This example shows how to use a stored procedure that executes inside itself a parameterized SELECT query to tables and returns table records that satisfy the query condition as the list of corresponding complex type objects.
The script for creating a stored procedure and a table for the SQL Server DBMS is as follows:
CREATE TABLE dbo.Department (
DeptNo int NOT NULL,
DName varchar(14),
Loc varchar(13),
PRIMARY KEY (DeptNo)
)
GO
CREATE TABLE dbo.Employee (
EmployeeID int IDENTITY PRIMARY KEY,
LastName nvarchar(20) NOT NULL,
FirstName nvarchar(10) NOT NULL,
Address nvarchar(60),
City nvarchar(15),
Country nvarchar(15),
DeptNO int NOT NULL,
FOREIGN KEY (DeptNO) REFERENCES dbo.Department(DeptNO)
)
GO
CREATE PROCEDURE dbo.SelectDeptsAndEmps
AS
SELECT *
FROM dbo.Department;
SELECT *
FROM dbo.Employee;
GO
First, we create a model and drag the required stored procedure from the Database Explorer window to the design area; in the displayed message box we click Yes to obtain metadata of procedure resultsets.
As a result we get 2 complex types with default names SelectDeptsAndEmpResult and SelectDeptsAndEmpResult1 and a method corresponding to the stored procedure. For convenience, we rename the complex types to DeptsResult and EmpsResult and get the following method:
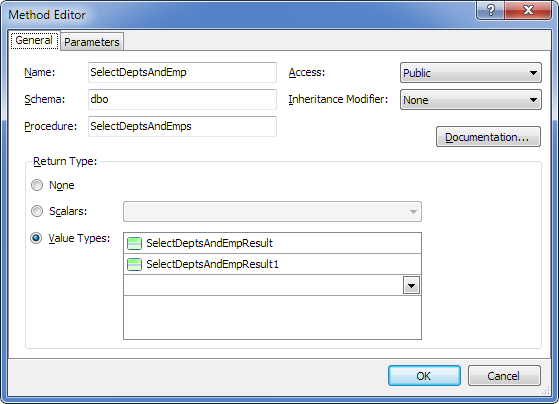
As a result of code generation for the model, the corresponding method of the model context will be generated having a signature close to the relevant stored procedure:
C#:
public SelectDeptsAndEmpMultipleResult SelectDeptsAndEmp ()
{
SelectDeptsAndEmpMultipleResult result = new SelectDeptsAndEmpMultipleResult();
DbConnection connection = this.Database.GetDbConnection();
bool needClose = false;
if (connection.State != ConnectionState.Open)
{
connection.Open();
needClose = true;
}
try
{
using (DbCommand cmd = connection.CreateCommand())
{
if (this.Database.GetCommandTimeout().HasValue)
cmd.CommandTimeout = this.Database.GetCommandTimeout().Value;
cmd.CommandType = CommandType.StoredProcedure;
cmd.CommandText = @"dbo.SelectDeptsAndEmps";
using (IDataReader reader = cmd.ExecuteReader())
{
while (reader.Read())
{
SelectDeptsAndEmpResult resultRow = new SelectDeptsAndEmpResult();
if (!reader.IsDBNull(reader.GetOrdinal("DeptNo")))
resultRow.DeptNo = (int)Convert.ChangeType(reader.GetValue(reader.GetOrdinal("DeptNo")), typeof(int));
if (!reader.IsDBNull(reader.GetOrdinal("DName")))
resultRow.DName = (string)Convert.ChangeType(reader.GetValue(reader.GetOrdinal("DName")), typeof(string));
else
resultRow.DName = null;
if (!reader.IsDBNull(reader.GetOrdinal("Loc")))
resultRow.Loc = (string)Convert.ChangeType(reader.GetValue(reader.GetOrdinal("Loc")), typeof(string));
else
resultRow.Loc = null;
result.SelectDeptsAndEmpResults.Add(resultRow);
}
reader.NextResult();
while (reader.Read())
{
SelectDeptsAndEmpResult1 resultRow = new SelectDeptsAndEmpResult1();
if (!reader.IsDBNull(reader.GetOrdinal("EmployeeID")))
resultRow.EmployeeID = (int)Convert.ChangeType(reader.GetValue(reader.GetOrdinal("EmployeeID")), typeof(int));
if (!reader.IsDBNull(reader.GetOrdinal("LastName")))
resultRow.LastName = (string)Convert.ChangeType(reader.GetValue(reader.GetOrdinal("LastName")), typeof(string));
if (!reader.IsDBNull(reader.GetOrdinal("FirstName")))
resultRow.FirstName = (string)Convert.ChangeType(reader.GetValue(reader.GetOrdinal("FirstName")), typeof(string));
if (!reader.IsDBNull(reader.GetOrdinal("Address")))
resultRow.Address = (string)Convert.ChangeType(reader.GetValue(reader.GetOrdinal("Address")), typeof(string));
else
resultRow.Address = null;
if (!reader.IsDBNull(reader.GetOrdinal("City")))
resultRow.City = (string)Convert.ChangeType(reader.GetValue(reader.GetOrdinal("City")), typeof(string));
else
resultRow.City = null;
if (!reader.IsDBNull(reader.GetOrdinal("Country")))
resultRow.Country = (string)Convert.ChangeType(reader.GetValue(reader.GetOrdinal("Country")), typeof(string));
else
resultRow.Country = null;
if (!reader.IsDBNull(reader.GetOrdinal("DeptNO")))
resultRow.DeptNO = (int)Convert.ChangeType(reader.GetValue(reader.GetOrdinal("DeptNO")), typeof(int));
result.SelectDeptsAndEmpResult1s.Add(resultRow);
}
reader.NextResult();
}
}
}
finally
{
if (needClose)
connection.Close();
}
return result;
}
public class SelectDeptsAndEmpMultipleResult
{
public SelectDeptsAndEmpMultipleResult()
{
SelectDeptsAndEmpResults = new List<SelectDeptsAndEmpResult>();
SelectDeptsAndEmpResult1s = new List<SelectDeptsAndEmpResult1>();
}
public List<SelectDeptsAndEmpResult> SelectDeptsAndEmpResults { get; private set; }
public List<SelectDeptsAndEmpResult1> SelectDeptsAndEmpResult1s { get; private set; }
}
If we need to retrieve the whole tables, we do the following: we drag the required stored procedure from the Database Explorer window to the design area; in the displayed message box we click No not to obtain metadata of procedure result set; then we drag the required tables from the Database Explorer window to the design area.
