
|
Connect to MySQL from Python using SSH |
|
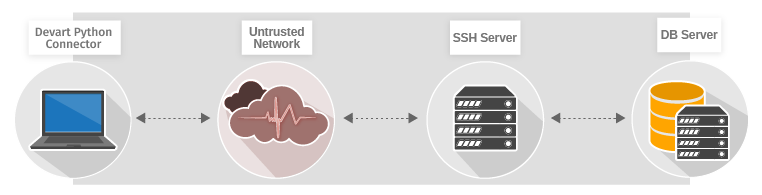
Secure Shell (SSH) is a cryptographic protocol for secure remote login, command execution, and file transfer over untrusted networks. It uses a client-server model to authenticate two parties and encrypt the data between them. All user authentication, commands, output, and file transfers are encrypted to protect against attacks in the network. The client and server authenticate to each other and exchange commands and output. SSH uses symmetric encryption, assymetric encryption, and hashing to secure the transferred data.
In symmetric key cryptography, a single key is used by both the sending and receiving parties to encrypt and decrypt messages. Assymetric encryption, on the other hand, requires two associated keys—the private key and the public key. The public key encrypts messages that can only be decrypted with the private key. The public key can be freely shared with any trusted party, while the private key must be kept secret. The client public key is stored in a location that is accessible by the SSH server, allowing the client to authenticate the server. Similarly, the server public key is placed on the client side, enabling the server to authenticate the client. Assymetric encryption is used during the initial key exchange process to generate a shared secret (session key) that encrypts messages for the duration of the session.
Our connector implements the SSH client functionality that enables you to connect to the SSH server on the remote machine. The SSH server listens for incoming TCP connections. The SSH client begins the initial TCP handshake with the server and verifies the server's identity. The client and server agree upon the encryption protocol and negotiate a session key. The server then authenticates the client and spawns a shell. The SSH server authenticates the client and allows the connector to establish a secure direct connection to MySQL.
import devart.mysqlconnect() module method and obtain a connection object.
my_connection = devart.mysql.connect(
Server="your_server",
Database="your_database",
UserId="your_username",
Password="your_password",
UseSSH="True",
SSHHostName="your_ssh_host",
SSHUserName="your_ssh_user",
SSHClientKey="path_to_priv_client_key",
SSHServerKey="path_to_pub_host_key",
SSHStoragePath="path_to_ssh_storage"
)Note: You don't have to install the SSH client on the client machine since the connector already implements the SSH client functionality.
The following table describes the SSH connection parameters.
|
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Enables SSH connections. |
|
|
The hostname or IP address of the SSH server |
|
|
The SSH port number. The default port is 22. |
|
|
The name of the SSH user |
|
|
The password of the SSH user. It's recommended that you also use an SSH key. |
|
|
The path to the client private key |
|
|
The passphrase for the client private key |
|
|
The path to the public host key |
|
|
The location where the connector will store its configuration files on the client machine |