Result output patterns
dbForge Studio for SQL Server provides two result output modes to match user preferences:
- Paged mode: Displays a fixed number of rows per page with manual pagination.
- Infinite scrolling: Continuously loads data as you scroll – no pagination needed.
Paged mode
The paged mode is well-suited for large datasets. It divides data into manageable pages, making navigation and review easier. This mode also reduces the load on the database server, improving overall performance.
By default, paged mode is turned on. To turn it off, select Paginal Mode on the top toolbar.
![]()
Turning off the paged mode activates the Infinite scrolling pattern.
To navigate through pages, use the corresponding options on the document toolbar:

| Option | Option Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
 |
First Page | Switches to the first page in the grid. |
 |
Previous Page | Switches to the previous page in the grid. |
 |
Next Page | Switches to the next page in the grid. |
 |
Last Page | Switches to the last page in the grid. |
Note
You can also turn on paged mode by selecting the corresponding option in the dialog that appears when retrieving data from a table with many records.
If not all records are displayed on one page while paged mode is enabled, a warning icon appears on the status bar. Hovering over the icon displays a notification indicating that the data is split across multiple pages.
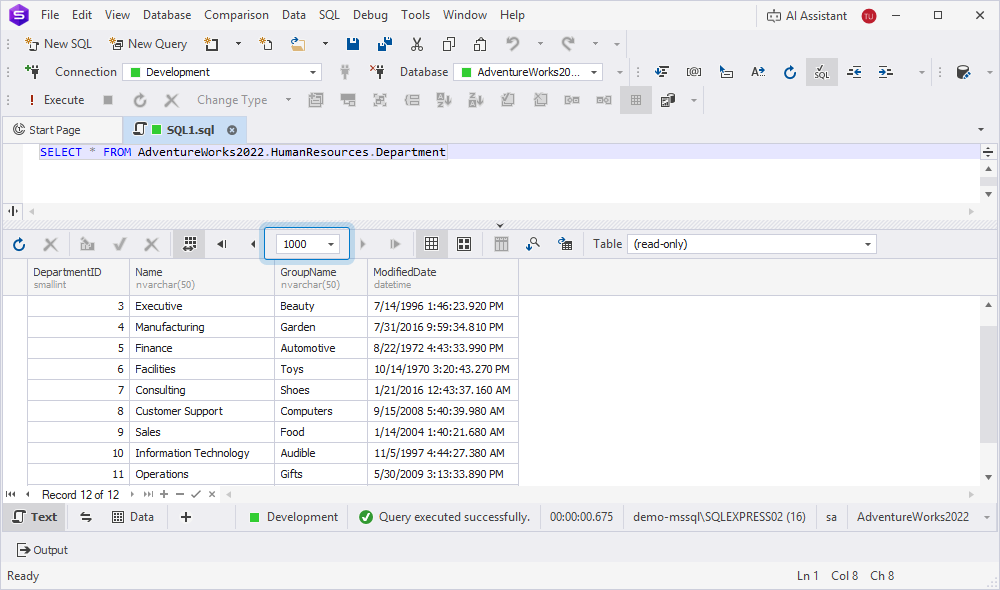
Set the number of records per page
To set the number of records per page, in the Page Row Count list, select the number of rows you want to display per page.
The possible values are 10, 100, and 1000. The default value is 1000.
Tip
You can set any page size in the Page Row Count field, for example, 250,000.
Set a custom number of records per page
1. In the Page Row Count field, enter the number of records.
2. Press Enter.
Note
You can also set a custom number using Data Editor or the Options dialog.