Then we double-click the method and in the Value Types drop-down list select the Department and Employee tables:
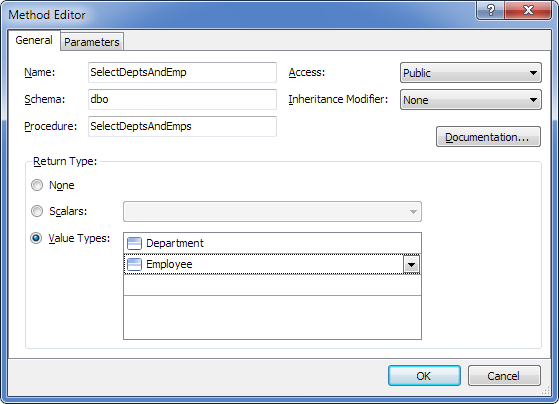
As a result of code generation for the model, the corresponding method of the model context will be generated having a signature close to the relevant stored procedure:
C#:
public SelectDeptEmpMultipleResult SelectDeptEmp ()
{
SelectDeptEmpMultipleResult result = new SelectDeptEmpMultipleResult();
DbConnection connection = this.Database.GetDbConnection();
bool needClose = false;
if (connection.State != ConnectionState.Open)
{
connection.Open();
needClose = true;
}
try
{
using (DbCommand cmd = connection.CreateCommand())
{
if (this.Database.GetCommandTimeout().HasValue)
cmd.CommandTimeout = this.Database.GetCommandTimeout().Value;
cmd.CommandType = CommandType.StoredProcedure;
cmd.CommandText = @"dbo.SelectDeptEmp";
using (IDataReader reader = cmd.ExecuteReader())
{
while (reader.Read())
{
Department resultRow = new Department();
if (!reader.IsDBNull(reader.GetOrdinal("DeptNo")))
resultRow.DeptNo = (int)Convert.ChangeType(reader.GetValue(reader.GetOrdinal("DeptNo")), typeof(int));
if (!reader.IsDBNull(reader.GetOrdinal("DName")))
resultRow.DName = (string)Convert.ChangeType(reader.GetValue(reader.GetOrdinal("DName")), typeof(string));
else
resultRow.DName = null;
if (!reader.IsDBNull(reader.GetOrdinal("Loc")))
resultRow.Loc = (string)Convert.ChangeType(reader.GetValue(reader.GetOrdinal("Loc")), typeof(string));
else
resultRow.Loc = null;
result.Departments.Add(resultRow);
}
reader.NextResult();
while (reader.Read())
{
Employee resultRow = new Employee();
if (!reader.IsDBNull(reader.GetOrdinal("EmployeeID")))
resultRow.EmployeeID = (int)Convert.ChangeType(reader.GetValue(reader.GetOrdinal("EmployeeID")), typeof(int));
if (!reader.IsDBNull(reader.GetOrdinal("LastName")))
resultRow.LastName = (string)Convert.ChangeType(reader.GetValue(reader.GetOrdinal("LastName")), typeof(string));
if (!reader.IsDBNull(reader.GetOrdinal("FirstName")))
resultRow.FirstName = (string)Convert.ChangeType(reader.GetValue(reader.GetOrdinal("FirstName")), typeof(string));
if (!reader.IsDBNull(reader.GetOrdinal("Address")))
resultRow.Address = (string)Convert.ChangeType(reader.GetValue(reader.GetOrdinal("Address")), typeof(string));
else
resultRow.Address = null;
if (!reader.IsDBNull(reader.GetOrdinal("City")))
resultRow.City = (string)Convert.ChangeType(reader.GetValue(reader.GetOrdinal("City")), typeof(string));
else
resultRow.City = null;
if (!reader.IsDBNull(reader.GetOrdinal("Country")))
resultRow.Country = (string)Convert.ChangeType(reader.GetValue(reader.GetOrdinal("Country")), typeof(string));
else
resultRow.Country = null;
if (!reader.IsDBNull(reader.GetOrdinal("DeptNO")))
resultRow.DeptNO = (int)Convert.ChangeType(reader.GetValue(reader.GetOrdinal("DeptNO")), typeof(int));
result.Employees.Add(resultRow);
}
reader.NextResult();
}
}
}
finally
{
if (needClose)
connection.Close();
}
return result;
}
public class SelectDeptEmpMultipleResult
{
public SelectDeptEmpMultipleResult()
{
Departments = new List<Department>();
Employees = new List<Employee>();
}
public List<Department> Departments { get; private set; }
public List<Employee> Employees { get; private set; }
}
Complex types and tables can be combined in one method.
 See Also
See Also
|
Stored Procedure without Result Stored Function with Scalar Result Stored Procedure and Stored Function With Resultset Working with Owned Types (Complex Types)
|