Table Editor overview
Table Editor is a visual tool to create, modify, and manage table structures within a database. You can define columns, data types, constraints, such as primary and foreign keys, unique constraints, indexes, and other table properties without writing SQL manually. You can also view the table data and preview a T-SQL script generated automatically.
Key features of Table Editor:
- Creating and modifying tables using a graphical interface without manual SQL.
- Defining column properties, data types, default values, constraints, and indexes.
- Renaming columns and editing table properties, such as comments, directly in the editor.
- Generating and previewing T-SQL scripts for user-defined changes.
- Managing DML triggers for table events, such as
INSERT,UPDATE, andDELETE. - Viewing and managing column statistics for query optimization.
- Configuring storage settings, including filegroups and partitioning.
Open Table Editor
To open Table Editor, do one of the following:
- In Database Explorer, right-click a database and select New Object > Table.
- In Database Explorer, right-click the Tables node and select New Table.
- In Database Explorer, right-click a table and select New Table and Open Editor.
Note
Selecting Open Editor opens Table Editor to modify an existing table.
Table Editor includes the following sections:
- Tabs - Provides access to specific editors, such as Columns, Constraints, Indexes, Statistics, Triggers, Storage, Data, and T-SQL.
- Table Details area - Displays a table name, a schema it belongs to, and a table description.
- Table Editor toolbar - Allows you to refresh the table and apply or script changes.
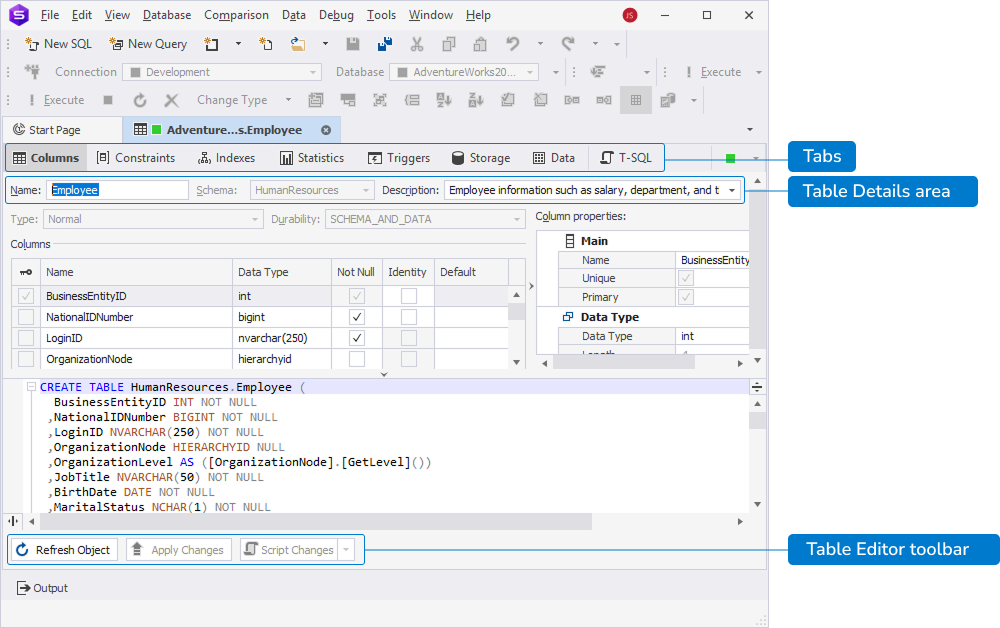
Table details area
You can specify the following details:
- Name – Enter the table name.
- Schema – Select the schema from the list to which the table belongs. The default schema is dbo.
- Description – Enter a table description and select OK to save the changes or Cancel to discard them.
Note
If you’re editing an existing table, you cannot update a schema.
Tabs
Tabs include:
- Columns – Displays and lets you manage table columns, including column names, data types, nullability (NULL/NOT NULL), default values, identity properties, and computed column settings if applicable.
- Constraints – Shows and allows you to edit rules that restrict the data in the table.
- Indexes – Displays and lets you manage indexes applied to the table, including the index name, types, indexed columns, uniqueness, etc. to speed up searches, joins, and sorts, and to improve query performance.
- Statistics – Shows and lets you view statistical data about the distribution of values in the table columns.
- Triggers – Shows triggers associated with the table.
- Storage – Displays how and where the table data is physically stored, including filegroups, partitioning info, space used, and row/page count.
- Data – Allows you to view and directly edit the table data.
- T-SQL – Displays the generated Transact-SQL script for the table structure, including any changes that have been made.
Note
After opening Table Editor, you can also use the top View menu to navigate between tabs.
Table Editor toolbar
On the Table Editor toolbar, you can do the following:
- Refresh Object - Updates the table to reflect the latest changes.
- Apply Changes - Saves and applies changes made to the table.
- Script Changes - Generates a SQL script, allowing you to review, modify, or execute the script manually instead of applying changes immediately.
- To script changes to a new SQL document, select the To New SQL Window option from the Script Changes list or press Shift+Alt+C.
- To copy to the clipboard, select the To Clipboard option from the Script Changes list.
Save the changes
An asterisk ( * ) on the table editor tab title indicates that there are unsaved changes. To save and apply them, select Apply Changes.
Note
Use Ctrl+F to locate column definitions or table settings in the DDL script.