Table Editor tab - Indexes
On the Indexes tab, you can create, modify, or delete indexes to optimize query performance.
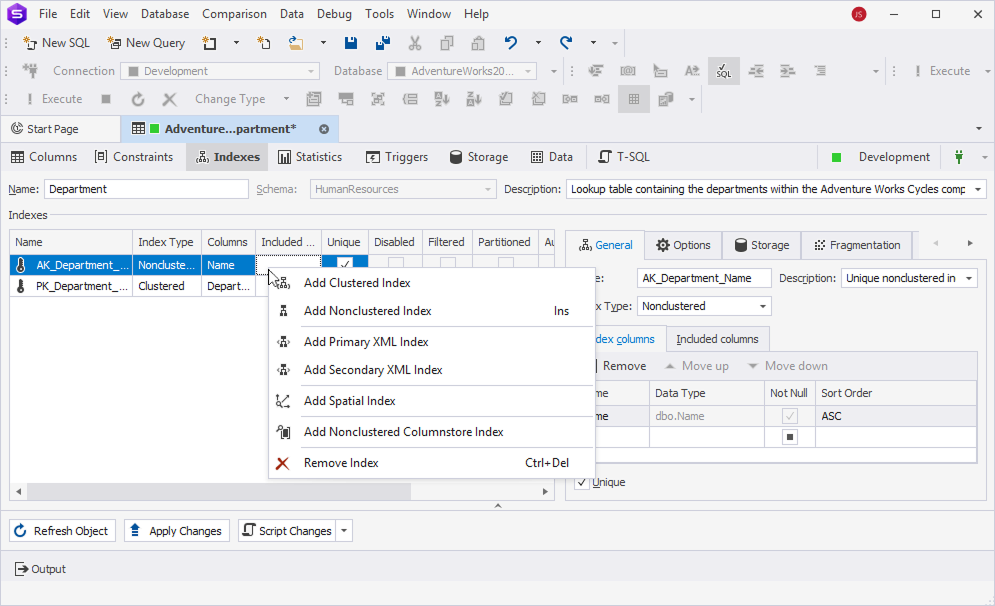
Indexes grid
Right-click the grid and select the required option:
- Add Clustered Index to create a clustered index.
- Add Non-Clustered Index to create a non-clustered index. Alternatively, press Ins.
- Add Primary XML Index to create a primary XML index.
- Add Secondary XML Index to create a secondary XML index.
- Add Spatial Index to create a spatial index.
- Add Clustered Columnstore Index to create a clustered columnstore index.
- Add Nonclustered Columnstore Index to create a non-clustered columnstore index.
- Remove Index to delete the selected index. Alternatively, press Ctrl+Del.
Note
To create a secondary XML index, first, you must add the primary XML index on the xml type column.
In the grid, you can view and configure index properties:
- Name – Index name.
- Index Type – Index type, such as clustered, nonclustered, primary or secondary XML, etc.
- Included columns – Columns to be stored in a non-clustered index.
- Unique – Select the checkbox to prevent duplicate values in the indexed column. This property is usually used for primary keys and unique constraints.
- Disabled – View whether the index is disabled. The index remains in the database and can be re-enabled when needed.
- Filtered – Check whether the indexed column contains a
WHEREclause to include only specific rows. - Partitioned – Check whether the index is split into smaller, manageable parts (partitions) based on a specified column.
- Auto Recompute Statistics – Check whether the index statistics are automatically updated when significant data changes occur.
- Ignore Duplicates – View whether the duplicate rows are ignored.
- Fill Factor – Specifies how much space is left free in index pages to allow for future inserts.
When you select the index in the grid, it is also highlighted in the T-SQL preview pane.
