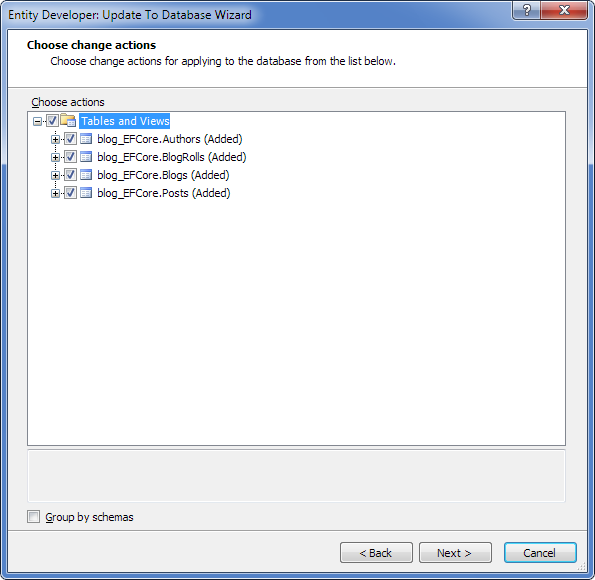
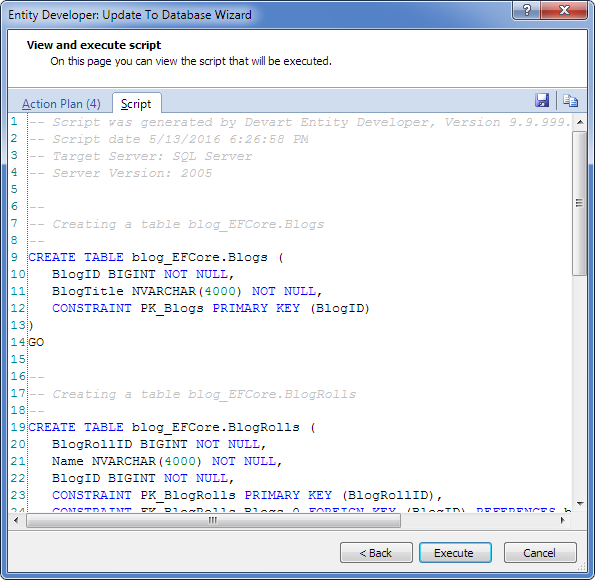
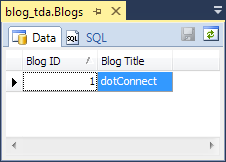
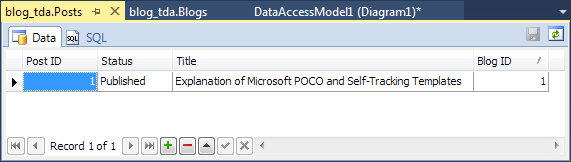
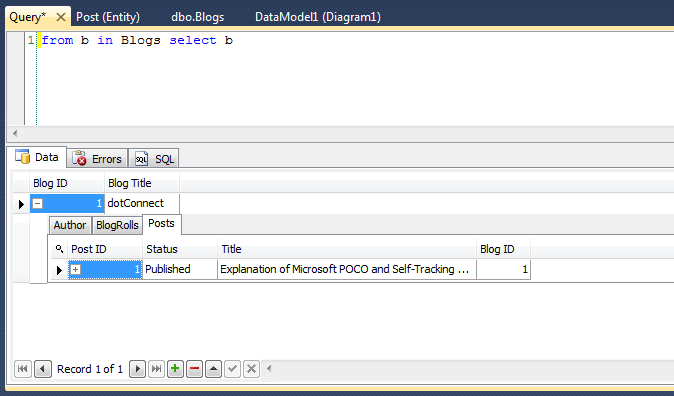
This section explains how to create a model using the Model-First approach.
