This section describes some of the column parameters that you can define when setting up the properties of entities in Entity Developer.
You can open the Column Editor dialog is accessible by clicking the ![]() ellipsis button on the right side of the Column field or by pressing Alt+E keys in the following dialogs:
ellipsis button on the right side of the Column field or by pressing Alt+E keys in the following dialogs:
| • | Association Editor |
| • | Class Editor |
| • | Complex Type Editor |
| • | Inheritance Editor |
| • | Join Tables Editor |
| • | Property Editor |
You can define the following parameters in the Column Editor dialog:
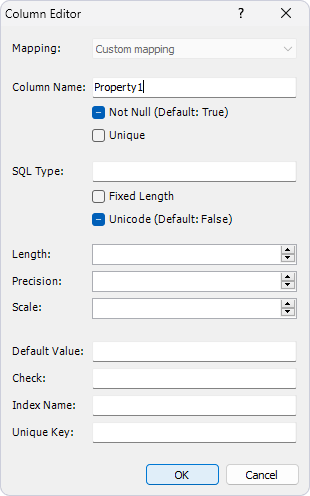
 Mapping
Mapping
The Mapping drop-down list sets the property mapping type to the column. For scalar properties, the value of this field is set to Custom mapping and cannot be changed. For properties of component type, one of the following values can be selected:
You can select mapping when you open a class editor and click the For more information, see the Component Mapping topic. |
By default, the column name is identical to the name of the corresponding property and follows the requirements defined in the naming sections of the Model Settings dialog. If, at some stage of model development, the naming rules or the name of the corresponding property is changed for any reason, the default column name is changed accordingly. However, you can set a custom name for the column by entering it in the Column Name field. Additionally, you can prohibit the use of null values in a column (by selecting the Not Null checkbox) and to create a unique key constraint on a column (by selecting the Unique checkbox).
|
In the Column Editor dialog, you can also make optional adjustments to the column data type. The SQL Type field specifies the type of the column that is to be created in the database. If this parameter is specified, the Fixed Length and Unicode checkboxes become unavailable. If selected, the Fixed Length checkbox indicates that the column stores fixed-length data for CHAR, BIT or BINARY data types on the server side. A CHAR/BINARY column is created instead of VARCHAR/VARBINARY. If selected, the Fixed Length checkbox specifies that the column stores fixed-length data for CHAR, BIT, or BINARY data types on the server side. The Unicode checkbox can be used, for example, to specify that the string data type in the model is to be matched with the NCHAR or NVARCHAR types in the database.
The Length field sets the maximal length for values of character or binary data types (such as CHAR, VARCHAR, BINARY, VARBINARY, BIT etc.) on the server side.
The Precision and Scale fields specify the exact parameters of numeric values, for example, of the DECIMAL type in SQL Server. The Precision field specifies the total number of significant digits, while the Scale field specifies the number of digits to the right of the decimal point.
The Default Value specifies the value to be used during generation of the database creation script by the NHibernate runtime or Entity Developer itself and inserted into the database column. The Check field specifies an SQL expression to be used for creating a check constraint for the column. The expression is used during generation of the database creation script by the NHibernate runtime or Entity Developer itself. The Index Name field assigns a name to an index, will include the column and be used during generation of the database creation script by the NHibernate runtime or Entity Developer itself. The Unique Key field specifies the name of a unique constraint, which will include the column and be used during generation of the database creation script by the NHibernate runtime or Entity Developer itself.
|