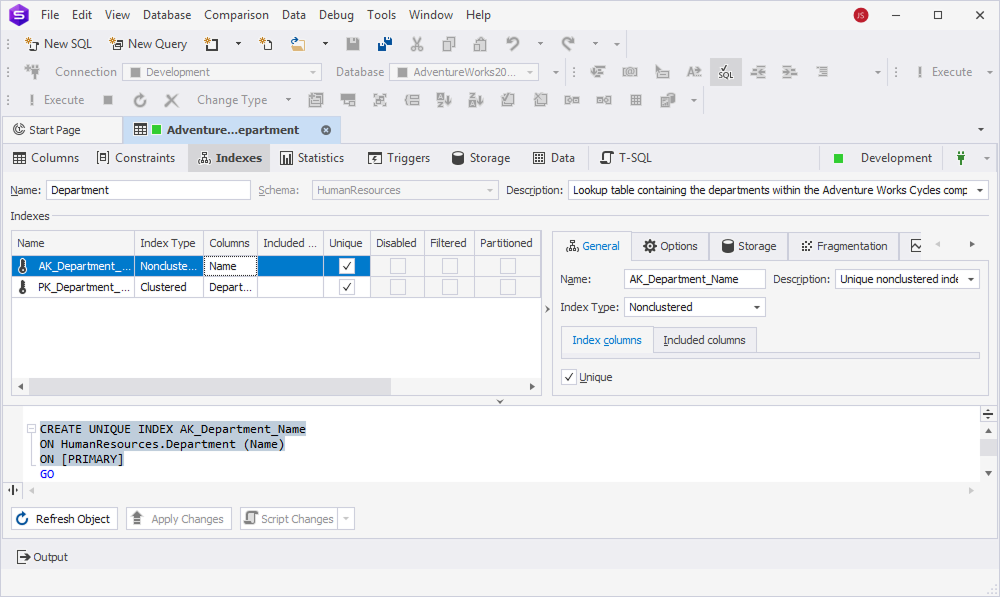
Editors
You can also set up additional properties for a specific index in the right grid.
The properties can be grouped into the following categories:
- General – Specify the index name, description, indexed and included columns, and index type. You can remove or sort indexed columns and specify a NULL or unique value.
- Options – Select or clear the checkboxes next to the options to customize the default behavior of indexes.
- Storage – Define how and where the index is stored within the database.
- Fragmentation – Measure how scattered the index pages are on the disk.
- Usage Statistics – View how often the index is used in queries.
General
The table describes the general settings.
| Name | Description | Used for index |
|---|---|---|
| Name | Specify the index name. | All types |
| Description | Specify the index description. When you enter the description in the Description box, click OK to save the description or Cancel to discard the changes. |
All types |
| Index Type | Choose an index type for the column. | All types |
| Index columns grid | Set up properties of the index columns. | Clustered Nonclustered Primary XML Spatial |
| Included columns grid | Set up properties of the included columns. | Nonclustered |
| Primary XML Index | Choose a primary XML index for the secondary index. | Secondary XML |
| Secondary XML Index Type | Choose the types of secondary indexes: PATH, VALUE, and PROPERTY. |
Secondary XML |
Index columns
The table describes the settings in the index columns grid.
| Name | Description | Used for index |
|---|---|---|
| Name | Choose the index column. | Clustered Nonclustered Spatial Primary XML |
| Data Type | Indicates a data type of the column. | Clustered Nonclustered Spatial Primary XML |
| Not Null | Indicates whether the column is NOT NULL. |
Clustered Nonclustered Spatial Primary XML |
| Sort Order | Allows you to sort indexed columns in ascending or descending order. | Clustered Nonclustered |
| Remove | Removes the selected column. Alternatively, select Remove Column from the shortcut menu. Shortcut: Ctrl+Del |
Clustered Nonclustered Spatial Primary XML |
| Move up | Moves the selected column up. Alternatively, select Move Column Up from the shortcut menu. Shortcut: Ctrl+Up |
Clustered Nonclustered Spatial Primary XML |
| Move down | Moves the selected column down. Alternatively, select Move Column Down from the shortcut menu. Shortcut: Ctrl+Down |
Clustered Nonclustered Spatial Primary XML |
Included columns
The table describes the settings for included columns.
| Name | Description | Used for |
|---|---|---|
| Name | Choose the included column. | Nonclustered |
| Data Type | Indicates a data type of the column. | Nonclustered |
| Not Null | Indicates whether the column is NOT NULL. |
Nonclustered |
| Remove | Removes the selected column. Alternatively, select Remove Column from the shortcut menu. Shortcut: Ctrl+Del |
Nonclustered |
| Move up | Moves the selected column up. Alternatively, select Move Column Up from the shortcut menu. Shortcut: Ctrl+Up |
Nonclustered |
| Move down | Moves the selected column down. Alternatively, select Move Column Down from the shortcut menu. Shortcut: Ctrl+Down |
Nonclustered |
Options
The table describes options of the index.