To create a model using the Model-First approach, perform the following sequence of actions:
| 1. | In the Solution Explorer window, right-click the name of your project. |
| 2. | From the shortcut menu, select the Add command and select the New Item option. |
|
|
In the standalone application click the Create New Model button on the Entity Developer toolbar.
|
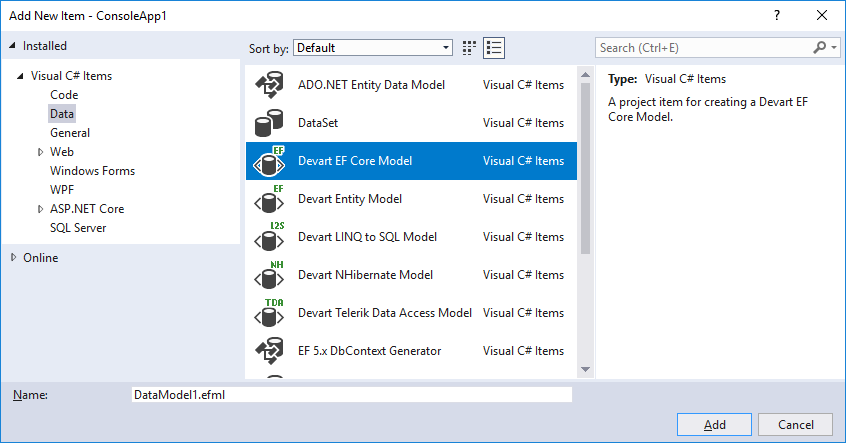
| 3. | In the Installed Templates column of the Add New Item window, select Data. |
| 4. | In the central column of the Add New Item window, select Devart Entity Framework Core Model. |
|
|
In the standalone application in the displayed New Model dialog select Devart Entity Framework Core Model and click Create.
|
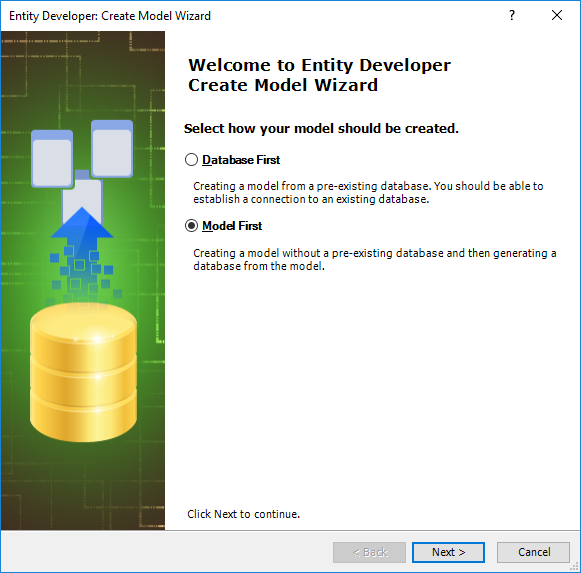
| 6. | On the Create Model Wizard welcome page, select Model First and click Next. |
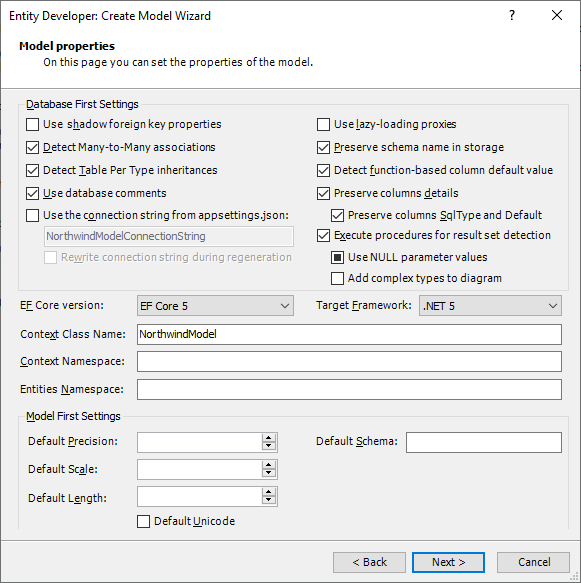
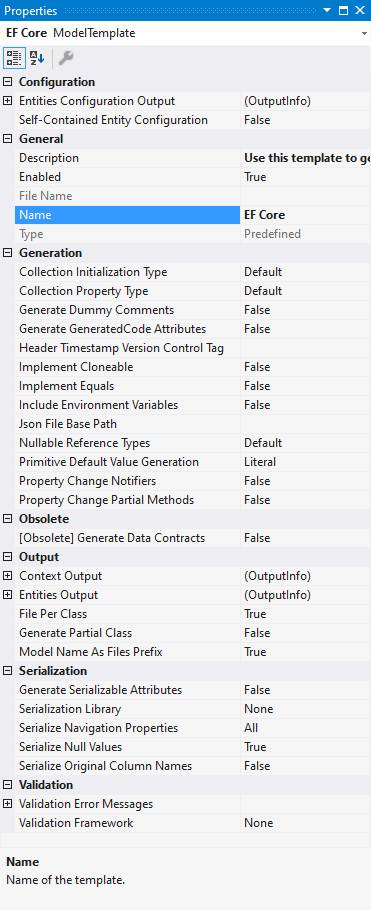
| 7. | On the Model properties page, define the settings of your model and click Next. Here you can select the target Entity Framework Core version from the ones, supported by the target .NET Framework of your project. |
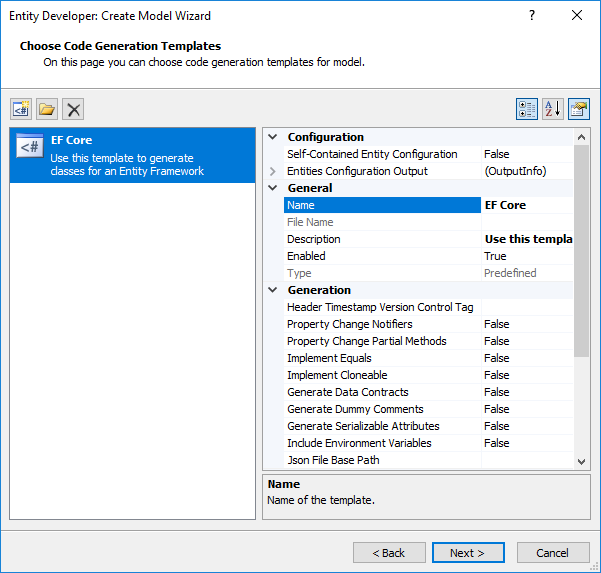
| 8. | The Choose Code Generation page allows you to select code generation templates you want to add to the new model. By default this page contains the most frequently used template; the properties area of this page allows you to configure the properties of the selected template. Three buttons at the top of this page allow you to add more templates from gallery, add existing templates from disk and remove templates from the list. |
