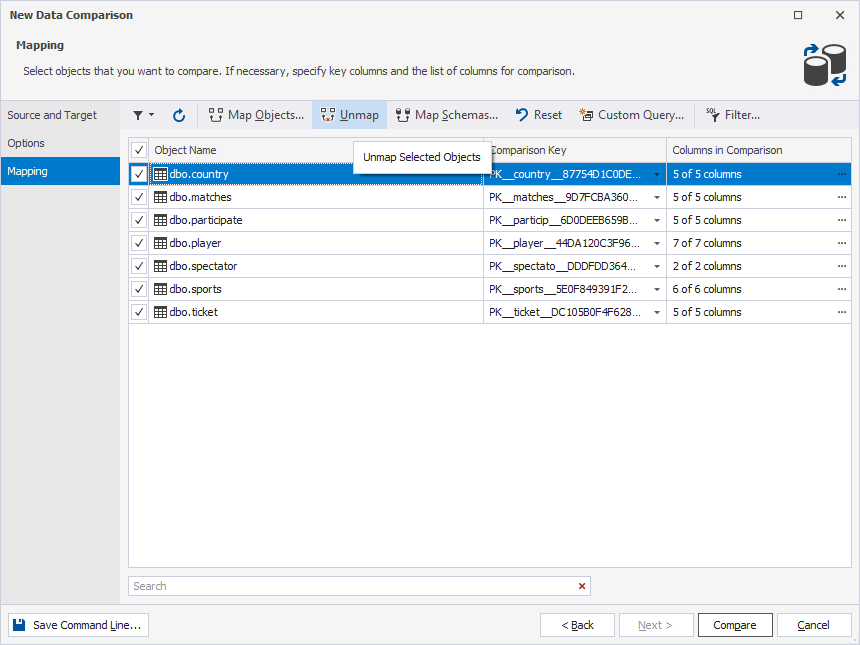
5. Click Custom Query.
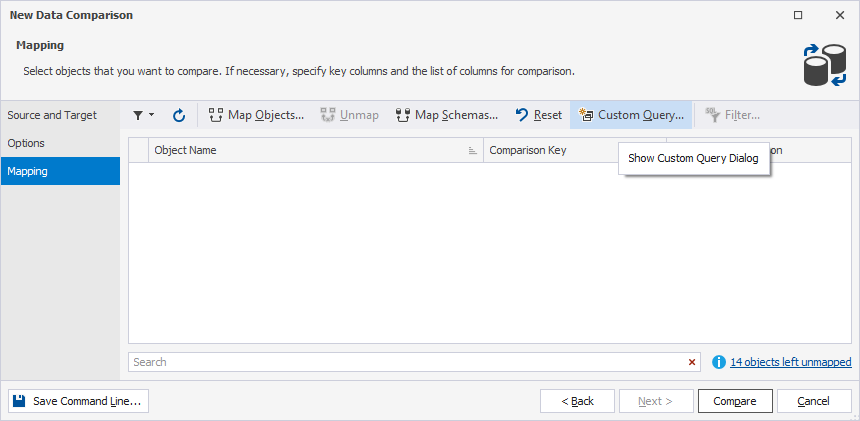
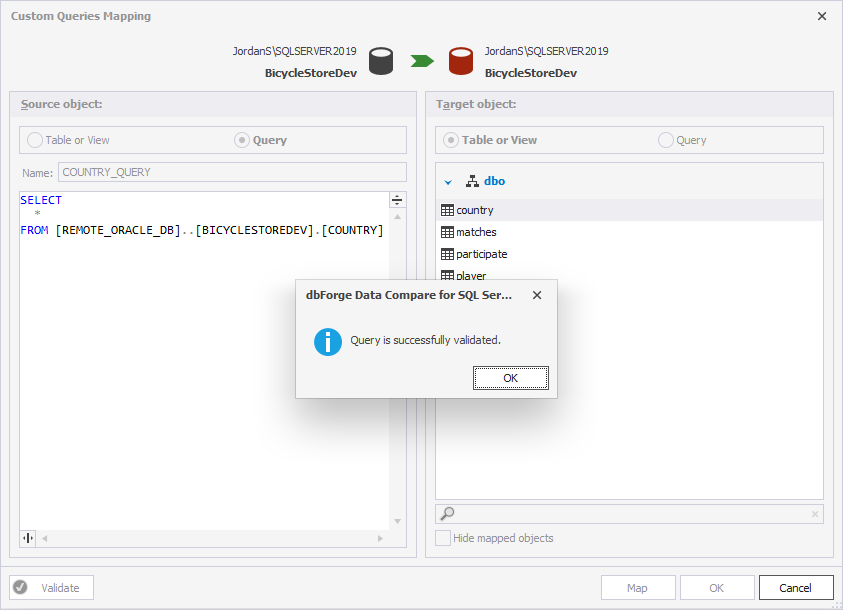
6. Under Source object, select Query and enter the query to retrieve data from the source table you want to compare.
SELECT * FROM [REMOTE_ORACLE_DB]..[BICYCLESTOREDEV].[COUNTRY]
7. Under Target object, select Table or View, then select the target table.
