
|
ODBC Driver for Amazon Redshift SSL Connection to Amazon Redshift via ODBC Driver |
|

|
ODBC Driver for Amazon Redshift SSL Connection to Amazon Redshift via ODBC Driver |
|
SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) is a standard protocol for secure access to a remote machine over untrusted networks. It runs on top of TCP/IP to secure client-server communications by allowing an SSL-enabled client to authenticate itself to an SSL-enabled server and vice versa. During server authentication, an SSL-enabled client application uses standard techniques of public-key cryptography to verify the server's identity by checking that the server's certificate is issued by a trusted certificate authority (CA) and proves the ownership of the public key.
Conversely, SSL client authentication allows the server to validate the client's identity. The client and server can also authenticate each other using self-signed certificates. However, you will rarely want to use a self-signed certificate, except for an Intranet or a development server. After establishing an SSL connection, the client and server can exchange messages that are symmetrically encrypted with the shared secret key. SSL is the recommended method to establish a secure connection to Amazon Redshift due to its easier configuration and higher performance, compared to SSH.
See the Amazon Redshift documentation for more information on how to configure security options.
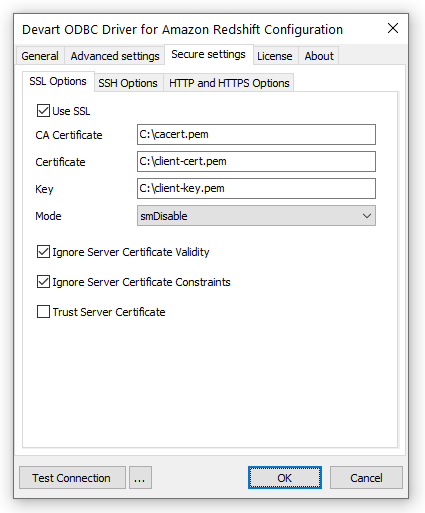
To establish an SSL connection to Amazon Redshift, specify the SSL certificates and client private key:
|
Option |
Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Enables SSL connections. |
|
|
The CA certificate. |
|
|
The client certificate. |
|
|
The private client key. |
|
|
The password for the private client key. Leave it empty if the client key is not encrypted. |
|
|
Specifies whether to check the server certificate validity period during an SSL handshake. The default value is |
|
|
Specifies whether to verify the server certificate for compliance with constraints during an SSL handshake. The default value is |
|
|
Specifies whether to verify the server certificate during an SSL handshake. By default, the driver verifies the server certificate. When the option is set to |
|
|
Specifies whether to verify the security of the server certificate's signature during an SSL handshake. The default value is |
|
|
Specifies whether and with what priority an SSL connection will be negotiated with the server. smRequire
The default value. Only SSL connections are allowed.
smPrefer
Negotiates, first trying an SSL connection, then if it fails, tries a regular non-SSL connection.
smAllow
Negotiates, first trying a non-SSL connection, then if it fails, tries an SSL connection.
smVerifyCA
Verifies the server's identity by validating the server certificate chain up to the root certificate installed on the client machine.
smVerifyFull
Verifies the server's identity by validating the server certificate chain up to the root certificate installed on the client machine and checks that the server's hostname matches the details in the server certificate.
|
|
DRIVER={Devart ODBC Driver for Amazon Redshift};Data Source=myServer;Database=myDatabase;User ID=myUsername;Password=myPassword;Port=myPort;Use SSL=True;SSL CA Cert=C:\myCaCertificate.pem;SSL Cert=C:\myClientCertificate.pem;SSL Key=C:\myPrivateClientKey.pem |