Using parameters
What is a parameter?
A parameter is a placeholder for a variable that contains a value of some type that is passed to a database server along with the SQL text at the query execution time. Also, a parameter can hold values returned by a server after the query or stored procedure execution.
You can benefit from using parameters in the following situations:
-
When you execute a query multiple times with different input values
-
When you debug a query from your application code
Adding parameters to a query text
Parameters are declared using @ prefix followed by the parameter name. A prefix is included in the name of the parameter.
For example:
SELECT
emp.*
FROM
HumanResources.Employee emp
WHERE
emp.MaritalStatus = @Status AND
emp.BirthDate = @DOB AND
emp.VacationHours = @Hours AND
emp.SalariedFlag = @Flag
@Status, @DOB, @Hours, @Flag are parameters in this query. If you run the query, you will see the following window:
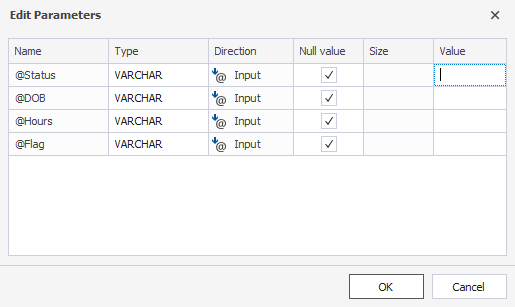
You can add required parameters, for example:
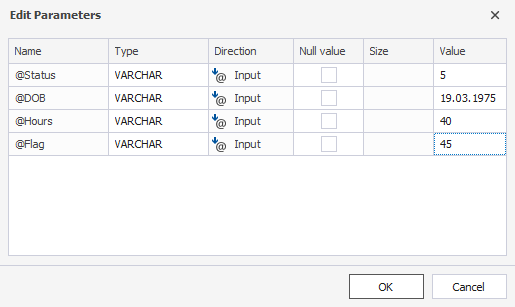
Then, if you run the query with the specified parameters, you will get the following output:
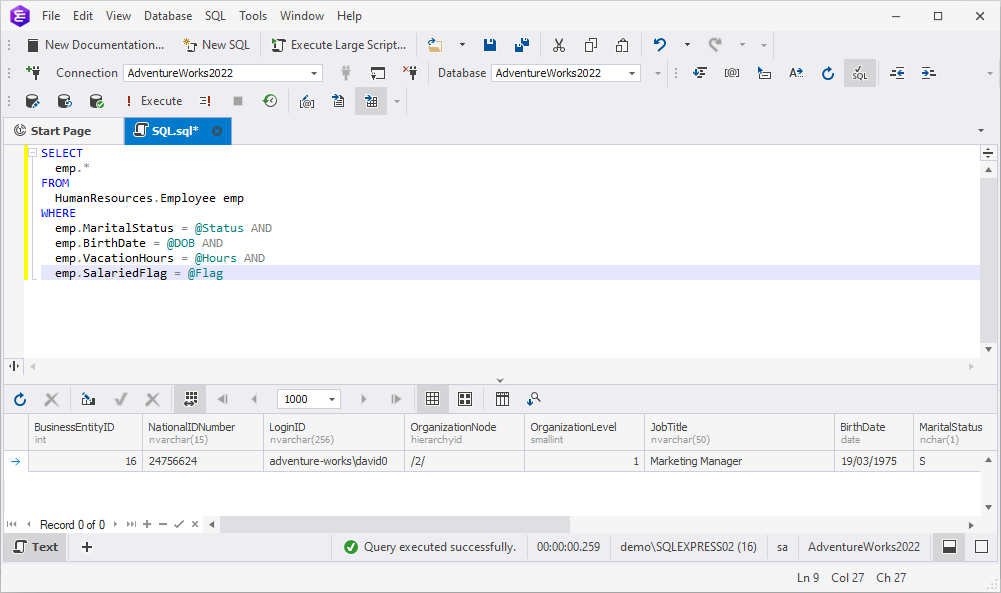
Modifying parameter values and types
When you run a query that contains parameters with empty values, you will automatically be prompted to initialize them.
To set parameter values and types, select Edit Parameters on the SQL toolbar or press F8. In the Edit Parameters dialog box, set the parameters’ type, value, and other properties.
Note
When you execute a query with preset parameter values, you will not be automatically prompted to edit them. To edit parameters, press F8 or select Edit Parameters on the SQL toolbar.