Association is one of the core objects of a model. It defines relationships between other model objects like classes and complex types established on the basis of foreign keys. Associations are mapped as foreign keys to the database and can be generated automatically from the foreign keys when reverse engineering an existing database.
An association has two objects engaged in it and these objects are known as its Ends. An association End defines the object and the number of object instances that can exist at this end of an association. It can also optionally define operations performed on the association end.
Model objects can have navigation properties, which are optional properties designed to navigate from one association end to the other. A navigation property defines the association it navigates and its ends.
Multiplicity of an association End defines the data type of a navigation property. If it equals 'Many', the navigation property's data type is 'collection'.
A model object can have multiple associations. On the diagram, associations are represented as dotted line connections with arrows.
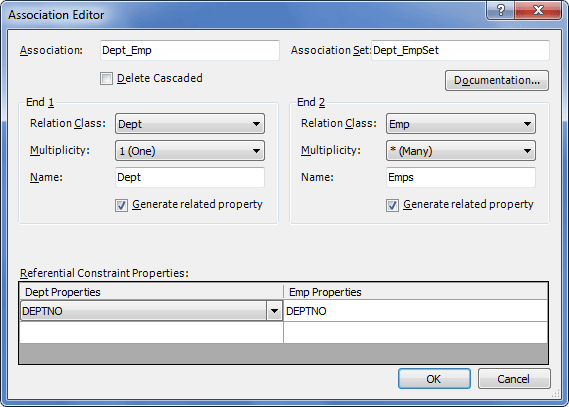
 Association Editor Dialog
Association Editor Dialog
To create an association, use the New Association
You can create three types of associations: one-to-many (default), one-to-one and many-to-many. For details on the appropriate procedures, refer to the corresponding sections. In the Association Editor dialog box you should set parent and child classes and referential constraint properties. You can also enable or disable corresponding property generation for parent and child class, specify the names of the corresponding properties, the number of instances of a child or parent class that can participate in the relationship.
|
 Entity Framework Association in the Conceptual and Storage Models
Entity Framework Association in the Conceptual and Storage Models
The following context menu options are available for Entity Framework associations: Select Storage - looks for a constraint in the Storage part, to which the association in the Conceptual model is mapped. Create Storage and Mapping - for an association in the Conceptual model, this option creates the corresponding constraint in the Storage part and the corresponding mapping between them. If this option is selected for an association already having a Storage counterpart and mapping, a dialog box will be displayed offering to create the Storage object and mapping anew. In fact this option is a manual call of synchronization for a particular object in the Conceptual model. For more information on how to turn mapping synchronization on and off, refer to Mapping Synchronization topic.
|
 See Also
See Also
|
|