8. Optional: Click Validate to check the mapping settings.
9. Click OK to apply the changes.
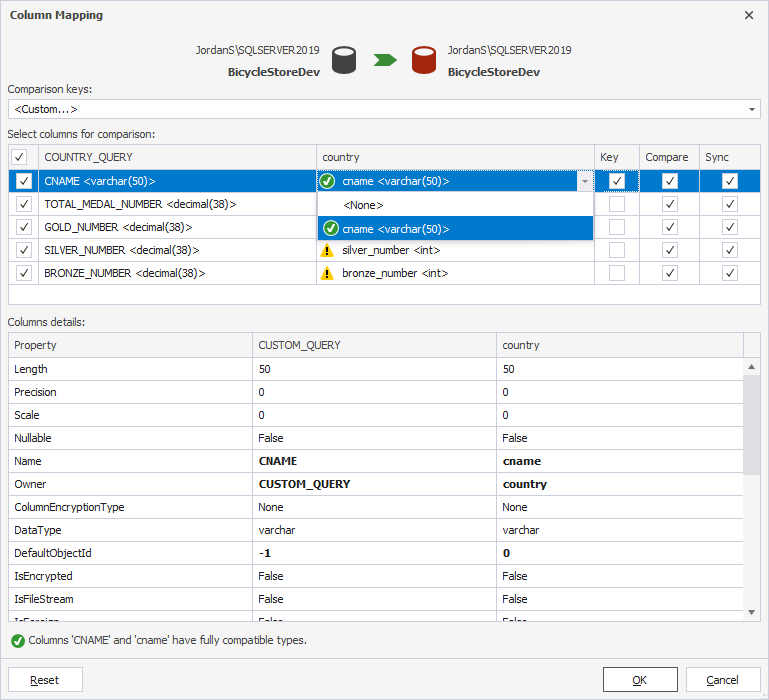
10. Map columns and set a comparison key:
- In the Comparison Key list, select Custom.
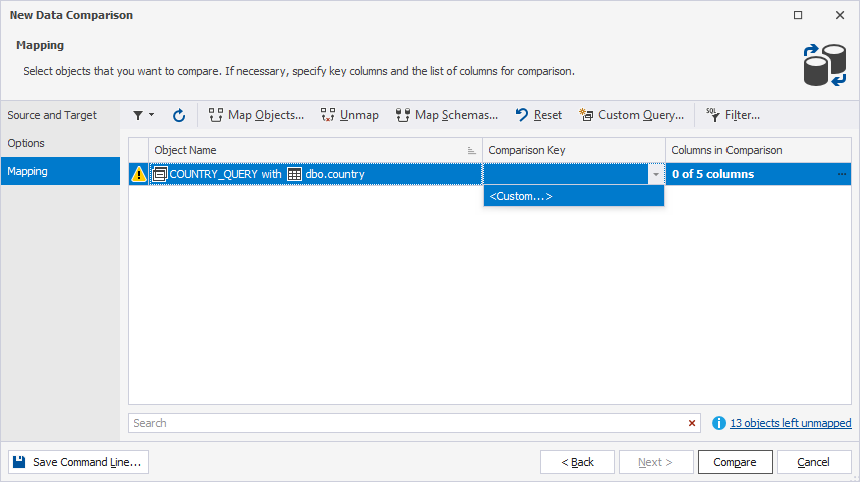
-
In the Column Mapping dialog, map the source and target columns.
