Connect SQL Server to Oracle
You can use a linked server in SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS) to connect to Oracle. Linked servers enable you to implement distributed databases and retrieve or modify data in other databases and cloud service providers. This approach facilitates integration with heterogeneous data sources, providing a unified method for accessing and managing disparate data sets from any origin. By creating linked servers for each data source, you can perform distributed queries and transactions directly within SSMS, regardless of where your data resides.
Prerequisites
- The driver and SQL Server must be installed on the same computer.
- A system DSN must be created for your data source. For instructions, see Configure a Windows DSN for Oracle.
- The driver, DSN, and SQL Server must be of the same bitness. For example, if you’re using a 64-bit SQL Server, install the 64-bit version of the driver and configure a 64-bit DSN.
Create a linked server
1. Connect to your SQL Server instance in SSMS.
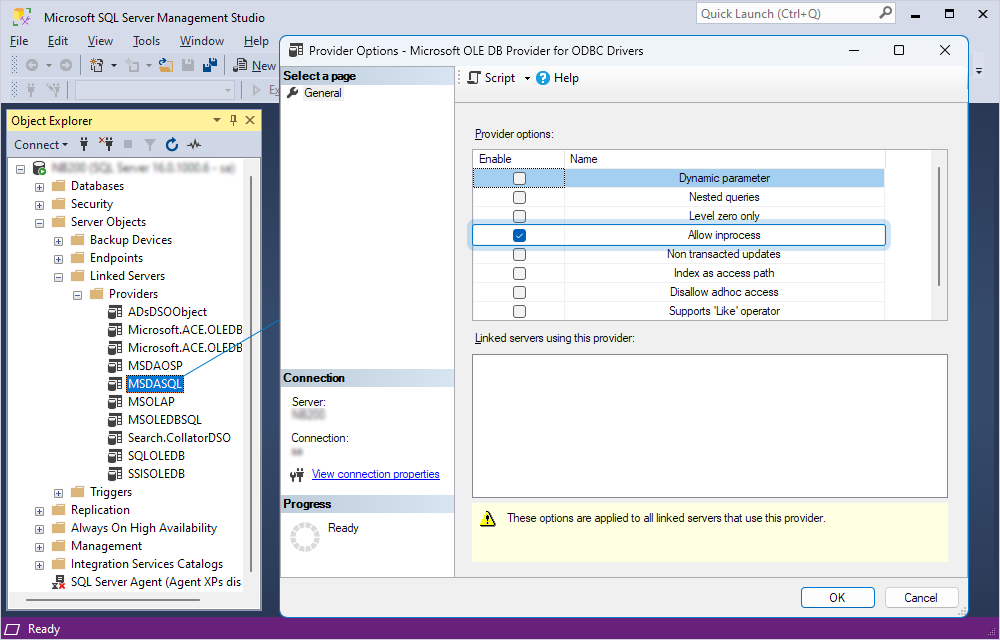
2. In the Object Explorer pane, select Server Objects > Linked Servers > Providers.
3. Double-click MSDASQL, then select Allow inprocess.