| 9. | Click the Add template button. |
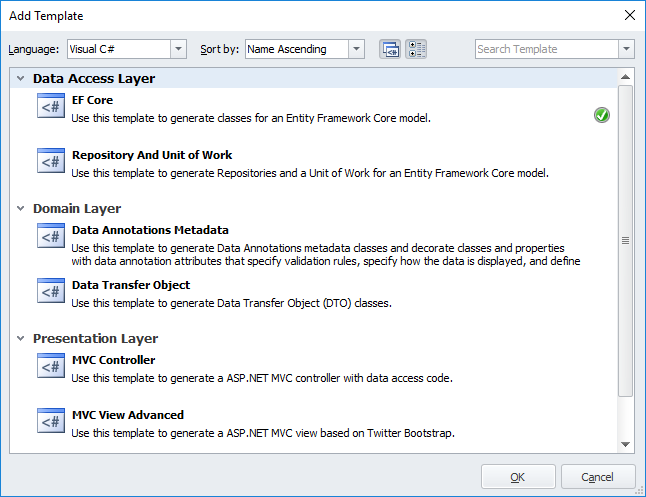
| 10. | The Add Template dialog box lists all predefined and shared templates. Choose the required one and click OK. The selected template will be added to the list on the Choose Code Generation page together with all related templates (without which the template would work incorrectly). |
| 11. | After all the required templates are added to the list on the Choose Code Generation page of the wizard, click Next. |
| 12. | On the final window of the wizard click Finish. |
After the empty diagram space is displayed, you can proceed to creating required classes, associations and inheritances.
The description of procedures for creating classes, associations and inheritances for the model is provided below.
Creating a Class
This procedure explains how to create a class. For the purpose of this example, we shall create the Blog class (see the picture below).
|
|
Before proceeding to creating classes, check that in the properties of your model identity is selected as the default generator. For this purpose, in the Model Explorer window, right-click your model, select Properties from the shortcut menu, and, in the Properties window, check that Default Identity Generator is set to identity.
