SQL Query History
The SQL Query History document records all queries executed within the SQL document. It allows users to view, search, edit, filter, and export executed queries to a .csv file.
Open the Query History document
To open the Query History document, do one of the following:
-
On the SQL toolbar, select
 Show Query History.
Show Query History.Note
To turn on the SQL toolbar, go to the View menu and select Toolbars > SQL.
- Go to the View menu at the top and select Other Windows > Query History.
- Press Ctrl+Alt+H.
The Query History document is divided into two sections:
- Query History grid: A tabular representation of the query history.
- Preview pane: An area to view detailed query information.
The grid includes the following columns:
- Status: The success or failure of the query execution.
- Query Text: The text of a SQL query that was executed.
- Size (Bytes): The memory footprint of the query.
- Executed On: The exact time and date the query was run.
- Duration: The time it took for the query to execute.
- File: The name of the file containing the SQL statement.
- Server: The server on which the query was executed.
- User: The user who executed the query.
When you hover over a query in the Query Text column, a tooltip appears with detailed information about the executed query, including the execution date, status, size, duration, associated file, the server on which the query was executed, a user who executed the query, and the whole query text.
When you select a query in the Query History grid, its full text appears in the Preview pane.
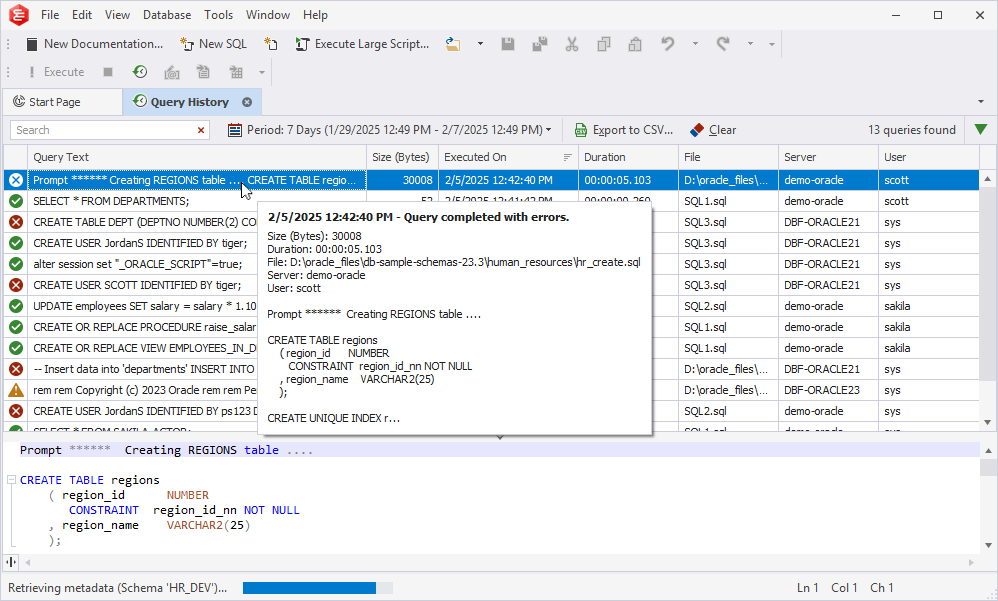
Set up the Query History behavior
To set up the Query History behavior:
1. Open the Options dialog by doing one of the following:
- On the Tools menu, select Options.
- In the upper-right corner of the Query History document, select
 and then select Options.
and then select Options.
2. In the Options dialog, navigate to Environment > Documents > Query History to configure how SQL queries can be stored and managed:
-
Store query history: When the option is selected (default state), the query history is stored automatically. To stop storing query history, clear the checkbox.
-
Storage location: By default, the query history is saved in
C:\Users\Username\AppData\Roaming\Devart\dbForge Documenter for Oracle\ExecutedQueries
whereUsernameis the name of the current user. To use a different directory, specify the correct storage path of the Query History database. -
Max script size: By default, the maximum script size is 1024 KB. To set a different script size, specify the correct value.
-
Automatically remove queries older than 60 d.: Executed queries are stored for 60 days by default, while the maximum interval you can set is 365 days. After the specified period has ended, the history is automatically deleted. You can also back up your history data by copying the file from the storage folder to another location on your computer.
Note
Once the data has been automatically deleted, the history files can no longer be reopened in the dbForge tool.
3. To save the changes, select OK. To restore the settings on a page to their default state, select Reset Page Defaults.
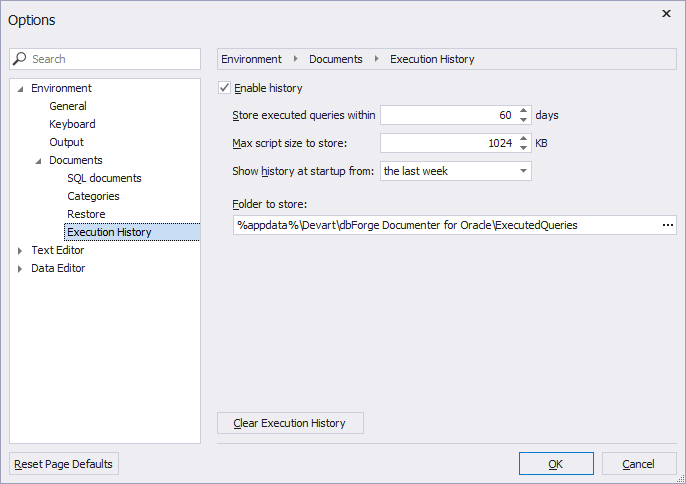
Filter query history
The tool allows you to filter queries using the search box or filters available for each column in the Query History grid.
Filter queries from the search box
In the Search box, enter the search string to find specific queries. The queries that match the search criteria will be filtered in the grid, and the matching text will be highlighted in green in the Preview pane.
To delete the text in the Search box, select ![]() Clear Filter in the Search box.
Clear Filter in the Search box.
