
|
Connecting to MySQL Through SSH in Delphi |

|
SSH is a protocol that allows users to securely log in and interact with remote systems on the internet by connecting a client program to an SSH server. SSH provides a mechanism for establishing a cryptographically secured connection between two endpoints, a client and a remote server, which authenticate each other and exchange messages. It employs different forms of symmetrical encryption, asymmetrical encryption, and hashing.
You can use SSH to secure the network connection between a Delphi application and a MySQL server. An SSH connection enables you to run shell commands as if you were physically operating the remote machine.
This page demonstrates how to use UniDAC to connect to a MySQL server securely via an SSH tunnel.
To follow the steps on this page, you need an SSH client and an SSH server. You can create them using SecureBridge, a solution provided by Devart. It enables you to embed an SSH client into your Delphi application and, if needed, configure an SSH server. For more information, see the SecureBridge tutorial on configuring an SSH server. You can also build the SSHServer demo project, which is distributed with SecureBridge.
Your MySQL server must be configured to accept connections from the SSH tunnel.
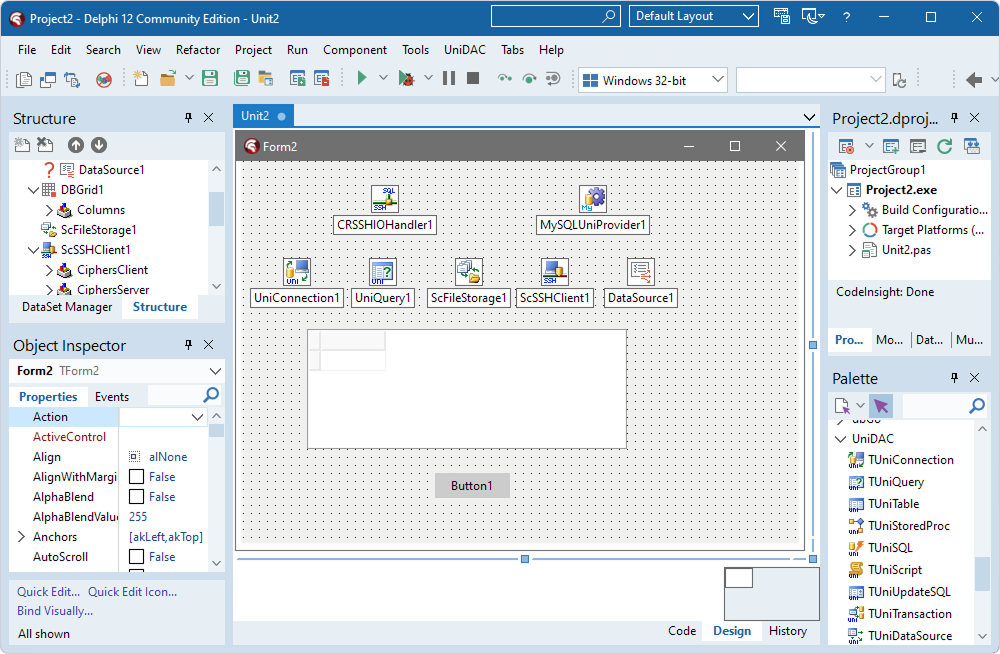
You can establish a secure SSH tunnel using SecureBridge without the need for third-party applications. SecureBridge provides all the necessary components to create an SSH client within your Delphi application.
Readme.html—by default, it is located in C:\Users\<user>\Documents\Devart\UniDAC for RAD Studio XX\Demos\TechnologySpecific\SecureBridge.
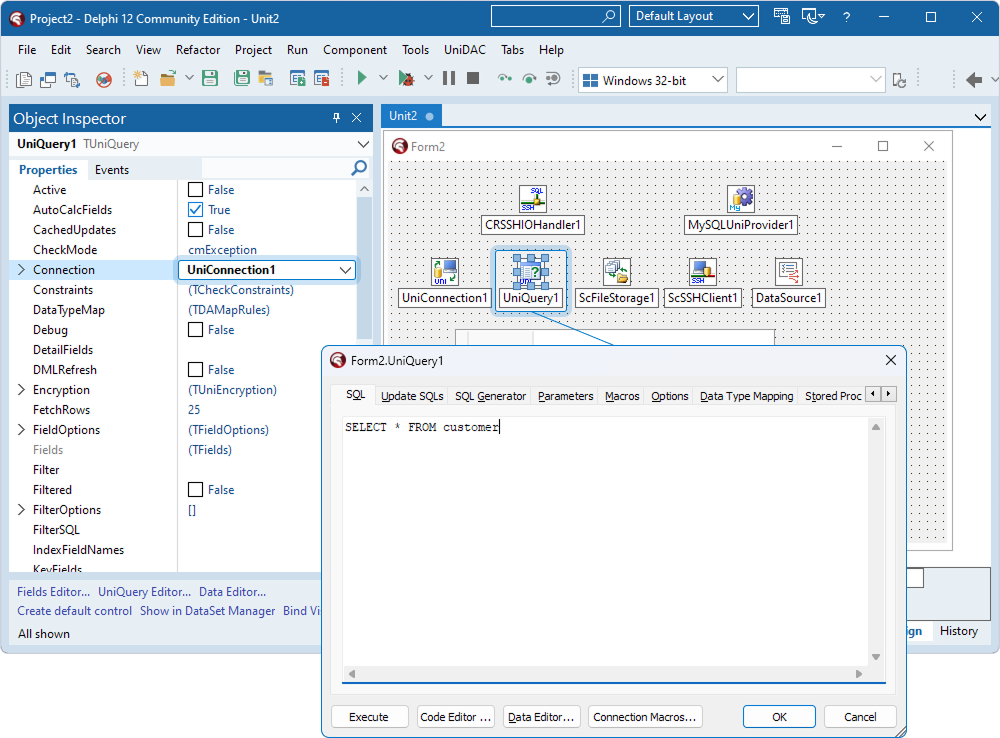
![]()
Using SecureBridge and its components is not obligatory—you can use any other server that implements the SSH protocol.
The following steps describe a simple case of using OpenSSH for Windows. For a detailed description of each command, see the OpenSSH documentation.
OpenSSH/bin folder.mkpasswd -l -u SSH_user >> ..\etc\passwd
mkgroup to create a group permissions file.
mkgroup -l >> ..\etc\group
net start opensshd
ssh.exe -L <SSH_port>:<MySQL_server>:<MySQL_server_port> <SSH_user>@<SSH_server>
<SSH_port> – The port number of the SSH client that will be redirected to the corresponding port of the MySQL server.
<MySQL_server> – The name or IP address of the machine where the MySQL server is installed.
<MySQL_server_port> – The number of the MySQL server port, usually 3306.
<SSH_user> – The name of the user created at step 2.
<SSH_server> – The name or IP address of the machine where the SSH server was installed at step 2.
For example, ssh.exe -L 3307:server:3306 [email protected].
At first launch, you'll be prompted to confirm the connection with the specified SSH server. Enter yes for confirmation.
At each launch of SSH, you must enter the password set at step 2.
TUniConnection.
UniConnection1.Server := <SSH_client>;
UniConnection1.Port := <SSH_port>;
If the SSH client was installed on the same machine as the MySQL client, you can assign localhost to UniConnection1.Server.
Note that in the provided steps, Windows checks the SSH_user authentication. For information about the methods of higher protection (key authentication, etc.), see the OpenSSH documentation.
For more information on using encrypted connections, see MySQL Reference Manual.