4. Click OK.
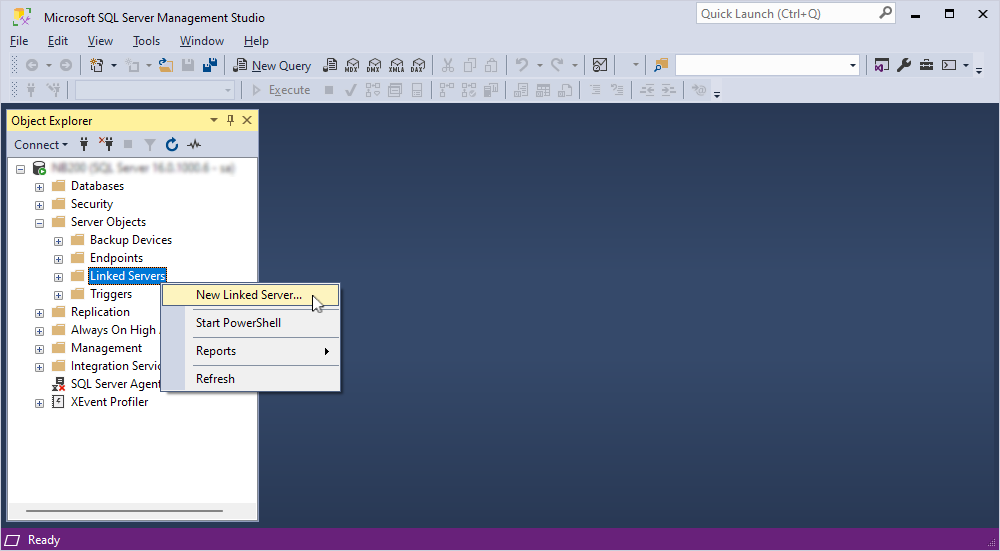
5. Right-click Linked Servers, then select New Linked Server.
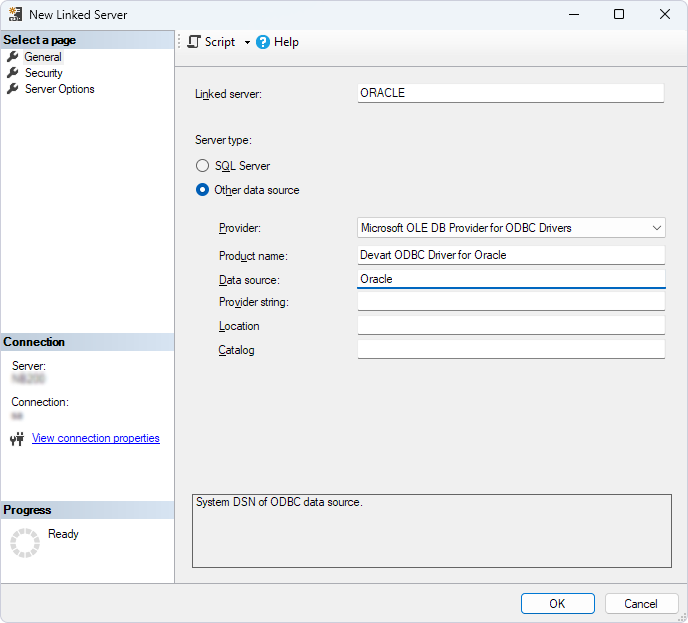
6. In the New Linked Server dialog, fill out the fields with the connection details:
- Linked server – Enter a name for the linked server.
- Server type – Select Other data source.
- Provider – Select Microsoft OLE DB Provider for ODBC Drivers.
- Product Name – Optional. You can enter Devart ODBC Driver for Oracle to remember what you used to set up the connection.
- Data source – Enter the name of your DSN.
Tip
You can enter the driver connection string in the Provider string field instead of specifying the Product Name and Data source.
7. Click OK.
A new linked server appears under Linked Servers.
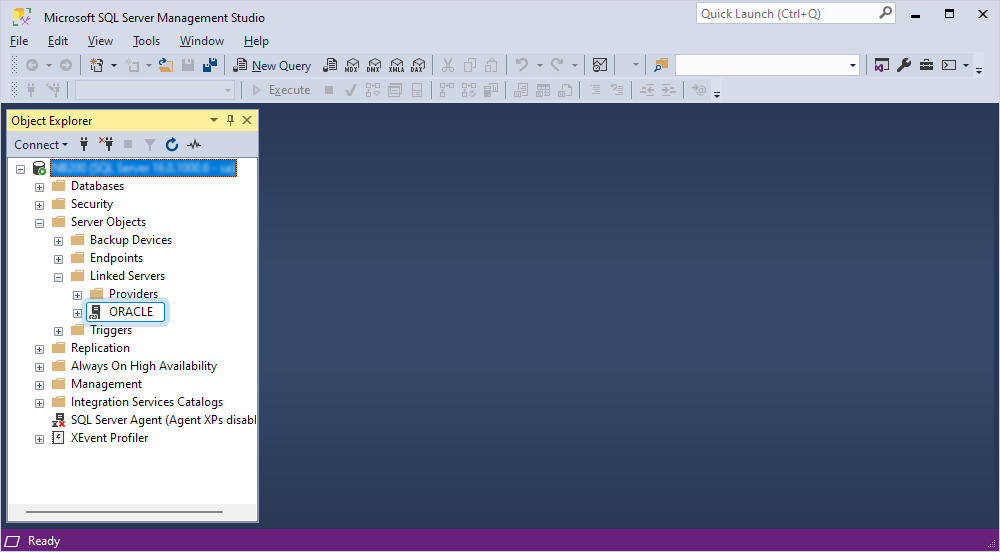
Retrieve data from Oracle
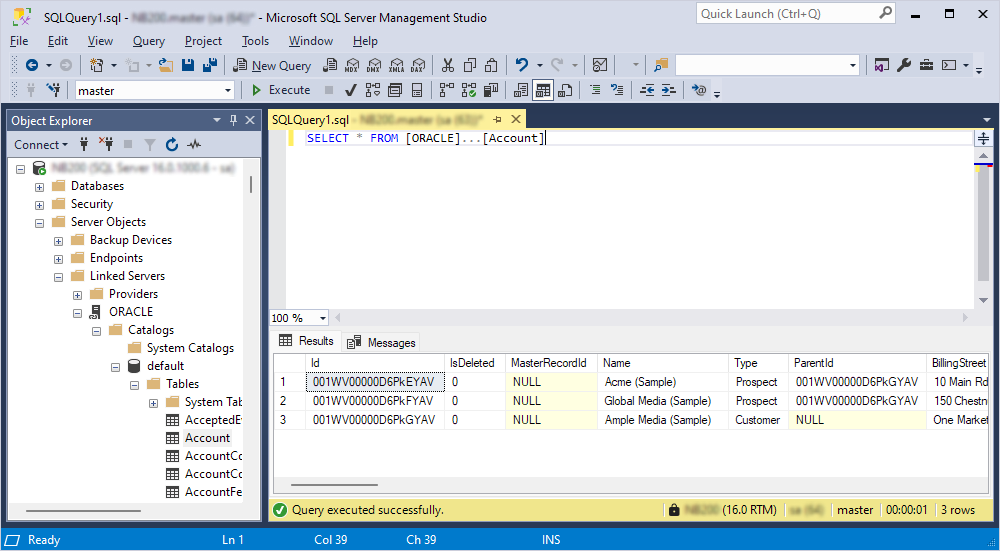
1. Click New Query on the toolbar.
2. Enter a SQL query in the following format:
SELECT * FROM [<linked_server_name>].[<database_name>].[<schema_name>].[<table_name>];
where [<linked_server_name>] and [<table_name>] are required, and [<database_name>] and [<schema_name>] are optional.
3. Click Execute.
The results are displayed under the query text window.