Connect to PostgreSQL using SSL
SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) is a standard protocol that secures communication between a client and a server over untrusted networks. It operates on top of TCP/IP and uses public-key cryptography to authenticate both parties and encrypt data transmission.
During server authentication, the SSL-enabled client verifies the server’s identity by checking that its certificate is issued by a trusted Certificate Authority and that it owns the corresponding public key.
Client authentication allows the server to verify the client’s identity. While self-signed certificates can be used for mutual authentication, they are generally recommended only for intranet or development environments.
After the SSL connection is established, both parties exchange data using symmetric encryption with a shared secret key. Compared to SSH, SSL is often preferred for PostgreSQL connections due to its simpler configuration and better performance.
For more information, see the PostgreSQL documentation: Secure TCP/IP Connections with SSL.
To connect to PostgreSQL using SSL:
1. In the ODBC Data Source Administrator, select your DSN, then click Configure.
2. Select the Security Settings tab.
3. Select Use SSL.
4. Fill out the fields with the connection details:
- CA Certificate – The certificate of the Certificate Authority.
- Certificate – The client’s certificate.
- Key – The client’s private key.
- Key Password – The password for the private key, if it’s encrypted.
- Mode – The SSL negotiation method and verification level used for connecting to the server. For more information, see SSL connection options.
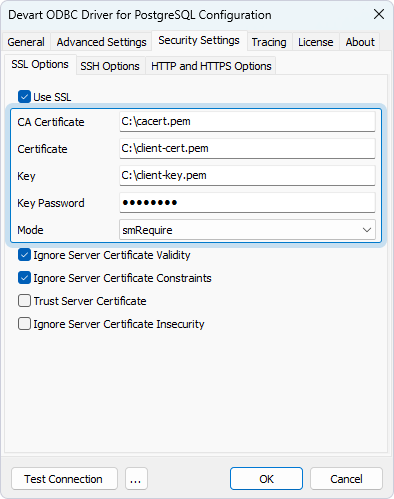
SSL connection options
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
Use SSL |
Enables SSL connections. |
CA Certificate |
The full path to the Certificate Authority certificate file. |
Certificate |
The full path to the client certificate file. |
Key |
The full path to the private client key file. |
Key Password |
The password for the private client key. Leave empty if the key isn’t encrypted. |
Ignore Server Certificate Validity |
If True, skips checking the validity period of the server certificate during the SSL handshake. The default value is True. |
Ignore Server Certificate Constraints |
If True, skips checking the server certificate for compliance with constraints. The default value is True. |
Trust Server Certificate |
If True, skips validating the certificate chain and trusts the server certificate. The default value is False. |
Ignore Server Certificate Insecurity |
If True, skips verifying the security of the server certificate’s signature. The default value is False. |
Mode |
Specifies how SSL connections are negotiated with the server and the level of verification applied. Available values:
|
Sample connection string
DRIVER={Devart ODBC Driver for PostgreSQL};Data Source=myServer;User ID=myUser;Password=myPassword;Database=myDatabase;Use SSL=True;SSL CA Cert=C:\myCaCertificate.pem;SSL Cert=C:\myClientCertificate.pem;SSL Key=C:\myPrivateClientKey.pem