Source Control overview
dbForge Studio for SQL Server enables version control for SQL Server databases. It connects your databases to popular source control systems - including Subversion (SVN), Microsoft Azure DevOps (TFVC), Git (with support for GitHub, GitLab, Bitbucket, and Azure DevOps), Perforce (P4), Mercurial, and SourceGear Vault - and tracks changes to database schemas and static data.
Key features of dbForge Source Control:
- Linking databases to version control repositories and keeping track of any changes made to the databases.
- Viewing and comparing differences between the database local copy and the remote repository.
- Viewing the change history – who made the changes, when, and why.
- Comparing the differences between the two change history versions.
- Managing and resolving conflicts between local and remote database copies.
- Supporting a shared or dedicated database development model.
- Rolling back changes in case of errors.
- Highlighting differences in the code of the local and remote database copies.
- Linking a database to a working folder.
How dbForge Source Control works
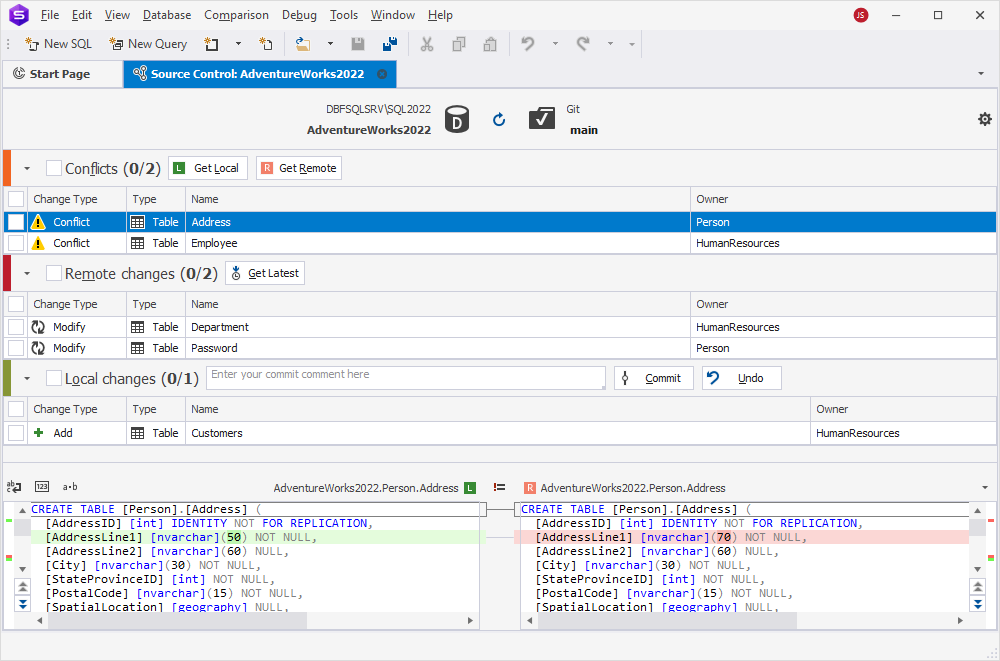
To begin, link a database or static data to a remote repository or working folder. dbForge Studio for SQL Server compares the current version of your database with the version in source control and opens the Source Control Manager, which displays changes to the database schema and static data.
Based on the detected changes, the Source Control Manager may display one, two, or all three of the following sections:
- Local changes – Allows you to commit changes to source control or undo them.
- Remote changes – Allows you to retrieve remote changes from source control and deploy them to the database.
- Conflicts – Allows you to resolve conflicts that occur when multiple developers modify the same object.
When you select a database object in the Source Control Manager, the bottom pane displays the differences between the local version and the version in the repository.
This comparison view helps you understand what has been added, removed, or modified before committing or applying changes.