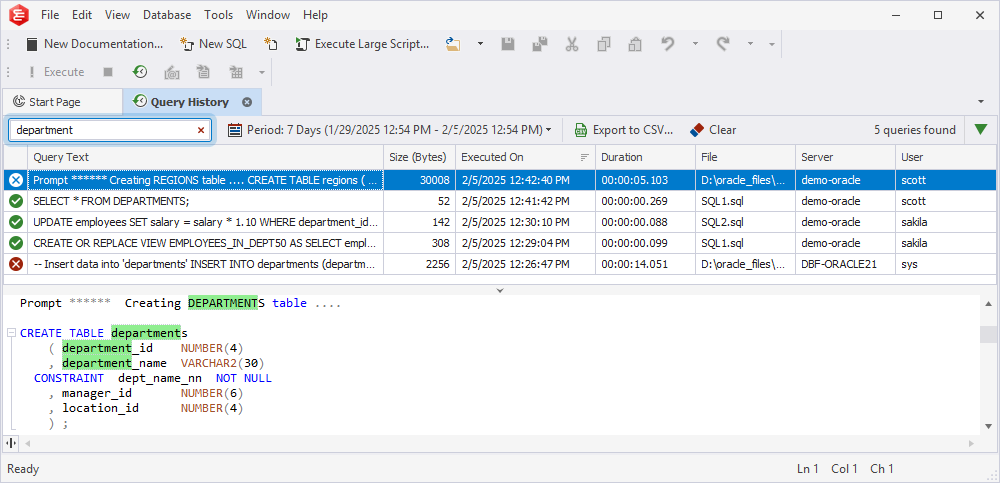
Filter queries per column
To filter queries per column, hover over the column header and select the filter icon in the upper-right corner:
![]()
Status
Select the checkboxes next to the query status you want to display in the Query History grid.
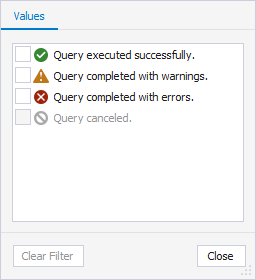
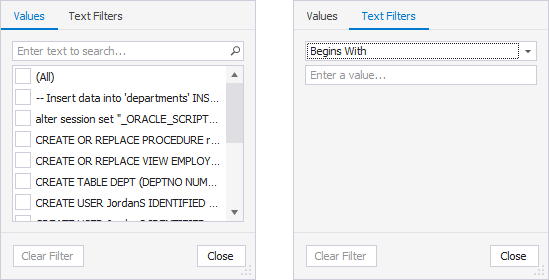
Query Text
On the Values tab, select the checkboxes next to the queries. Alternatively, select a condition from the list and specify a value on the Text Filters tab.
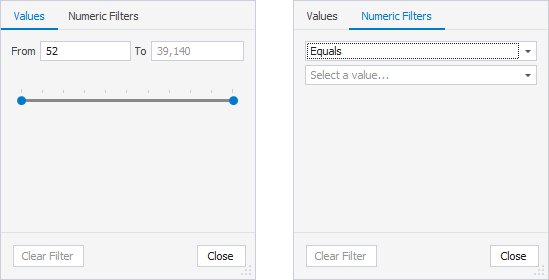
Size (Bytes)
On the Values tab, use the slider to set the minimum and maximum values or enter them manually in the From and To boxes. Alternatively, select a condition from the list and specify a value on the Numeric Filters tab.
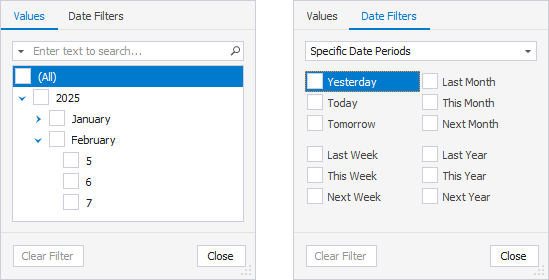
Executed On
On the Values tab, select the checkboxes next to the date range from the list. Alternatively, select the checkboxes next to the filters on the Date Filters tab.
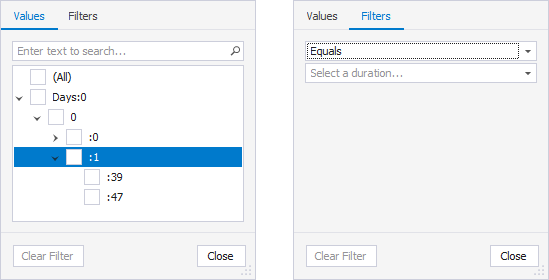
Duration
On the Values tab, select the checkboxes next to the query duration from the list. Alternatively, select a condition from the list and specify a value on the Filters tab.
File
On the Values tab, select the checkboxes next to the files. Alternatively, select a condition from the list and specify a value on the Text Filters tab.
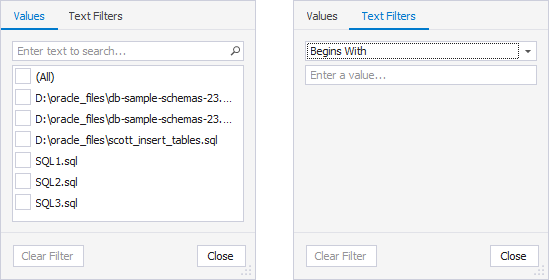
Server
On the Values tab, select the checkboxes next to the servers from the list. Alternatively, select a condition from the list and specify a value on the Text Filters tab.
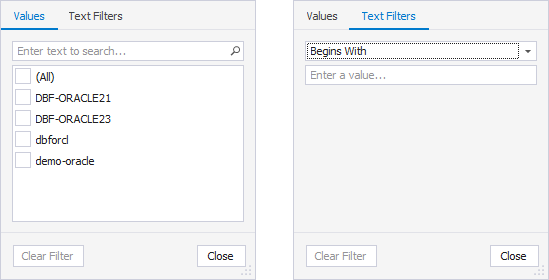
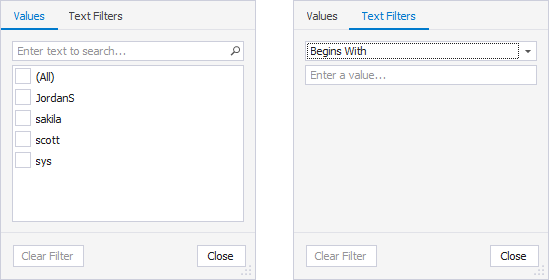
User
On the Values tab, select the checkboxes next to the users from the list. Alternatively, select a condition from the list and specify a value on the Text Filters tab.
