This example shows how to use a stored procedure that executes an INSERT query inside itself and doesn't return any result, for example, like this one:
The script for creating a stored procedure and a table for the SQL Server DBMS is as follows:
CREATE TABLE dbo.Department (
DeptNo int NOT NULL,
DName varchar(14),
Loc varchar(13),
PRIMARY KEY (DeptNo)
)
GO
CREATE PROCEDURE dbo.Department_Insert
@PDeptNo INT,
@PDName VARCHAR(14),
@PLoc VARCHAR(13)
AS
INSERT INTO dbo.Department(DeptNo, DName, Loc) VALUES (@PDeptNo, @PDName, @PLoc);
GO
Create a model and add a new method to it corresponding to the procedure (either at the stage of creation at the Select database objects page of Create Model Wizard, or by dragging the corresponding stored procedure from the Database Explorer window to the diagram area or in the Model Explorer window of an already existing model).
As a result, we will get a method in the model corresponding to the stored procedure:
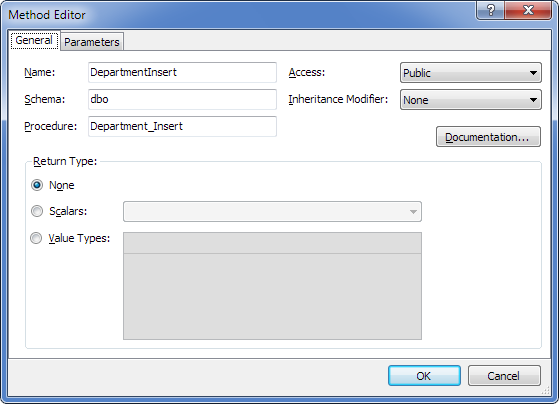
With the following parameters:
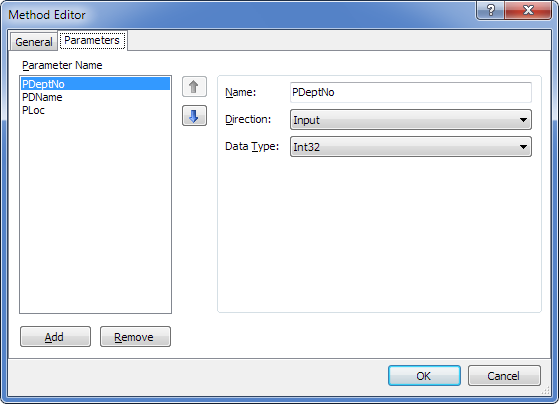
As a result of code generation for the model, the corresponding method will be generated having a signature close to the relevant stored procedure:
C#:
public void DepartmentInsert (System.Nullable<int> PDeptNo, string PDName, string PLoc)
{
DbConnection connection = this.Database.GetDbConnection();
bool needClose = false;
if (connection.State != ConnectionState.Open)
{
connection.Open();
needClose = true;
}
try
{
using (DbCommand cmd = connection.CreateCommand())
{
if (this.Database.GetCommandTimeout().HasValue)
cmd.CommandTimeout = this.Database.GetCommandTimeout().Value;
cmd.CommandType = CommandType.StoredProcedure;
cmd.CommandText = @"dbo.Department_Insert";
DbParameter PDeptNoParameter = cmd.CreateParameter();
PDeptNoParameter.ParameterName = "PDeptNo";
PDeptNoParameter.Direction = ParameterDirection.Input;
if (PDeptNo.HasValue)
{
PDeptNoParameter.Value = PDeptNo.Value;
}
else
{
PDeptNoParameter.DbType = DbType.Int32;
PDeptNoParameter.Size = -1;
PDeptNoParameter.Value = DBNull.Value;
}
cmd.Parameters.Add(PDeptNoParameter);
DbParameter PDNameParameter = cmd.CreateParameter();
PDNameParameter.ParameterName = "PDName";
PDNameParameter.Direction = ParameterDirection.Input;
if (PDName != null)
{
PDNameParameter.Value = PDName;
}
else
{
PDNameParameter.DbType = DbType.String;
PDNameParameter.Size = -1;
PDNameParameter.Value = DBNull.Value;
}
cmd.Parameters.Add(PDNameParameter);
DbParameter PLocParameter = cmd.CreateParameter();
PLocParameter.ParameterName = "PLoc";
PLocParameter.Direction = ParameterDirection.Input;
if (PLoc != null)
{
PLocParameter.Value = PLoc;
}
else
{
PLocParameter.DbType = DbType.String;
PLocParameter.Size = -1;
PLocParameter.Value = DBNull.Value;
}
cmd.Parameters.Add(PLocParameter);
cmd.ExecuteNonQuery();
}
}
finally
{
if (needClose)
connection.Close();
}
}
Now it is possible to use this stored procedure in the application with the help of method wrapper. This allows working with the stored procedure with all possible convenience, as wrapper methods are strongly typed, are found by IntelliSense and have signatures close to the corresponding stored procedures.
 See Also
See Also
|
Stored Function with Scalar Result Stored Procedure and Stored Function With Resultset Stored Procedure with Multiple Resultsets
|