-
In the Key column, select the checkbox for the column you want to set a comparison key.
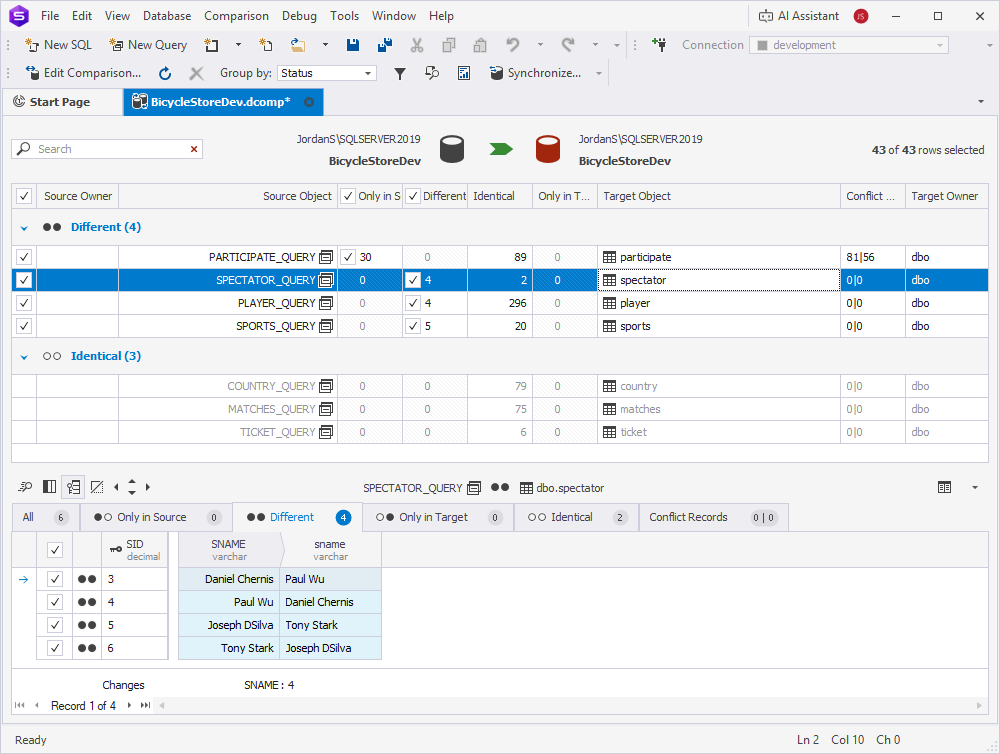
11. Repeat these steps for each table you want to include in the comparison.
12. Click Compare.
Object reference variations
When you connect to different DBMSs through ODBC and Linked Server, there are specific code standards for referencing objects remotely.
To reference objects on a remote server, use the following syntax:
SELECT * FROM [<linked_server_name>].[<database_name>].[<schema_name>].[<object_name>]
However, some DBMSs do not include the DATABASE component (for example, Oracle) or the SCHEMA component (for example, MySQL). In some cases, such as with Salesforce, neither the database nor the schema is included. In these scenarios, object references are modified as follows:
1. Cases without a database:
SELECT * FROM [<linked_server_name>].[].[<schema_name>].[<object_name>]
2. Cases without a schema:
SELECT * FROM [<linked_server_name>].[<database_name>].[].[<object_name>]
3. Cases without a schema and a database:
SELECT * FROM [<linked_server_name>].[].[].[<object_name>]