Filter queries by time period
From the Period list, select the required timeframe to filter queries by their execution period.
To specify a custom timeframe, select Custom Range. In the Custom Range dialog that opens, set the time period and select OK to apply the filter. To discard the changes, select Cancel.
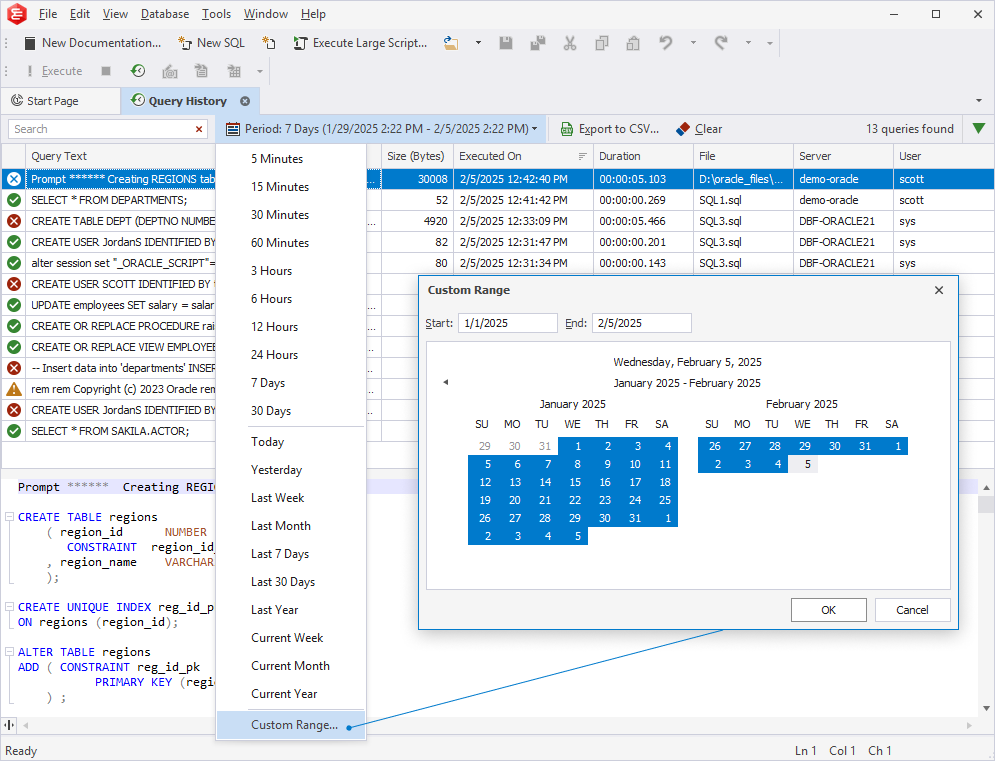
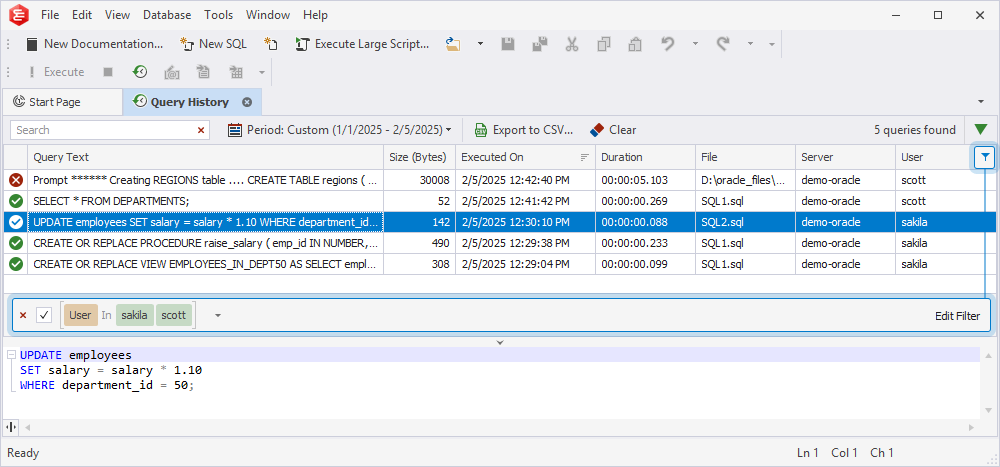
Manage filters
The tool allows you to add, edit, or delete filters using the Filter panel or the Filter Editor dialog.
Use the Filter panel
The Filter panel appears at the bottom of the Query History grid after a filter is applied. It allows you to:
- View the applied filters.
- Clear the checkbox to delete the filter.
- Select the
 delete icon to remove the filter.
delete icon to remove the filter.
Use the Filter Editor dialog
To open the Filter Editor dialog, do one of the following:
- In the Query History grid, right-click the column header and select Filter Editor.
- In the Filter panel, select Edit Filter.
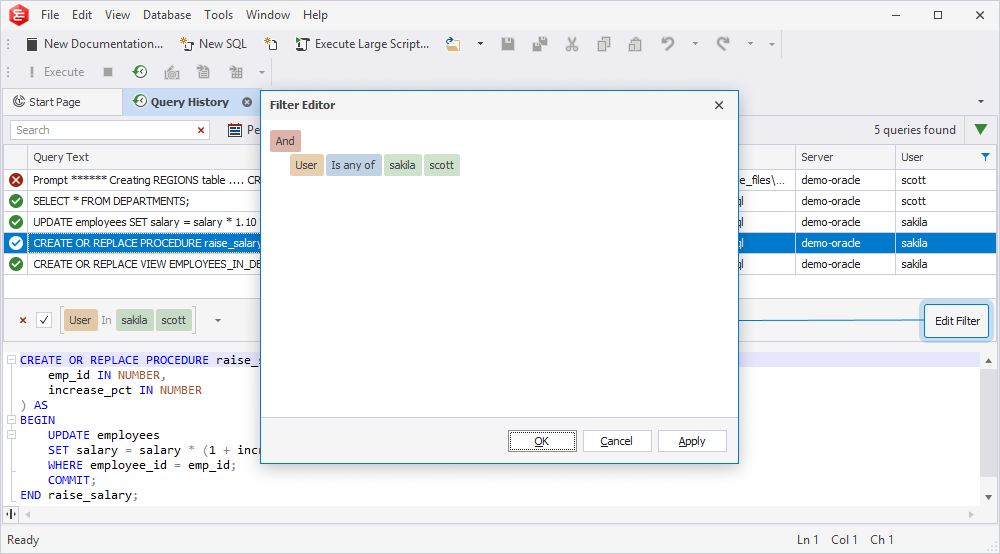
The Filter Editor dialog allows you to:
- Add or remove a filter condition or group.