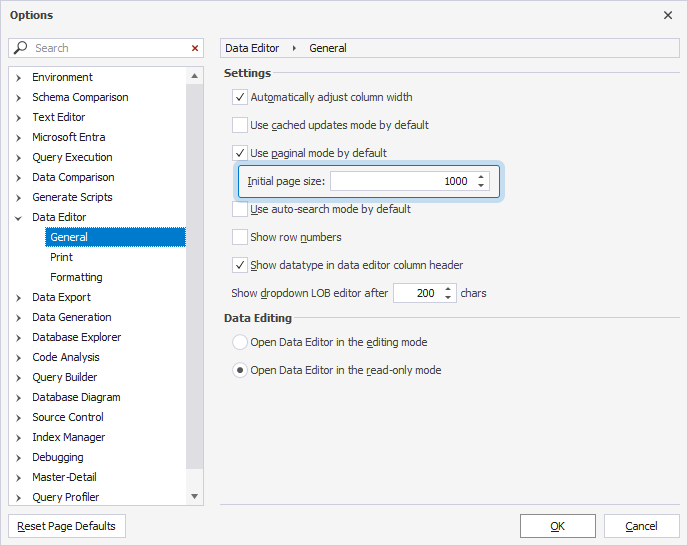
Set a custom initial page size
1. Select Tools > Options.
2. Select Data Editor > General.
3. In Initial page size, enter the number of records per page.
4. To save the changes, select OK.
Infinite scrolling
The infinite scrolling pattern is activated when the paged mode is off. The pattern loads data continuously as the user scrolls down the grid, allowing all data to be retrieved at once.
If a table contains more than 1,000 records and the paged mode is off, the tool can return more than 302 records after the SELECT statement execution. This means that the first 302 records are read in the infinite scrolling mode, and the + sign means that there is more to load. To see the rest of the data, you need either to scroll through the data in the grid (for instance, by pressing Page Down) or to press Ctrl + End.
If you want to retrieve all data from a table with a large number of records, you will get the following message warning you about the possibility of the Out of memory error.
The table contains many records. Retrieving all of them can cause an 'Out of Memory' error. You might avoid it by using paginal mode.
Press 'Continue' to continue retrieving.
Press 'Cancel' to cancel retrieving.
Press 'Paginal Mode' to switch paginal mode on.
You can choose to continue retrieving data, cancel retrieving data, or turn on the paged mode.
Output patterns comparison table
The following table explains the advantages and disadvantages of paged mode and infinite scrolling.
Paged mode
| Pros | Cons |
| Faster data retrieval: The paged mode view can help speed up data retrieval times since only a limited number of records are displayed on each page. This can be particularly helpful when dealing with large datasets. | Scrolling required for full data view: The paged mode requires users to navigate multiple pages to view all table data, making it difficult to get a complete overview of the data at once. |
| Less load on database server: When using the paged mode, the number of records displayed on each page is limited, meaning that the database server is only queried for a subset of the data at a time. | Export limitations: When using the paged mode, data export from the grid is limited to only the data displayed on the current page, which can be a drawback for users who need to export larger datasets. |
| Lower RAM usage: In the paged mode, only a limited number of records are loaded into memory at any given time, typically the records displayed on the current page and a few surrounding pages. | Count limitations: The paged mode does not show immediate record count, but users can find it by clicking Go to Last Page in the paged mode control located on the Data Editor toolbar. |
Lock-free SELECTs: The paged mode does not lock tables for DDL (Data Definition Language) operations when executing a SELECT statement. |
Limited sorting options: The paged mode can limit the available sorting options to those that apply only to the currently displayed page rather than allowing for sorting across the entire dataset. |
| Ease of navigation: By breaking the dataset into smaller, more manageable pieces, the paged mode can make it easier for users to navigate and find the specific data they need. | Limited searching options: When searching for specific data in a paginated view, users may need to perform multiple searches on each page rather than across the entire dataset. |
Infinite scrolling
| Pros | Cons |
| Less load on database server: When using infinite scrolling, the data is selected as it is scrolled, which means that the database server is only queried for a subset of the data that is currently being viewed. | Locked SELECTs: Infinite scrolling locks tables for DDL (Data Definition Language) operations when executing a SELECT statement. |
| Full data export: When using infinite scrolling, the user can export all the data directly from the grid without being limited to the records displayed on the current page. | Increased RAM usage: Infinite scrolling requires the local computer to load more data within a given time period, resulting in a heavier load on RAM. |
| Better user experience: With infinite scrolling, users can continuously scroll through content without manually clicking to load new pages, which can provide a more seamless experience. | Increased chances of memory overflow: Selecting and viewing large amounts of data from an SQL database can cause memory overflow due to the limited capacity of the computer’s memory to handle and store the data. |
| Reduced clicks: Infinite scrolling can reduce the number of clicks required to navigate through the data, which can save time and increase efficiency. | Less control: With infinite scrolling, users cannot easily navigate to specific parts of the dataset, and the scroll position can be easily lost. |