Review the action plan and warnings
You can review the synchronization action plan and any warnings that may affect synchronization on the Summary page of the Data Synchronization Wizard.
Open the Data Synchronization Wizard
You can open the Data Synchronization Wizard in one of these ways:
-
At the top of the document, click
 .
. -
Right-click the grid and select Synchronize.
-
Press F8.
-
On the Comparison toolbar, click
 .
.
Action plan
On the Action Plan tab of the Summary page, you can view synchronization actions in the order they are to be performed. The action plan is organized in collapsible categories.
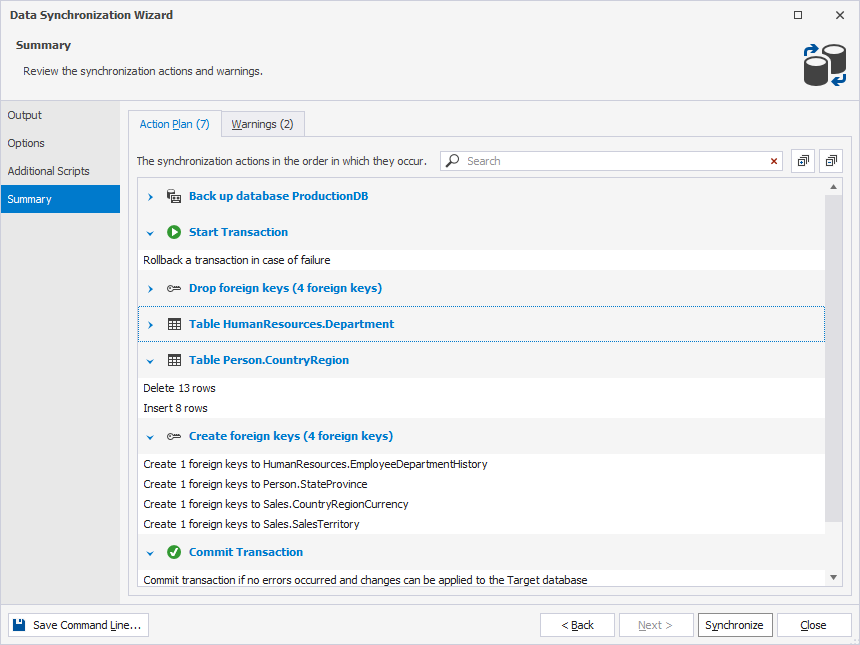
Expand the action plan
You can expand all sections in the action plan in one of these ways:
-
Right-click the action plan and select Expand all.
-
In the upper-right corner of the page, click
 .
.
Collapse the action plan
You can collapse all sections in the action plan in one of these ways:
-
Right-click the action plan and select Collapse all.
-
In the upper-right corner of the page, click
 .
.
Search for options
To search for options, type a search query in the search box.
Search behavior:
- Matching text is highlighted in yellow.
- The number of matches appears in the search box.
- The search is case-insensitive. For example, searching for Backup matches Backup and backup.
- If the query contains multiple words, each word is matched separately, and all matches are highlighted.
To clear the search results, click  in the search box.
in the search box.
Keyboard shortcuts in the search box
The table provides keyboard shortcuts you can use in the search box.
| Keyboard shortcut | Description |
|---|---|
| Ctrl+A | Selects all. |
| Ctrl+Left Arrow (←) | Moves the caret to the beginning of the word. |
| Ctrl+Right Arrow (→) | Moves the caret to the end of the word. |
| Ctrl+Shift+Left Arrow (←) | Selects text from the current caret position to the beginning of the current word and moves the caret to the beginning of the word. |
| Ctrl+Shift+Right Arrow (→) | Selects text from the current caret position to the end of the current word and moves the caret to the end of the word. |
| Ctrl+Backspace | Deletes the word to the left of the caret. |
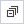
Warnings
The Warnings tab lists issues that may affect synchronization. Warnings appear only when updates or insertions are required in the target table.
If warnings are present, synchronization may fail or result in data loss, for example, due to truncation or rounding. A warning with an error icon indicates an issue that will definitely occur when the synchronization script is executed.
To avoid this, exclude the affected tables or records by clearing their checkboxes in the Data Comparison results grid.
Note
Review all synchronization warnings carefully and exclude any database objects that may cause errors during synchronization.
Synchronization warnings
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Disable foreign key | A foreign key might not recover after synchronization. |
| Foreign key Warning | Table X has a foreign key to table Y. Synchronization may fail. |
| Keys and Indexes Warning | Synchronization may cause loss of disabled keys and indexes. |
| ‘Restore constraints with CHECK’ option is enable | If the Restore constraints with CHECK option is selected, the constraints dropped before synchronization will be restored with data checking. This may result in an error, and constraints will not be restored. |
| ‘Reseed identity columns’ option is enabled | If the table contains data, setting the IDENTITY value to less than the current maximum in the identity column may lead to one of the following results:
|
| History table Warning Exclude | Historical tables are not included in synchronization; additions, deletions, or updates to a temporal table are not reflected in the historical table. |
| History table Warning Include | Synchronizing the history table may cause a conflict if the link between the temporal and history tables is broken and cannot be reestablished. |
| Conversion Incompatible | Columns A and B have incompatible types. |
| Source column allows Nulls which can not be stored in target | The source column allows NULL values which can not be stored in the target column; data migration may cause an error. |
| Conversion is possible, but may fail in case of incompatible data | Conversion between columns A and B is possible, but may fail in case of incompatible data. |
| Columns have different precisions | Columns A and B have different precisions; data migration may cause overflow. |
| Date or time columns have different data format | Columns A and B with date or time have different data format; data migration may cause truncation. |
| Decimal columns have different precisions or scales | Columns A and B with decimal have different precisions or scales; data migration may cause rounding or overflow. |
| Decimal and Integer columns have different precisions | Columns A and B with decimal and integer have different precisions; data migration may cause rounding or overflow. |
| Float and Integer columns have different precisions | Columns A and B with float and integer have different precisions; data migration may cause rounding or overflow. |
| Numeric columns have different precisions or scales | Columns A and B with numeric have different precisions or scales; data migration may cause rounding |
| Columns have different sizes | Columns A and B have different sizes; data migration may cause truncation |
| Columns have different collations | Columns A and B have different collations. |
| XML columns have different XML collection types | Columns A and B have different XML collection types. |
| XML columns have different storage types CONTENT or DOCUMENT | Columns A and B with xml have different storage types: CONTENT or DOCUMENT. |
| Computed column is not mapped as PERSISTED | Columns can’t be mapped because one of them was excluded from comparison. A computed column must be marked as PERSISTED. |