- Choose a relation type and enter a value to set up a filter condition.
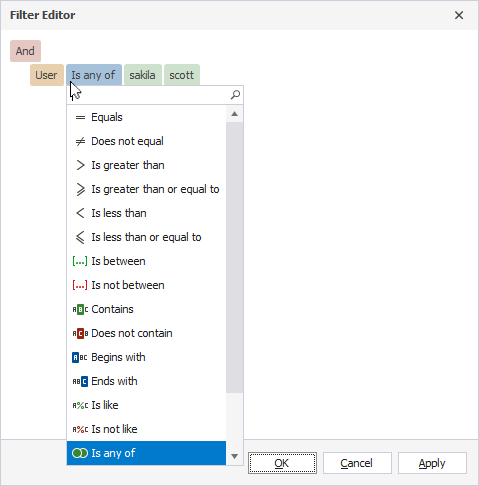
- Choose a logical operator. To change a group logical operator, click it and select another one from the menu.
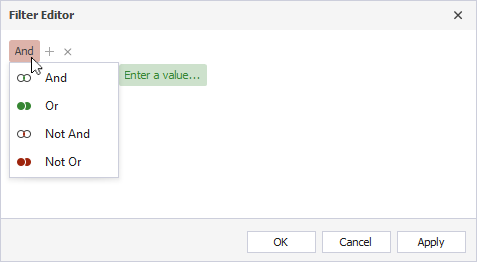
- Add a condition or a group united with a logical operator. Then, choose a database, a relation type, and a value by which the queries will be filtered.
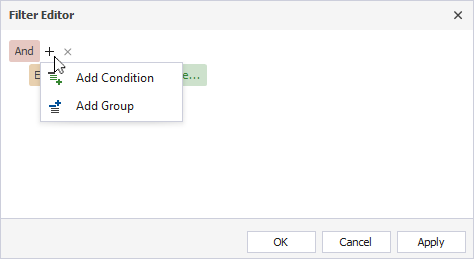
To apply the filter, select Apply. This keeps the dialog open, and you can edit the filter.
To save the changes and close the dialog, select OK.
To discard the changes, select Cancel.
Use shortcut options
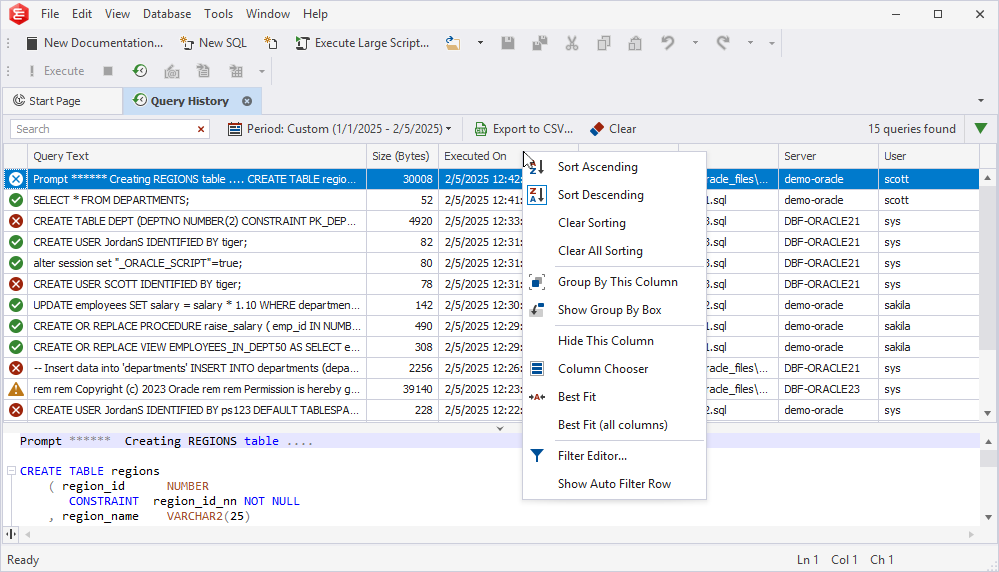
Right-clicking the column header calls the shortcut menu with the following options:
- Sort Ascending: Apply ascending sort order to the column.
- Sort Descending: Apply descending sort order to the column.
- Clear Sorting: Remove sorting for the selected column.
- Clear All Sorting: Reset sorting to default.
- Group By This Column: Group queries by the selected column.
- Show/Hide Group By Box: Show\Hide the Group By Box pane.
- Hide This Column: Hide the selected column.
- Column Chooser: Open the Customization window to remove the columns from the Query History grid or add them back.
- Best Fit: Ditto for the selected column.
- Best Fit (all columns): Ditto for all columns.
- Filter Editor: Open the editor with filtering options.
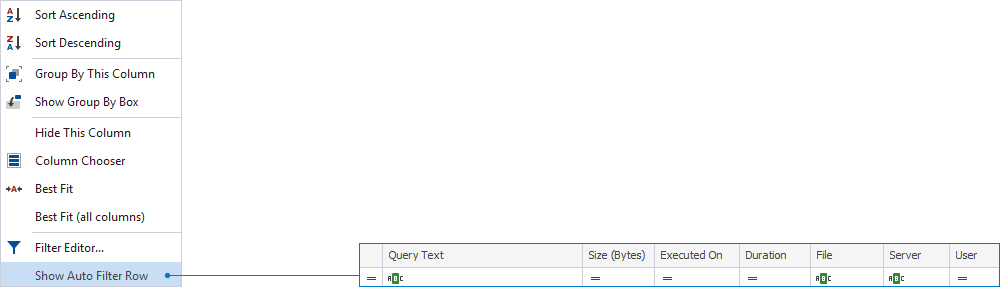
- Show/Hide Auto Filter Row: Show or hide a row to filter data directly from the grid.
