Command-line Wizard
Data Generator incorporates a built-in Command-line Wizard that allows converting the project data generation options into command-line syntax and saving them as a *.bat file. Later you can use the .bat file to schedule or automate data generation with a script or any task scheduler tool, for example, Windows Task Scheduler.
You can save command-line file settings as a *.bat file in the Command line execution file settings window. To open the window, click Save Command Line in the following wizards:
- Data Generator Project Properties Window
- Data Population Wizard
Options of the Command Line Wizard
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Project File | Specify the data generation template to use. |
| Connection | Specify the connection settings. |
| Password | Specify the server password. It overrides the password specified in the connection. |
| Error Mode | Define the application behavior in case an error is detected. |
| Treat Warning as Error | Specify whether to treat warnings as errors or not. When the option is selected, the further behavior is determined by the Error Mode option. |
| Echo OFF | Disable or enable echoing all commands in the batch file. When enabled, all the text in the batch file is enclosed in the @Echo OFF … @Echo ON command. |
| Keep opened | Set a pause command at the end of the batch file text. The command window will be opened. |
| PowerShell | Generate the & symbol at the beginning of the batch file text. This makes the batch file compatible with PowerShell. |
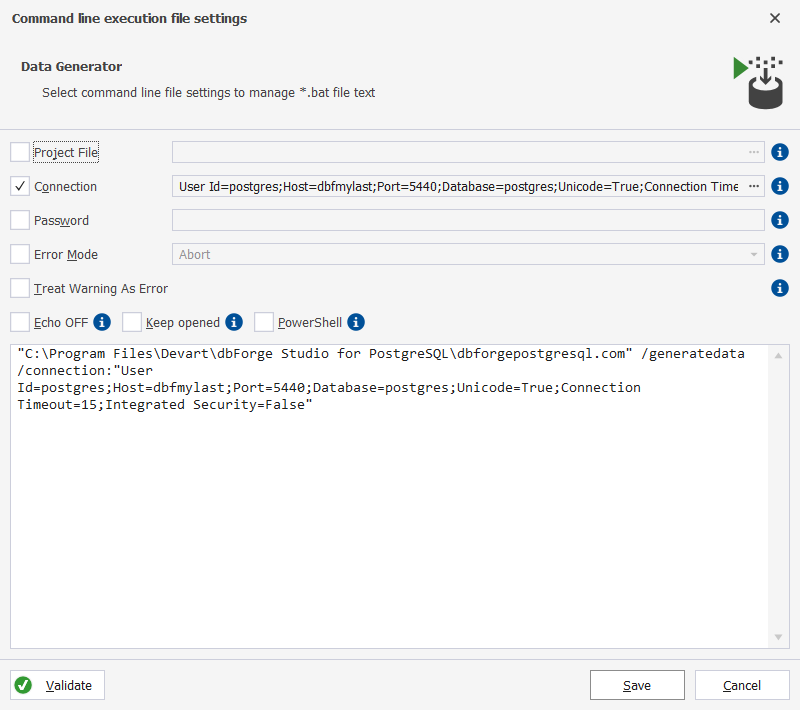
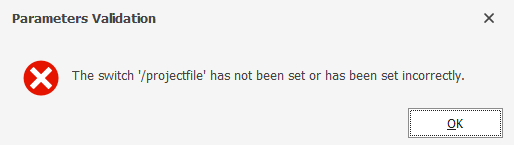
After setting the required options for the script, you can click Validate to check the accuracy of the code.
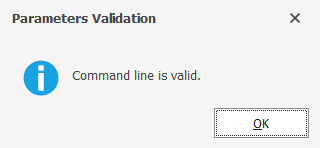
If the syntax is valid, you receive the following message:
Otherwise, the corresponding warning will be displayed:
After validating the code, you can save the script as a *.bat file by clicking Save and specifying a path to its location.