|
1. Right-click on the empty diagram space and select New Class from the Add submenu of the shortcut menu.
| 2. | Click the default name of the class (Class1), enter Blog and press ENTER. |
| 3. | Right-click the created class and select New Property from the Add submenu of the shortcut menu. |
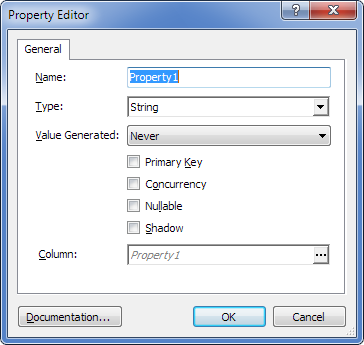
| 4. | In the Name box, enter the name of the property (BlogID). |
| 5. | From the Type drop-down list, select Int64. |
| 6. | Select the Primary Key check box. |
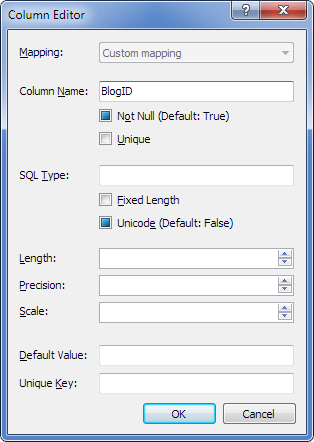
| 7. | (Optional) To change the default parameters of the database column, to which this property is to be mapped, click the three-dotted button in the Column field and, in the Column Editor window (see below), enter the desired values of the parameters and click OK. |
| 9. | To create the second property (BlogTitle), right-click the created class and select New Property from the Add submenu of the shortcut menu. |
| 10. | In the Name box, enter the name of the property (BlogTitle). |
| 11. | From the Type drop-down list, select Varchar. |
| 12. | (Optional) To change the default parameters of the database column, to which this property is to be mapped, click the three-dotted button in the Column field and, in the Column Editor window (see above), enter the desired values of the parameters and click OK. |
| 13. | Leave the other settings as they are and click OK. |
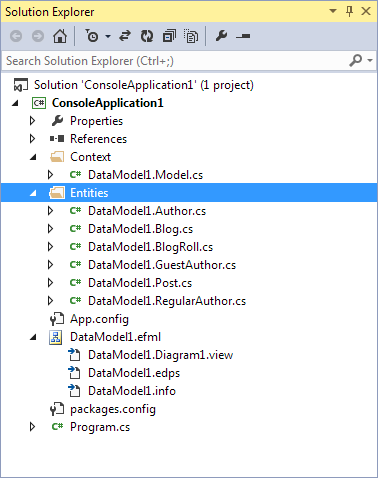
All the other classes in the model are created similarly. For more information on how to create classes, see Classes.
Creating an Association
This procedure describes how to create an association. For the purpose of this procedure, we suppose that at least the Blog and Post classes have been created (see the picture of the example model in the Creating a Model Using Model-First Approach section). The association that is created in this procedure is of the One-to-Many type.
To create an association, perform the following sequence of actions:
| 1. | On the model diagram, right-click the Blog class and, from the Add submenu of the shortcut menu, select New Association. |
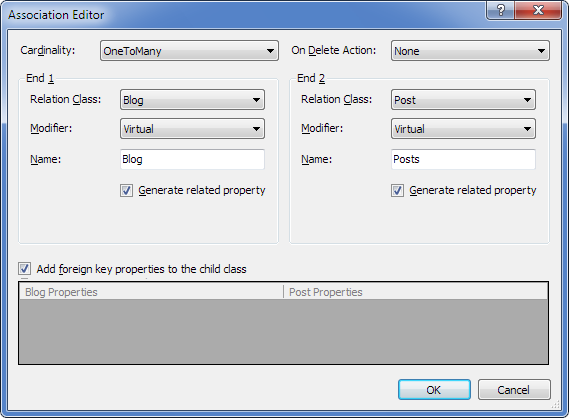
| 2. | In the End 1 area, set Class to Blog and leave other settings set to their default values. |
| 3. | In the End 2 area, set Class to Post and leave other settings set to their default values. |
| 4. | In the Cardinality list select OneToMany. |
| 5. | (Optional) To create an association using a unique property instead of the primary key, under Foreign key references, select Unique property of Blog and, from the drop-down list, select the required unique property. |
| 6. | (Optional) To change the default parameters of the database column, in the Columns mapping area, click the three-dotted button in the Column field and, in the Column Editor window, enter the desired values of the parameters and click OK. |
| 7. | On the Association editor page, click OK. |
For information on how create other types of associations, see Working with Associations.