Note
Query History is saved in the ExecutedQueries.db file. The default path of the file is
%appdata%\Devart\dbForge Documenter for Oracle\ExecutedQueries.
To specify a different path, go to the Tools menu and select Options. In the Options dialog that opens, select Environment > Documents > Query History.Note that this file does not store your connection passwords.
Group executed queries by column
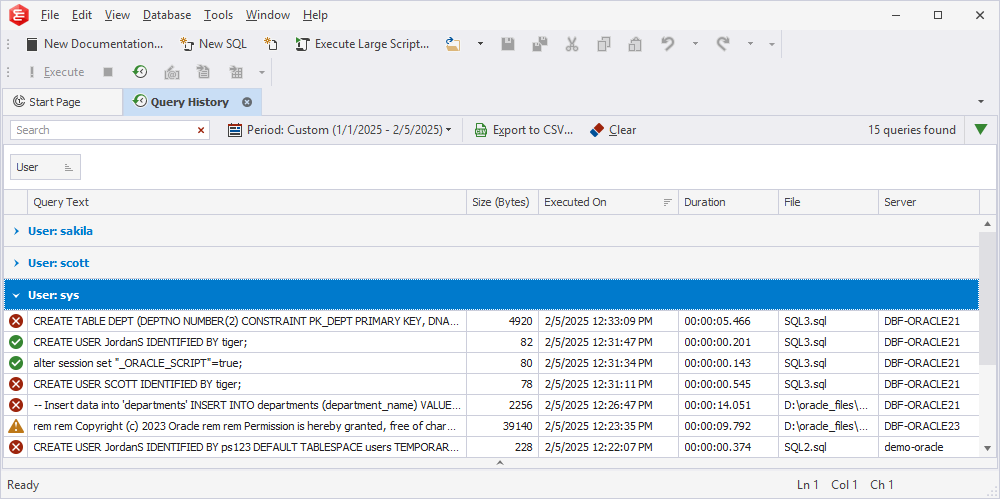
To group executed queries by column, do one of the following:
- In the Query History grid, right-click the column header and select Group By This Column. This command displays data in groups, each represented by a collapsed node. The column header is then moved to the Group by Box pane.
- In the Query History grid, right-click the column header and select Show Group by Box to open the Group by Box pane. It appears above the grid. Drag a column header to the pane.
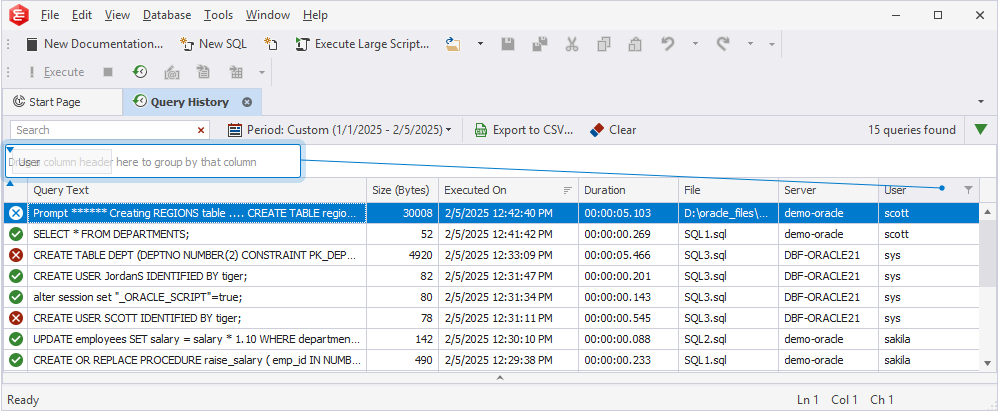
Group executed queries by multiple columns
To group executed queries by multiple columns, drag as many column headers as you need to the Group by Box pane. In this case, the grid will display a tree of nested groups you can expand or collapse by using the corresponding arrows.
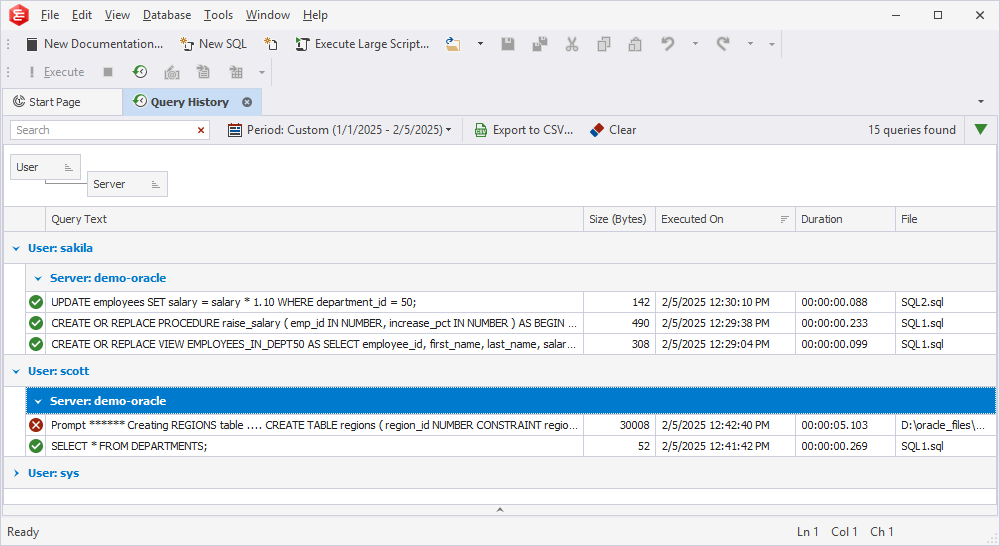
Manage grouped data
To sort the grouped data, do one of the following:
- Select a sort glyph on the column header.
