How to set up automatic log sending in the event of a comparison error
Automatic log sending in case of a database comparison error ensures prompt notification, efficient troubleshooting, proactive issue resolution, and the availability of historical documentation, all of which contribute to maintaining a reliable and robust comparison process.
The functionality of dbForge Schema Compare for SQL Server allows the user to configure the automatic sending of the schema comparison log file in case of comparison failure. More than that, the user can explicitly specify in the BAT file the exit codes to trigger email sending. In this article, we will provide a step-by-step walkthrough of how to achieve that.
Prerequisites
Installed and configured SMTP server
Workflow
- Create a PowerShell script file to email a log file
- Create a .bat file to initiate schema comparison
- Launch the .bat file
Create a PowerShell script file to email a log file
To begin with, you need to create a file with the PowerShell script to send a log file from a specified location on your PC to a desired email address using an SMTP server.
To create a PowerShell script file:
1. In a third-party text editor, such as Notepad, Notepad++, or Visual Studio Code, open a new blank document.
2. Enter the following script:
#Input data:
$From = "[email protected]"
$To = "[email protected]"
$SMTPServer = "smtp.gmail.com"
$SMTPPort = "587"
$Username = "[email protected]"
$Password = "[password]"
$subject = "Synchronization log"
$body = "Database synchronization failed"
$file = "D:\logs\CompareResult.log"
#Message in the HTML format:
$message = New-Object System.Net.Mail.MailMessage $From, $To
$message.Subject = $subject
$message.IsBodyHTML = $true
$message.Body = $body
$att = new-object Net.Mail.Attachment($file)
$message.Attachments.Add($att)
#Recipient info:
$smtp = New-Object System.Net.Mail.SmtpClient($SMTPServer, $SMTPPort)
$smtp.EnableSSL = $true
$smtp.Credentials = New-Object System.Net.NetworkCredential($Username, $Password)
$smtp.Send($message)
$att.Dispose()
Where:
$From is the sender’s email address
$To is the recipient’s email address
$SMTPServer is the mail server address that forwards emails from a sender to a recipient
$SMTPPort is the port for encrypted email transmissions using SMTP Secure (SMTPS)
$Username is the username for SMTP Gmail
$Password is the SMTP app password
$subject is the email subject
$body is the email body
$file is the path to a log file to be sent
Note
You need to modify the variables in the script to align with your specific working context.
3. Save the file with a .ps1 extension.
Create a .bat file to initiate schema comparison
The next step is to create a .bat file that will initiate schema comparison, generate a log file, and in the event of an exit code 40 or 100, sends a log file to a specified email address.
To create a .bat file:
1. In a third-party text editor, such as Notepad, Notepad++, or Visual Studio Code, open a new blank document.
2. Enter the following script:
Set Compare="C:\Program Files\Devart\Compare Bundle for MySQL Standard\dbForge Schema Compare for MySQL\schemacompare.com"
Set Sender= powershell.exe
Set HostS= [source server name]
Set HostT= [target server name]
Set DB1= SakilaDev
Set DB2= SakilaTest
%compare% /schemacompare /source connection:"User Id=<username>; Database=%DB1%; Host=%HostS%; Port=3306; Password=<password>; Character Set=utf8" /target connection:"User Id=<username>; Database=%DB2%; Host=%HostT%; Port=3306; Password=<password>; Character Set=utf8" /log:"D:\logs\CompareResult.log"
echo exitcode: %ERRORLEVEL%
set Send=F
if %ERRORLEVEL% EQU 40 set Send=T
if %ERRORLEVEL% EQU 100 set Send=T
if %Send%==T (%Sender% -File D:\logs\SendLog\sendlog.ps1)
Where:
- Set Compare is a path to dbForge Schema Compare for SQL Server
- Set Sender is a tool that will execute a Powershell script
- Set HostS is the source database connection
- Set HostT is the target database connection
- Set DB1 is the name of the source database
- Set DB2 is the name of the target database
- User Id is a user name to connect to a database
- Password is a password to connect to a database
Note
You need to modify the variables in the script to align with your specific working context.
Note
You can modify the script to send a log file in the event of another exit code. Refer to the Exit codes used in the command line documentation topic to see the list of all Schema Compare’s exit codes.
3. Save the file with the .bat extension.
Launch the .bat file
Now, launch the .bat file.
