Connect to Oracle using SSH
SSH (Secure Shell) is a cryptographic network protocol that enables secure remote login, command execution, and file transfer over untrusted networks. It uses a client-server architecture, where an SSH client communicates with an SSH server. Both parties authenticate each other and exchange encrypted data.
To secure the transmitted data, SSH employs several cryptographic techniques:
- Symmetric encryption: Uses a single shared key to encrypt and decrypt messages.
- Asymmetric encryption: Uses a key pair—public and private. The public key encrypts data, while the private key decrypts it. The public key can be shared freely, whereas the private key must remain confidential. Asymmetric encryption is primarily used during the initial handshake to produce a shared secret (session key), which is then used for symmetric encryption throughout the session. After the symmetric encryption has been established, SSH key pairs can be used for authentication. The client’s public key must be stored on the SSH server to authenticate the client, and the server’s public key must be stored on the client side to authenticate the server.
- Hashing: Ensures data integrity by verifying that transmitted data hasn’t been altered.
The SSH server typically listens for incoming TCP connections on port 22 (can be changed). The SSH client initiates a TCP handshake and verifies the server’s identity. The client and server negotiate the encryption protocol and generate a shared session key. The server then authenticates the client and initiates the appropriate user environment for the session. ODBC Driver for Oracle includes built-in SSH client functionality, allowing it to connect to an SSH server and establish a secure direct connection to Oracle. A simplified SSH tunneling process is presented on the following diagram.
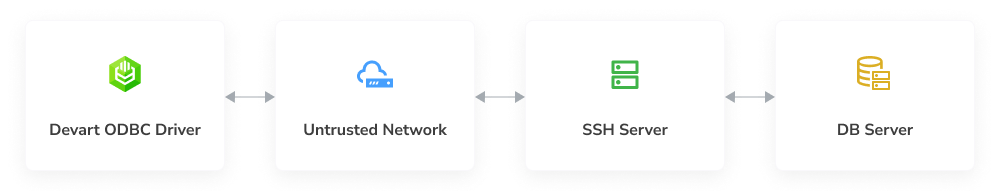
Note
You don’t need to install a separate SSH client—this functionality is integrated into the ODBC Driver for Oracle.
Configure the connection
1. Open ODBC Data Source Administrator, select your DSN, and click Configure.
2. Select Security Settings > SSH Options.
3. Select Use SSH.
4. Fill out the fields with the connection details:
- Host Name – The host name or IP address of the SSH server.
- Port – The SSH port number.
- User Name – The username for the SSH server account.
- Password – The password for the SSH server account.
- Client Private Key – The name of the client’s private key file for key-based authentication.
- Password for Key – The passphrase for the client’s private key.
- Server Public Key – The name of the SSH server’s public key file.
- Storage Path – The full path to the directory where encryption keys are stored.
Tip
When connecting to Oracle Cloud, you can use the default username opc. In this case, you don’t need to specify the password and the server’s public key.

SSH connection options
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
Use SSH |
Enables SSH tunneling. |
SSH Host name |
The host name or IP address of the SSH server. |
SSH Port |
The SSH port number (default is 22). |
SSH User Name |
The username for the SSH server account. Oracle Cloud: You can use the default username—opc. |
SSH Password |
The password for the SSH server account. Oracle Cloud: If you’re using opc as the username, leave empty. |
SSH Client Key |
The name of the client’s private key file for key-based authentication. |
SSH Client Key Password |
The passphrase for the client’s private key. |
SSH Server Key |
The name of the SSH server’s public key file. Oracle Cloud: Leave empty. |
SSH Storage Path |
The full path to the directory where encryption keys are stored. |
Sample connection string
DRIVER=Devart ODBC Driver for Oracle;Direct=True;Host=myHost;Service Name=myServiceName;User ID=myUsername;Password=myPassword;Use SSH=True;SSH Host name=mySshHost;SSH User Name=mySshUsername;SSH Password=mySshPassword;SSH Client Key=myPrivateClientKey.pem;SSH Client Key Password=myClientKeyPassphrase;SSH Server Key=myPublicServerKey.pem;SSH Storage Path=myDirectoryWithKeys