- Right-click the column header and select Sort Ascending or Sort Descending.
To manage the grouped data, right-click the Group By Box pane and select the required option from the shortcut menu:
- Full Expand: Display all nested elements.
- Full Collapse: Hide all nested elements.
- Clear Grouping: Remove all applied groupings from the Group by Box pane.
- Hide Group By Box: Hide the Group By Box pane.
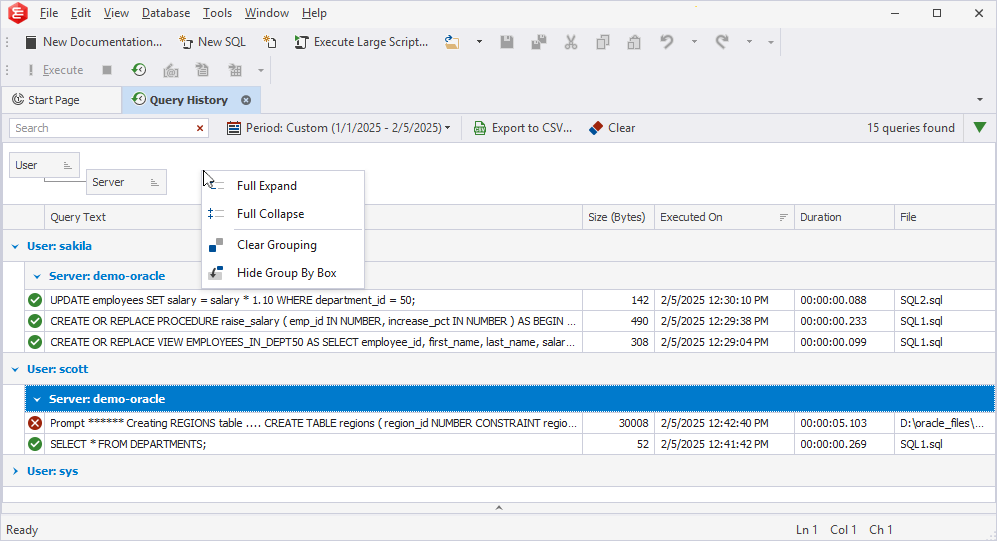
To ungroup data, do one of the following:
- In the Group By Box pane, right-click the required column header and select Ungroup.
- Right-click anywhere in the Group By Box pane and select Clear Grouping.
To hide the Group By Box pane, do one of the following:
- Right-click anywhere in the Group By Box pane and select Hide Group By Box.
- In the Query History grid, right-click the column header and select Hide Group By Box.
Use the Customization window
The Customization window displays the column headers from the Query History grid. The window allows you to remove, sort, or manage the columns.
Remove columns from the Query History grid
1. In the Query History grid, right-click the column header and select Column Chooser to open the Customization window.
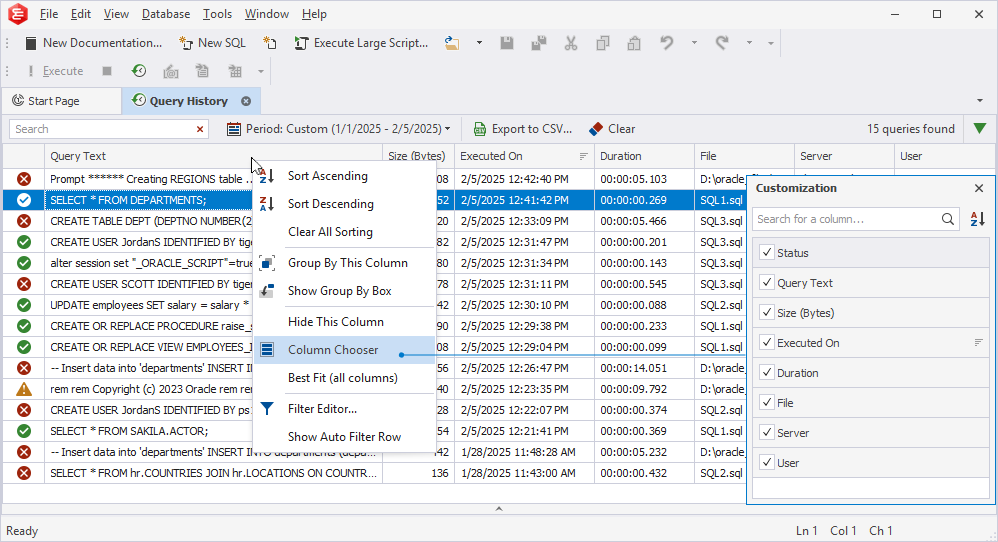
2. In the window, all the columns are selected by default. Clear the checkboxes next to the columns you want to remove from the grid.
Manage columns using options from the shortcut menu
In the Customization window, right-click the column to open the shortcut menu to manage columns on the grid.
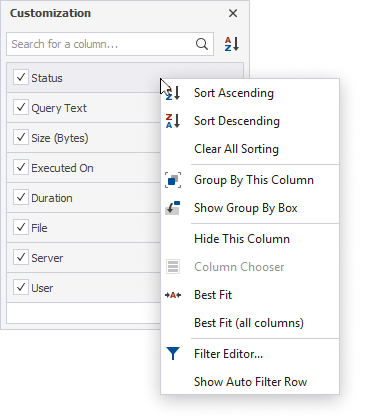
Sort columns
The sort glyph indicates the current sort order of a column. To remove sorting, select Clear Sorting. If the column is not sorted, the sort glyph is hidden.
![]()
Show/Hide Auto Filter Row
In the Query History grid, right-click the column header and select Show Auto Filter Row.