| Name | Category | Description | Used for |
|---|---|---|---|
| Auto recompute statistics | General | When the option is enabled, SQL Server automatically updates the statistics as data changes. | Clustered Nonclustered Spatial |
| Ignore duplicate values | General | When the option is enabled, SQL Server ignores duplicate rows instead of causing an error. | Clustered Nonclustered |
| Allow page locks | Locks | When the option is enabled, SQL Server can lock entire pages of data when accessing the index. When the option is disabled, SQL Server doesn’t acquire page locks on the index and uses row-level or table-level locks instead. Note: This may lead to blocking or deadlocks if multiple users try to access rows on the same page. |
Clustered Nonclustered Primary XML Secondary XML Spatial |
| Allow row locks | Locks | When the option is enabled, SQL Server can lock individual rows in the index or table. When the option is disabled, SQL Server cannot acquire row-level locks for that index and uses page-level or table-level locks instead. Note: This may lead to blocking or deadlocks if multiple users try to access rows on the same page. |
Clustered Nonclustered Primary XML Secondary XML Spatial |
| Maximum degree of parallelism | Operation | Controls how many CPU cores SQL Server can use in parallel to build or rebuild that index. | All types |
| Fill factor | Storage | Specifies the percentage of space to fill on each leaf-level page with data, reserving the remaining space for future inserts or updates. | Clustered Nonclustered Primary XML Secondary XML Spatial |
| Pad Index | Storage | When the option is enabled, SQL Server applies the FILLFACTOR option to the intermediate-level pages of the index. When the option is disabled, SQL Server fills the intermediate index pages almost fully, with minimal space left for one additional maximum-sized row. |
Clustered Nonclustered Primary XML Secondary XML Spatial |
| Sort in tempdb | Storage | When the option is enabled, SQL Server uses the tempdb system database for sorting during index creation, after which the completed index is written to the target database. When the option is disabled, SQL Server performs the sort operation within the user database. |
Clustered Nonclustered Primary XML Secondary XML Spatial |
| Expression | Filter | Specify a WHERE clause to include only specific rows. |
Clustered Nonclustered |
| Cells per Object | Spatial General | Defines the maximum number of cells that tessellation can count per object. | Spatial |
| Tessellation Scheme | Spatial General | Identifies a tessellation scheme for the index. | Spatial |
| X-min | Spatial Bounding box | Identifies an x-coordinate of the lower-left corner of the bounding box. | Spatial |
| Y-min | Spatial Bounding box | Identifies a y-coordinate of the lower-left corner of the bounding box. | Spatial |
| X-max | Spatial Bounding box | Identifies an x-coordinate of the upper-right corner of the bounding box. | Spatial |
| Y-max | Spatial Bounding box | Identifies a y-coordinate of the upper-right corner of the bounding box. | Spatial |
| Level 1 | Spatial Grids | Represents coarsest grid cells (lowest resolution). | Spatial |
| Level 2 | Spatial Grids | Represents medium grid cells. | Spatial |
| Level 3 | Spatial Grids | Represents finer grid cells. | Spatial |
| Level 4 | Spatial Grids | Represents finest grid cells. | Spatial |
Storage
The table describes storage options.
| Name | Description | Used for |
|---|---|---|
| Regular data space | Specifies the filegroup where the main table data will be physically stored. To update a list of filegroups, click Note: PRIMARY is the default filegroup created with the database unless otherwise specified.Shortcut: Ctrl+R |
Clustered Nonclustered Spatial Clustered columnstore Nonclustered columnstore |
| Partition column | Defines a column that splits the data in multiple partitions, each stored in a different filegroup. When the setting is disabled, partitioning is not configured for this table. |
Clustered Nonclustered Spatial Clustered columnstore Nonclustered columnstore |
| Filestream data space | Defines where SQL Server will store FILESTREAM-enabled columns. When it is set to <Default>, it implies that FILESTREAM data (binary large objects, such as documents or images) will use the default storage settings. To update a list of filegroups, click Shortcut: Ctrl+R |
Clustered Nonclustered Spatial Clustered columnstore Nonclustered columnstore |
| Text/Image filegroup | Controls where to store TEXT, NTEXT, or IMAGE data types.To update a list of filegroups, click Shortcut: Ctrl+R |
Clustered Nonclustered Spatial Clustered columnstore Nonclustered columnstore |
Fragmentation
The fragmentation settings are available only for clustered and nonclustered indexes. They determine how data is distributed and stored in a database based on the primary/unique key. They include size, leaf-level rows, average row size, maximum and minimum row size, etc.
Usage Statistics
Usage statistics is available only for clustered and nonclustered indexes. It lets you monitor operations, such as reads, writes, or page I/O used by the index in the database.
Save the changes
An asterisk ( * ) on the table editor tab title indicates that there are unsaved changes.
To save and apply them, on the Table Editor toolbar, select Apply Changes.
Note
Use Ctrl+F to locate column definitions or table settings in the DDL script.