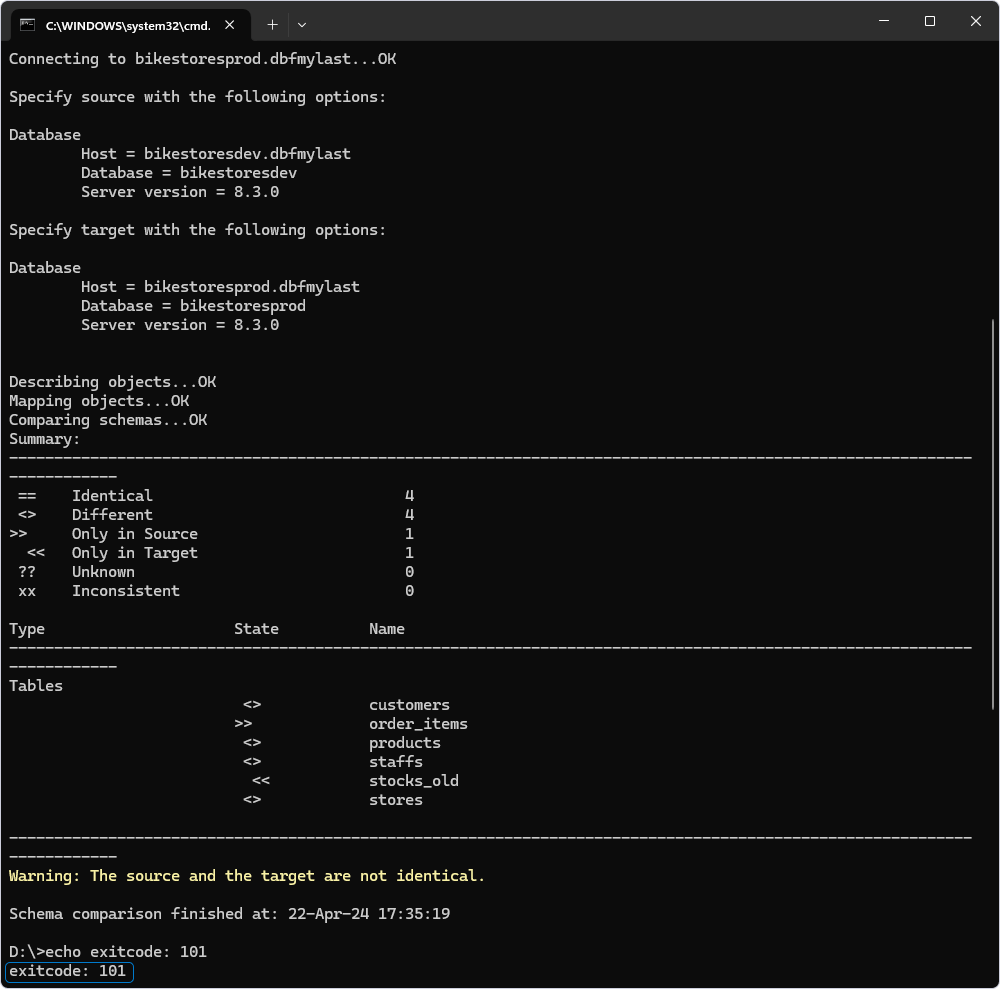
In our example, the databases are not identical, and the script returns the exit code 101. You can navigate to the log file and see the result.
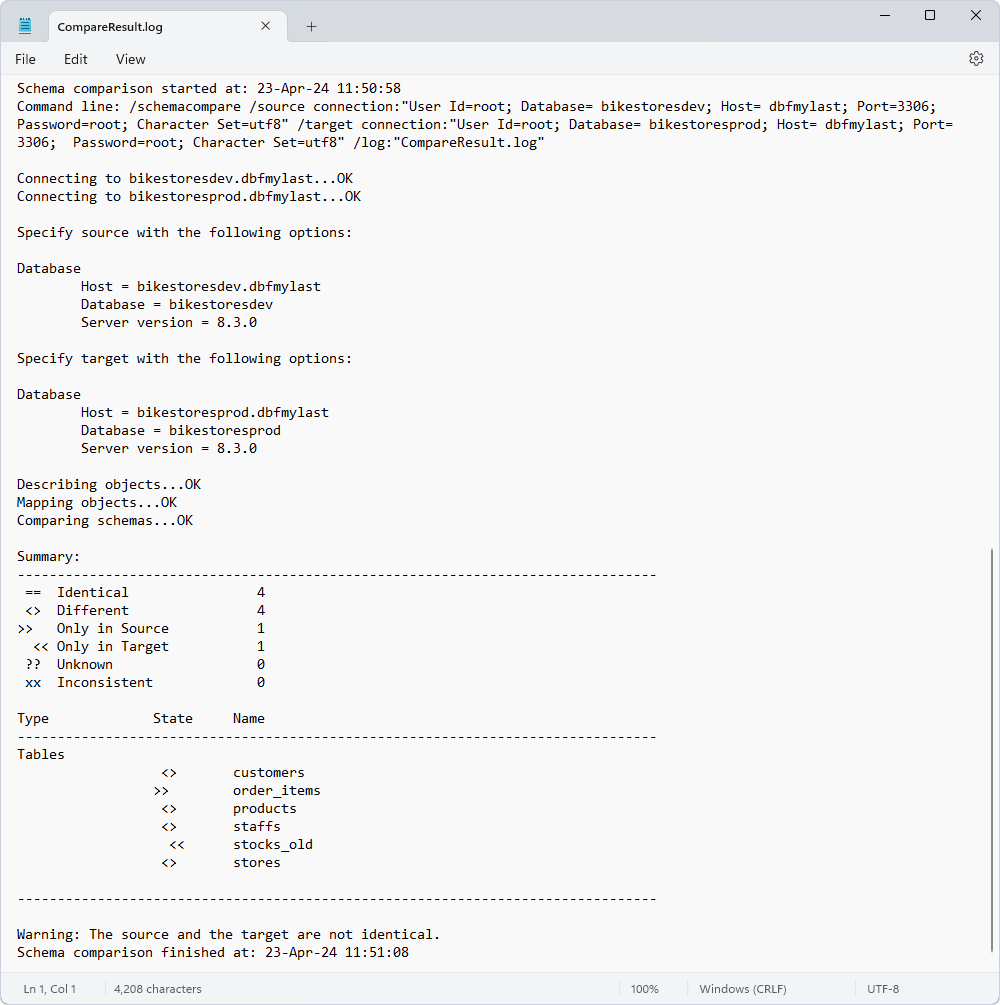
When the exit code 100 is encountered, the log file is sent to the email address specified in the script.
Note
You can schedule the .bat file execution using the Windows Task Scheduler so the computer can perform the task automatically.