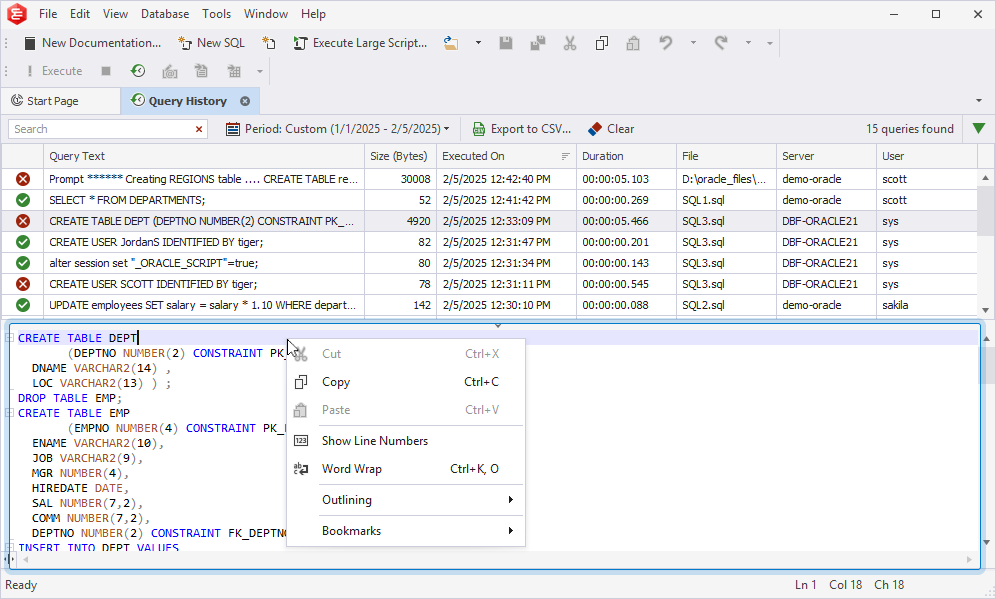
Manage the query text from the Preview pane
The Preview pane displays the text of the selected query. To manage the query text, right-click anywhere in the Preview pane and select the required option.
Edit a query
You can edit the query by doing one of the following:
Double-click the required query:
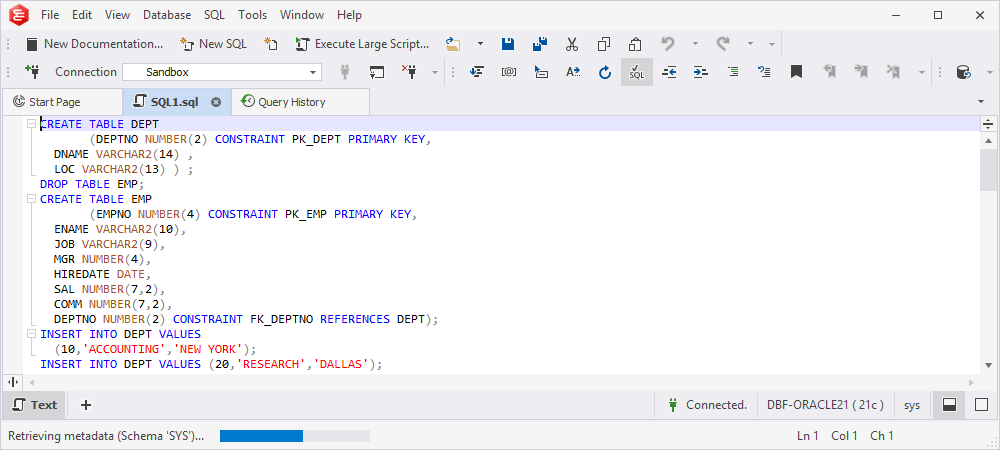
In the Query History grid, double-click the required query. This action opens the query in a new SQL document where you can edit and execute it.
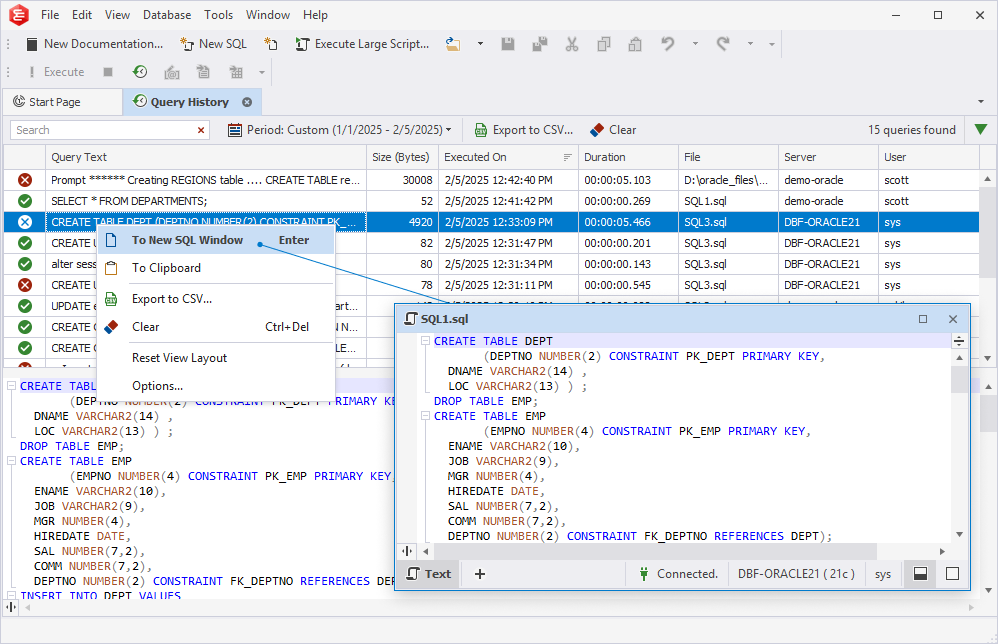
Use the ‘To New SQL Window’ option:
In the Query History grid, right-click the selected query and then select To New SQL Window. This command opens the query in a new SQL document.
