Execute SQL statements
Data Compare for MySQL enables you to execute SQL scripts in various ways, including running entire scripts, selected blocks of text, or individual statements.
Entire script
To execute the entire script, click the  button on the SQL toolbar.
button on the SQL toolbar.
Alternatively, on the SQL menu, select the Execute command.
Selected block of text
To execute an arbitrary text block:
1. Select the text block using the mouse or keyboard.
2. Run the Execute command like while executing the entire script. Alternatively, select Execute from the shortcut menu of SQL Editor.
Current statement
To execute a current statement, click the Execute Current Statement  button on the SQL toolbar.
button on the SQL toolbar.
Alternatively, right-click a required statement, and select Execute Current Statement command on the shortcut menu.
Execute to cursor
To execute script to the current position of the cursor:
1. Move the cursor to the required position.
2. Click the Execute to Cursor command from the SQL menu.
Alternatively, you can press Ctrl+Shift+F10.
If your statement is complex and contains multiple queries or T-SQL commands, the Execute To Cursor option will execute all statements above the cursor, including the statement where the cursor is placed. All statements that are below the cursor will not be executed.
Note
To better understand the Execute To Cursor option, study the following examples:
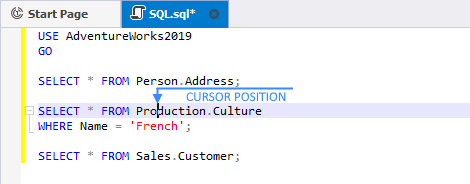
Example 1.
In this worked example, the SELECT Address and SELECT Culture queries will be executed. Please note, that the WHERE clause of the SELECT Culture query will also be executed. The SELECT Customer query won’t be executed.
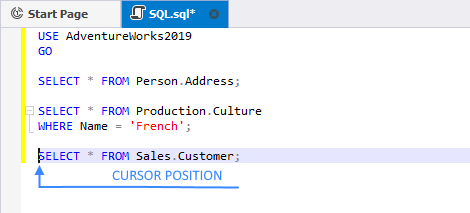
Example 2.
In this case, the SELECT Address, SELECT Culture, and SELECT Customer queries will be executed.
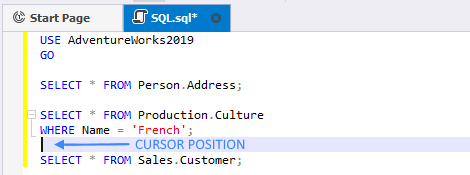
Example 3.
In this case, the SELECT Address and SELECT Culture queries will be executed whereas the SELECT Customer query won’t be executed.
How to stop execution
To stop SQL execution, click Stop Execution on the SQL toolbar or press Alt+Pause.
Represent query execution results
The query execution results can be represented in two ways - in text and in grid formats.
1. To represent results as text, click  on the SQL toolbar before query execution.
on the SQL toolbar before query execution.
2. To represent results as grid, click  on the SQL toolbar before query execution.
on the SQL toolbar before query execution.
SQL Query History
dbForge Data Compare for MySQL delivers a number of features that help optimize query performance. One of them is SQL Query History. It stores the main information about the executed SQL statements for a particular period. Additionally, it is possible to see who and when executed a query, as well as get other valuable information.
To open the SQL Query History, either press Ctrl+Alt+H or click View on the main toolbar, point to Other Windows, and select SQL Query History. This is what the SQL Query History window looks like.
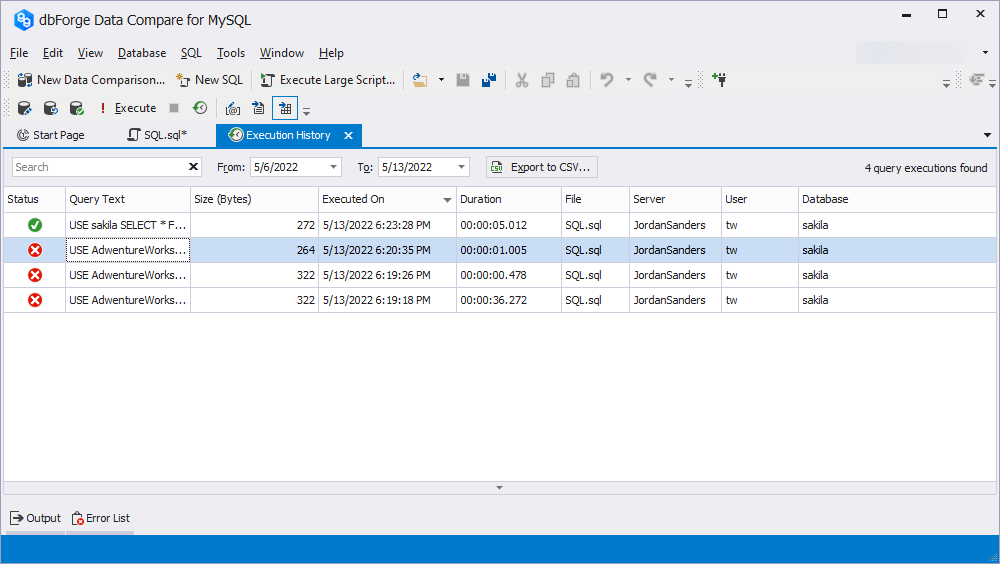
If you point to the Query Text column, you will be able to see the entire executed script without having to go back to the SQL document.