Creating an Inheritance
This procedure describes how to create an inheritance. For the purpose of this procedure we suppose that the Author and RegularAuthor classes have already been created (see the picture of the example model in the Creating a Model Using Model-First Approach section). The inheritance that is created in this procedure is of the Table-per-Hierarchy type (Flat inheritance).
To create an inheritance, perform the following sequence of actions:
| 1. | On the model diagram, right-click the Author class and, from the Add submenu of the shortcut menu, select New Inheritance. |
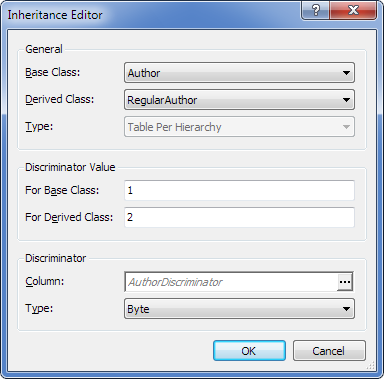
| 2. | From the Base Class drop-down list, select Author. |
| 3. | From the Derived Class drop-down list, select RegularAuthor. |
| 4. | From the Type drop-down list, select Table Per Hierarchy. |
| 5. | In the For Base Class box of the Discriminator Value area, specify the value for the base class (for example, "0") |
| 6. | In the For Derived Class box of the Discriminator Value area, specify the value for the derived class (for example, "1"). |
| 7. | In the Discriminator area, from the Type drop-down list, select the appropriate type for the discriminator column. You can change the default settings of the column by clicking the three-dotted button in the Column box and specifying the required values on the Column editor page. |
| 8. | Leave the other settings set to their default values. |
Repeat these steps to create the Author - GuestAuthor inheritance.
For more information on how to create inheritances of other types, see Working with Inheritances.
Summary Description of the Model
The resulting model should contain the following items:
| o | Blog - Post, Blog - BlogRoll (one-to-many); |
| o | Blog - Author (one-to-one); |
| o | Author - Regular Author; |
Below is the example of the resulting model:
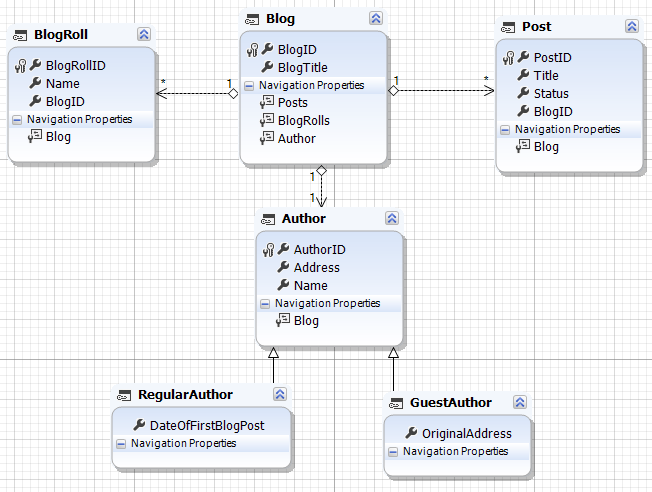
|
 Creating a Model Using Model-First Approach
Creating a Model Using Model-First Approach Code Generation Setup
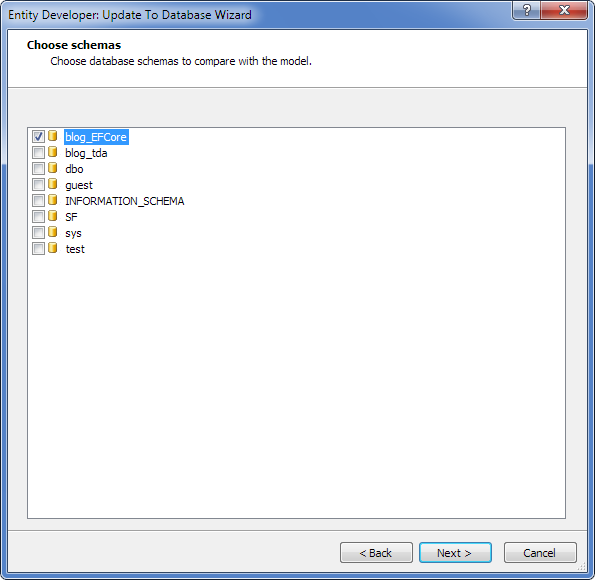
Code Generation Setup Updating the Database from the Model
Updating the Database from the Model Testing the Model
Testing the Model