Export query history to a .csv file
1. On the toolbar of the Query History document, select Export to CSV.
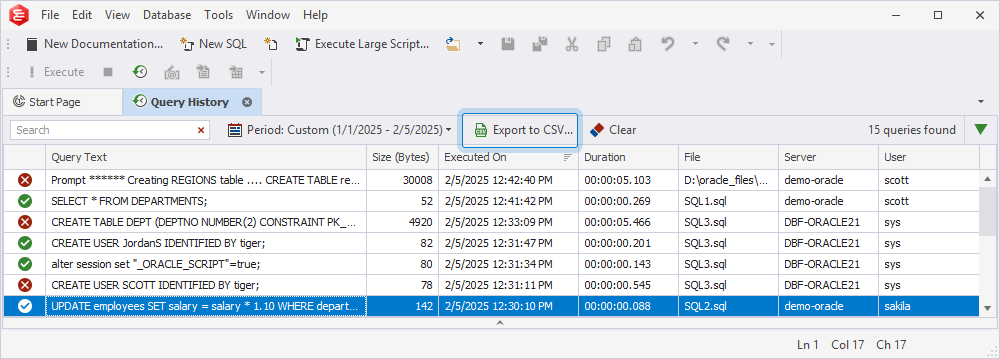
2. In the Save As window that opens, select the folder to store the file and specify the file name.
3. Select Save to save the changes.
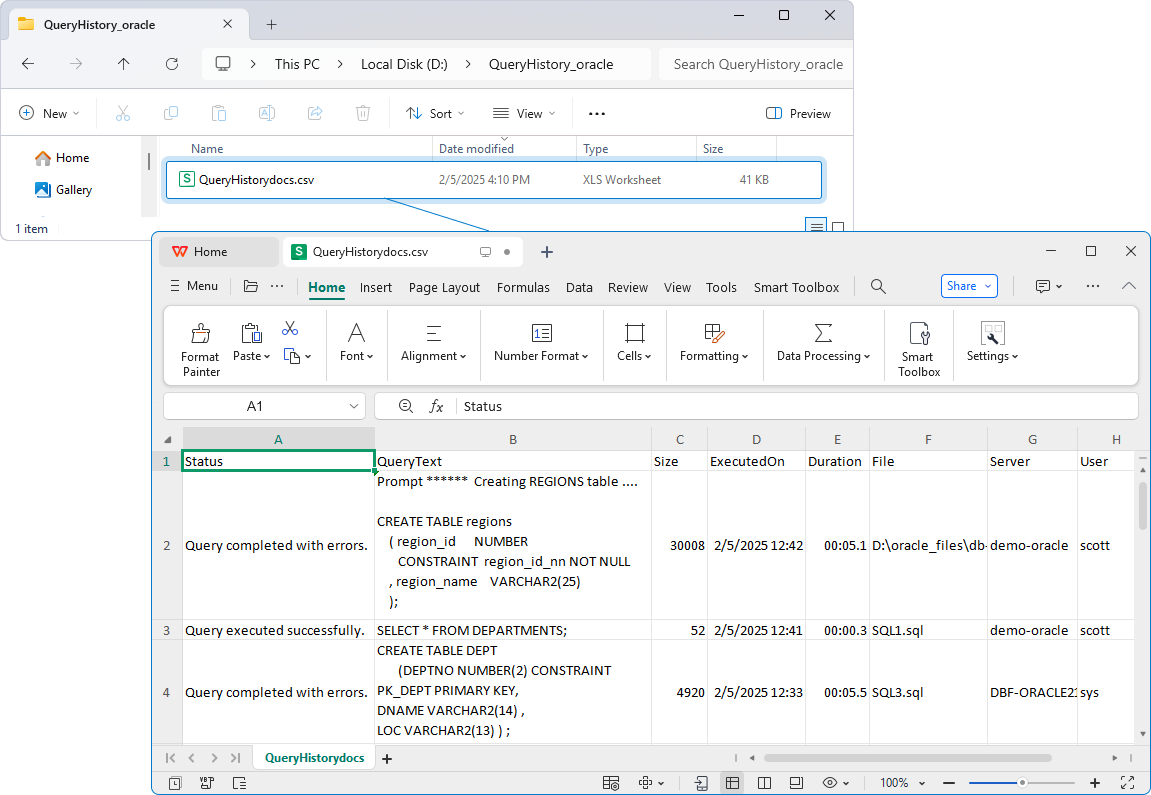
To open the file with exported query history, navigate to the folder containing the file and double-click it to open the file.
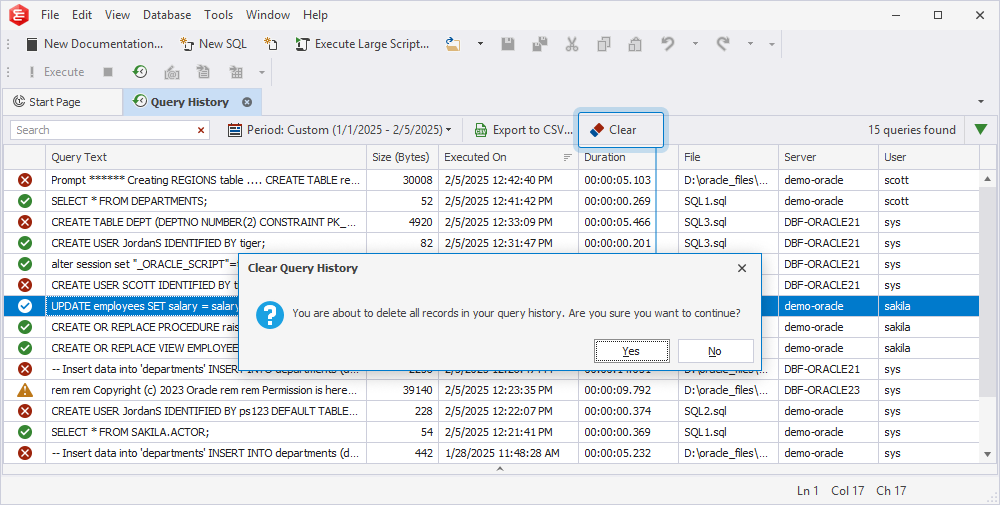
Clear the query history
1. On the Query History document, select Clear or press Ctrl+Del.
2. A message appears notifying you that all records in the query history will be deleted.
3. Select Yes to confirm the deletion or select No to cancel it.
Reset view layout
In the upper-right corner of the Query History document, select ![]() and then select Reset View Layout to restore the default view layout.
and then select Reset View Layout to restore the default view layout.